UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xff in position 0
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xff in position 0
The Python "UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xff in position 0: invalid start byte" occurs when we specify an incorrect encoding when decoding a bytes object.
To solve the error, specify the correct encoding, e.g. utf-16 or open the
file in binary mode (rb or wb).
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_bytes = 'hello ÿ'.encode('utf-16') # ⛔️ UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xff in position 0: invalid start byte my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8')
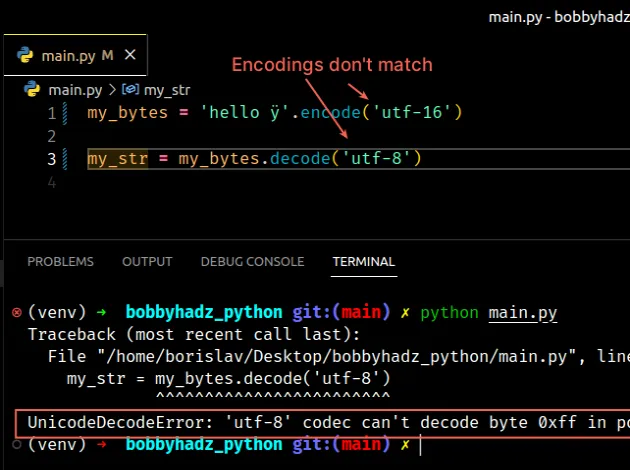
We used the utf-16 encoding to encode the string to bytes but then tried to
use the utf-8 encoding to decode the bytes object to a string.
The mismatch of encodings causes the error.
string to a bytes object and decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string.# Use the same encoding that was used to encode the string to bytes
When decoding a bytes object, we have to use the same encoding that was used to encode the string to a bytes object.
In the example, we can set the encoding to utf-16.
my_bytes = 'hello ÿ'.encode('utf-16') my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-16') print(my_str) # 👉️ "hello ÿ"
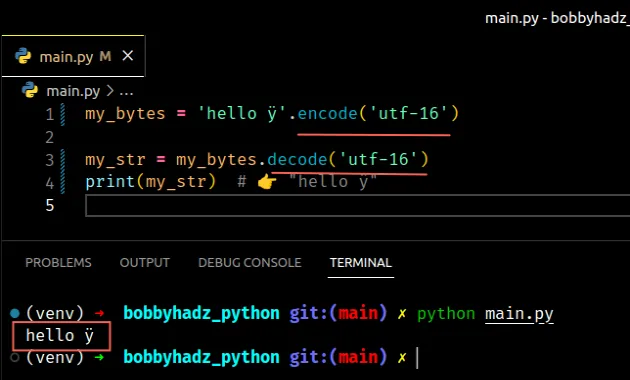
The utf-16 encoding was used to encode the string to bytes, so it should be
used when decoding the bytes object.
You should try using the utf-16 encoding even if you aren't sure if it was
used to encode the string.
# Specifying the correct encoding when opening a file
You can also set the encoding in the call to the native open() function.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-16') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
Try setting the encoding to utf-16 as shown in the code sample.
# Set the encoding to utf-16 when using pandas
If you get the error when using the
pandas module, set the encoding to
utf-16 in the call to
pandas.read_csv().
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv( 'employees.csv', sep=',', encoding='utf-16' ) print(df)
The read_csv method takes an encoding keyword argument that is used to set the
encoding.
# Setting the errors keyword argument to ignore
If you don't know the correct encoding, try setting the
errors keyword argument
to ignore.
my_bytes = 'hello ÿ'.encode('utf-16') my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore') print(my_str) # hello
When the errors keyword argument is set to ignore, an error isn't raised.
Instead, characters that cannot be decoded get dropped from the result.
It should be noted that ignoring characters that cannot be decoded can lead to data loss.
# Setting the errors keyword argument to ignore when opening a file
You can use the same approach when working with a file.
# 👇️ Set errors to ignore with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-16', errors='ignore') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
We set the errors keyword argument to ignore, so characters that cannot be
decoded are ignored.
Opening the file with an incorrect encoding with errors set to ignore won't
raise a UnicodeDecodeError.
# You can open a file in binary mode without decoding it
If you get the error when opening a file, you can open the file in binary mode without decoding it.
with open('example.txt', 'rb') as f: data = f.read() # b'first line\nsecond line\nthird line\n' print(data)
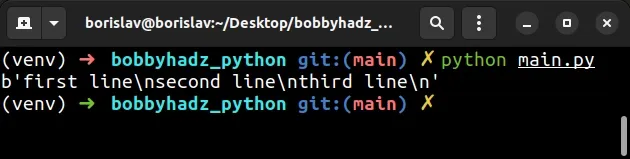
We opened the file in binary mode (using the rb (read binary) mode), so the
lines list contains bytes objects.
You shouldn't specify encoding when opening a file in binary mode.
Make sure you don't specify the encoding when opening the file in binary mode.
# Try setting the encoding to ISO-8859-1
Another thing you can try is to set the encoding to ISO-8859-1 when decoding
the bytes object or opening the file.
my_bytes = 'hello ÿ'.encode('utf-16') my_str = my_bytes.decode('ISO-8859-1') print(my_str) # ÿþhello ÿ
You won't get an error when the encoding is set to ISO-8859-1, however, you might get illegible results.
The ISO-8859-1 encoding defines a character for each of the 256 possible byte
values, so no error is raised.
Here is an example of using the encoding when reading from a file.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='ISO-8859-1') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
# Try to open the file with the utf-16 encoding
If none of the suggestions helped, try to set the encoding to utf-16.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-16') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
# Trying to find the encoding of the file
You can try to figure out what the encoding of the file is by using the file
command.
The command is available on macOS and Linux, but can also be used on Windows if you have Git and Git Bash installed.
Make sure to run the command in Git Bash if on Windows.
Open your shell in the directory that contains the file and run the following command.
file *
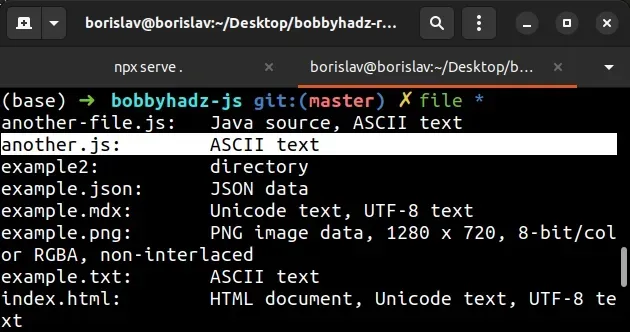
The screenshot shows that the file uses the ASCII encoding.
This is the encoding you should specify when opening the file.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='ascii') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
If you are on Windows, you can also:
- Open the file in the basic version of Notepad.
- Click on "Save as".
- Look at the selected encoding right next to the "Save" button.
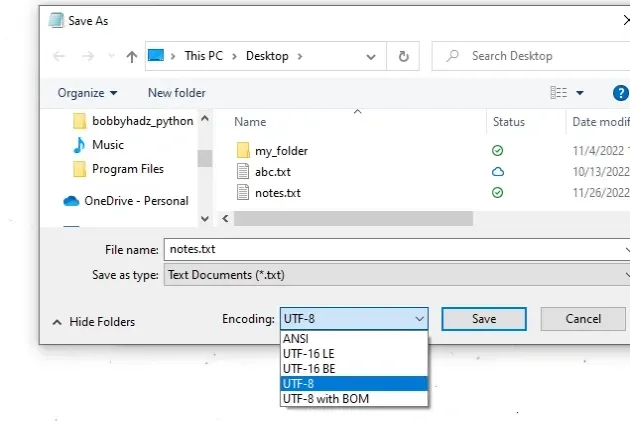
The screenshot shows that the encoding for the file is UTF-8, so that's what
we have to specify when calling the open() function.
If you specify an encoding that is not supported, you'll get the LookupError: unknown encoding in Python error.
# Find the encoding of the file with chardet
You can also use the chardet Python module to try to find the encoding of the file.
First, install the module by running the following command.
pip install chardet # 👇️ or pip3 pip3 install chardet
Now run the chardetect command as follows.
chardetect example_file
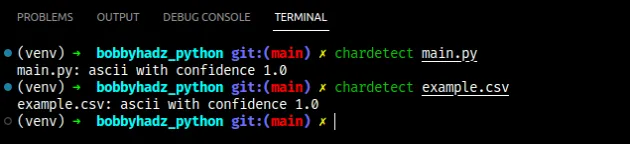
The package should give you a guess regarding which encoding is used by the file, including a confidence score.
You can then try to use the encoding when opening the file.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='your_encoding') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
You can also try to open the file in binary mode and use the chardet package
to detect the encoding of the file.
import chardet with open('example.txt', 'rb') as f: print(chardet.detect(f.read()))
We used the rb (read binary) mode and fed the output of the file to the
chardet.detect() method.
The encoding you get from calling the method is the one you should try when opening the file in reading mode.
# How the error is caused
Encoding is the process of converting a string to a bytes object and
decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string.
When decoding a bytes object, we have to use the same encoding that was used to encode the string to a bytes object.
Here is an example that shows how using a different encoding to encode a string to bytes than the one used to decode the bytes object causes the error.
my_text = 'hello ÿ' my_binary_data = my_text.encode('utf-16') # ⛔️ UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xff in position 0: invalid start byte my_text_again = my_binary_data.decode('utf-8')
We can solve the error by using the utf-16 encoding to decode the bytes
object.
my_text = 'hello ÿ' my_binary_data = my_text.encode('utf-16') my_text_again = my_binary_data.decode('utf-16') print(my_text_again) # 👉️ "hello ÿ"

