UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can't encode character in position
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can't encode character in position
The Python "UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can't encode character in
position" occurs when we use the ascii codec to encode a string that contains
non-ascii characters.
To solve the error, specify the correct encoding, e.g. utf-8.
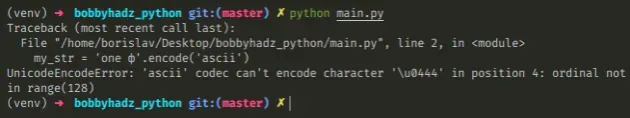
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_str = 'one ф' # ⛔️ UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can't encode character '\u0444' in position 4: ordinal not in range(128) my_bytes = my_str.encode('ascii')
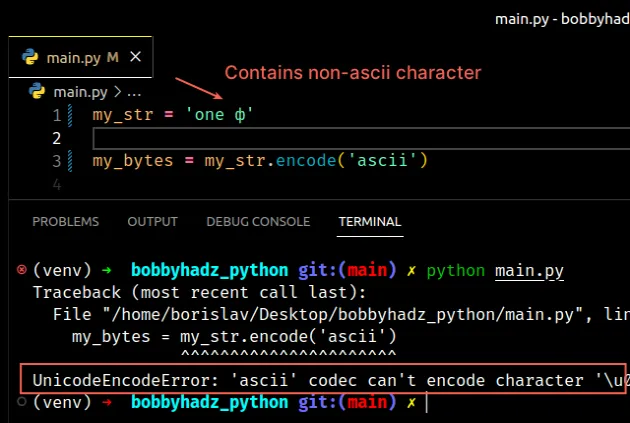
The error is caused because the string contains non-ASCII characters.
# Use the correct encoding to encode the string
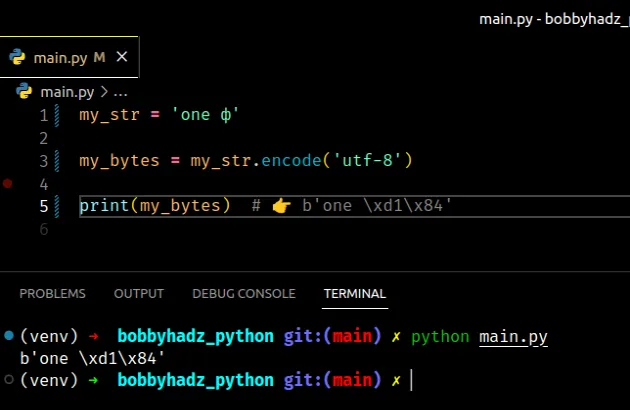
To solve the error, use the correct encoding to encode the string, e.g. utf-8.
my_str = 'one ф' my_bytes = my_str.encode('utf-8') print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b'one \xd1\x84'
utf-8 encoding is capable of encoding over a million valid character code points in Unicode.If you get the error when opening a file, set the encoding keyword argument to
utf-8 in the call to the
open() function.
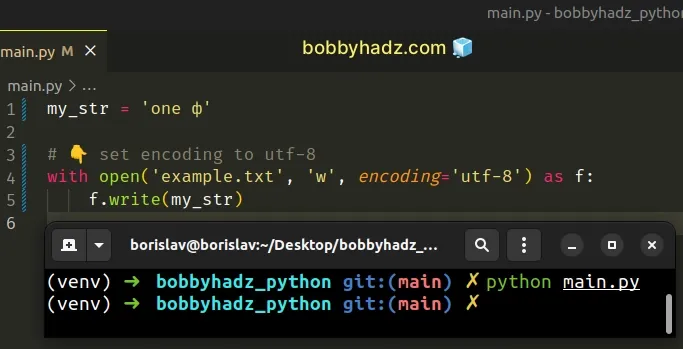
my_str = 'one ф' # 👇️ Set the encoding to utf-8 with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(my_str)
You can view all of the standard encodings in this table of the official docs.
string to a bytes object and decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string.Here is what the complete process looks like.
my_str = 'one ф' # 👇️ Encode str to bytes my_bytes = my_str.encode('utf-8') print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b'one \xd1\x84' # 👇️ Decode bytes to str my_str_again = my_bytes.decode('utf-8') print(my_str_again) # 👉️ "one ф"
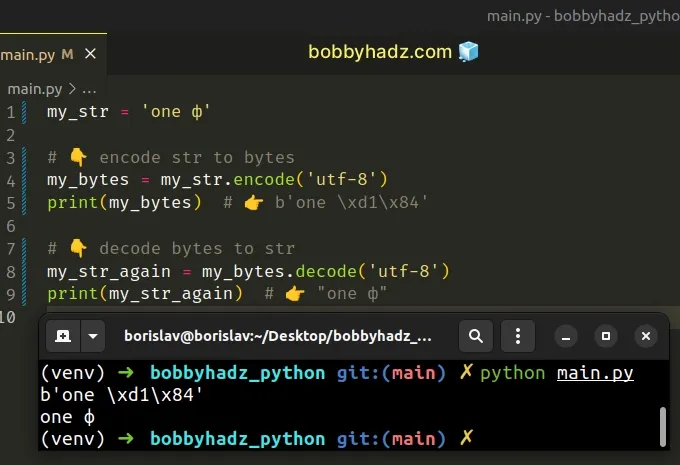
When decoding a bytes object, we have to use the same encoding that was used to encode the string to a bytes object.
The str.encode() method is used to convert a string to bytes.
The bytes.decode() method is used to convert a bytes object to a string.
Make sure to not mix the two as that often causes issues.
# Set the errors keyword argument to ignore
If the error persists when using the utf-8 encoding, try setting the
errors keyword argument
to ignore to ignore characters that cannot be encoded.
my_str = 'one ф' # 👇️ Encode str to bytes my_bytes = my_str.encode('utf-8', errors='ignore') print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b'one \xd1\x84' # 👇️ Decode bytes to str my_str_again = my_bytes.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore') print(my_str_again) # 👉️ "one ф"
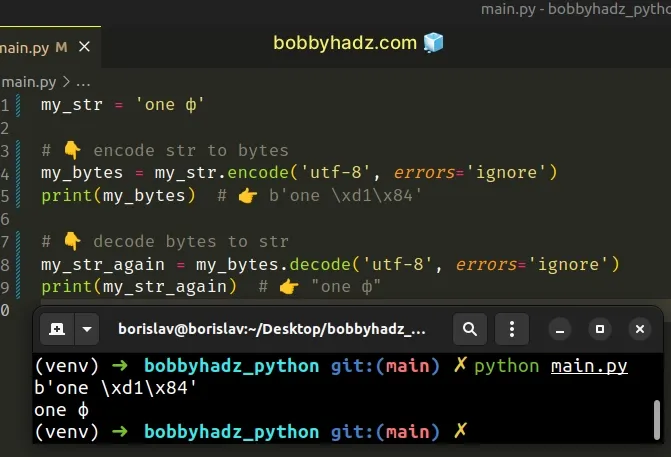
Note that ignoring characters that cannot be encoded can lead to data loss.
# Try using the ascii encoding to encode the string
You can also try using the ascii encoding with errors set to ignore to
ignore any non-ASCII characters.
my_str = 'one ф' # 👇️ Encode str to bytes my_bytes = my_str.encode('ascii', errors='ignore') print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b'one ' # 👇️ Decode bytes to str my_str_again = my_bytes.decode('ascii', errors='ignore') print(my_str_again) # 👉️ "one"
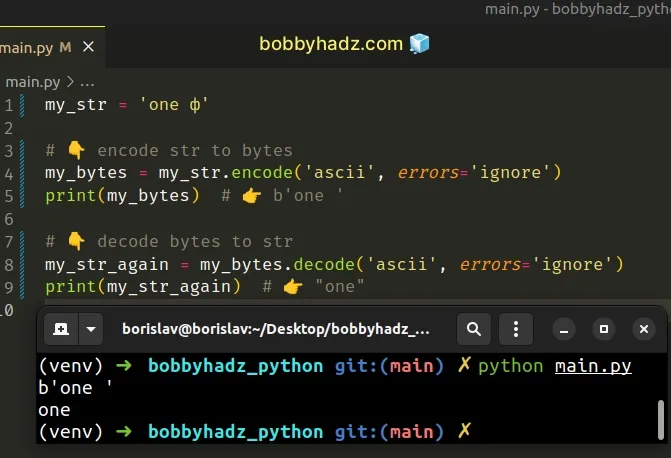
Notice that the last character (which is a non-ASCII character) got dropped when we encoded the string into bytes.
# Set the encoding keyword argument to utf-8 when opening a file
If you got the error when opening a file, open the file with
encoding
set to utf-8.
my_str = 'one ф' # 👇️ Set encoding to utf-8 with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(my_str)
You can also set the errors keyword argument to ignore to ignore any
encoding errors when opening a file.
my_str = 'one ф' with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8', errors='ignore') as f: f.write(my_str)
# Setting the encoding globally with an environment variable
If the error persists, try to set the encoding globally using an environment variable.
# on Linux and macOS export PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8 # on Windows setx PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8 setx PYTHONLEGACYWINDOWSSTDIO=utf-8
Make sure to use the correct command depending on your operating system.
The environment variables must be set before running your script.
If the
PYTHONIOENCODING
environment variable is set before running the interpreter, it overrides the
encoding used for stdin and stdout.
On Windows, you also have to set the PYTHONLEGACYWINDOWSSTDIO environment variable.
If the error persists, try to add the following lines at the top of your file.
import sys sys.stdin.reconfigure(encoding='utf-8') sys.stdout.reconfigure(encoding='utf-8')
The sys module can be used to set the encoding globally if nothing else works.
Make sure the lines at added at the top of your file before you try to write to a file or encode a string to bytes.
# Set the encoding keyword argument to utf-8 when sending emails
If you got the error when using the smtplib module, encode the string using
the utf-8 encoding before sending it.
my_str = 'one ф' encoded_message = my_str.encode('utf-8') server.sendmail( 'from@gmail.com', 'to@gmail.com', encoded_message )
Notice that we passed the encoded message as an argument to server.sendmail().
If you don't encode the message yourself, Python will try to encode it using the
ASCII codec when you call the sendmail() method.
Since the message contains non-ASCII characters, the error is raised.
# Setting the LANG and LC_ALL environment variables incorrectly
If you are on Debian (Ubuntu), you might get the error if you've set the following 2 environment variables incorrectly.
LANG- Determines the default locale in the absence of other locale-related environment variables.LC_ALL- Overrides all locale variables (exceptLANGUAGE).
You can print the environment variables with the echo command.
echo $LANG echo $LC_ALL
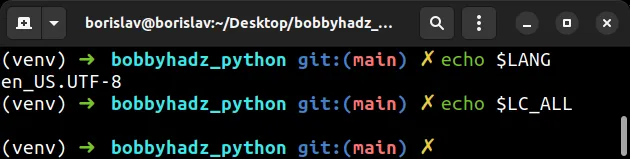
The LANG environment variable should be set to en_US.UTF-8 and the LC_ALL
environment variable should not be set.
You can run the following commands if you need to correct the values of the environment variables.
# ✅ Set LANG environment variable export LANG='en_US.UTF-8' # ✅ Unset LC_ALL environment variable unset LC_ALL
If the error persists, try to install the language-pack-en package from your
terminal.
sudo apt-get install language-pack-en
This might help if your operating system is out of date and has missing dependencies.

