TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable in Python [Fixed]
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable in Python
The Python "TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable" occurs when we try to
call a boolean value (True or False) as a function.
To solve the error, correct the assignment and resolve any clashes between function and variable names.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
is_subscribed = True # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable is_subscribed()
And, here is another example.
is_subscribed = True # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable if is_subscribed(): print('The user is subscribed')
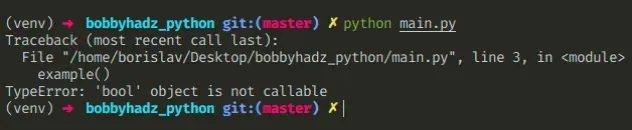
Boolean values are not callable in Python, so they can't be invoked with parentheses.
is_subscribed = True # ✅ Removed the parentheses if is_subscribed: print('The user is subscribed')
If you added the parentheses by mistake, remove them when checking if a boolean
value is True.
True or False) and correct the assignment to a function or class, or remove the parentheses.# Overriding the built-in bool function
Make sure you aren't overriding the built-in bool() function.
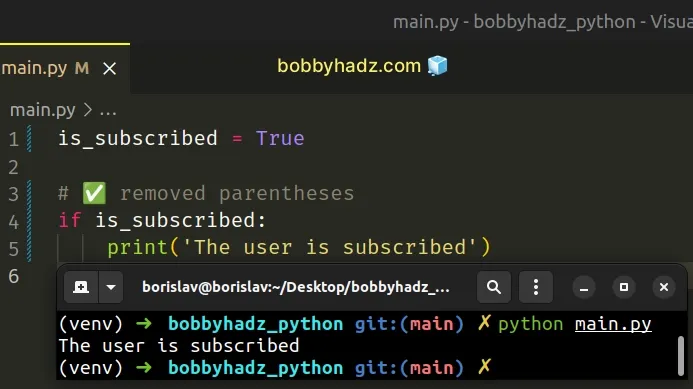
# 👇️ overrides built-in bool() function bool = True # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable print(bool('abc'))
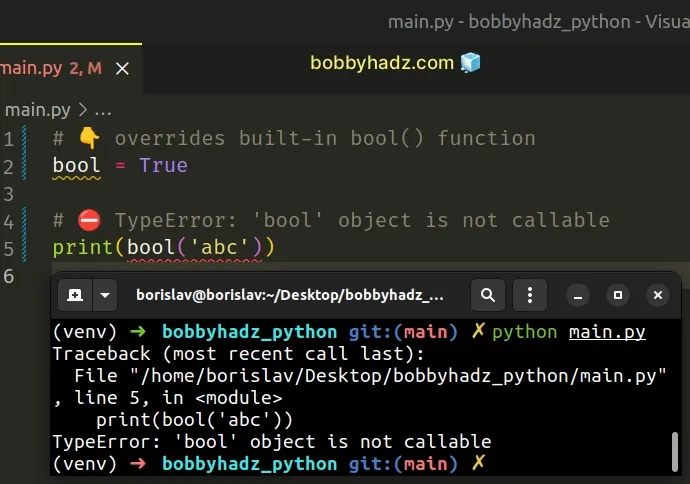
We override the built-in bool function, setting it to a boolean primitive and
try to call it as a function.
When we call bool() in the example, we actually call the primitive True
value because we shadowed the built-in bool function.
To solve the error, rename your variable and restart your script.
# ✅ Not overriding the built-in bool() anymore my_bool = True print(bool('hello'))
Now the variable no longer shadows the built-in bool() function, so the issue
is resolved.
# Common causes of the error
The "TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable" error occurs for multiple reasons:
- Trying to call a boolean value (
TrueorFalse) with parentheses. - Calling a function that returns a boolean value twice.
- Having a function and a variable with the same name.
- Overriding a built-in function by mistake and setting it to a boolean.
- Having a class method and a class property with the same name.
# Trying to call a function that returns a boolean twice
Make sure you aren't trying to call a function that returns a boolean twice.
def is_subscribed(): return True # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable is_subscribed()() # 👈️ Remove the extra set of parentheses
Calling the function once returns True
and calling the function a second time, with the second set of parentheses,
tries to call the True value as a function.
To solve the error, remove the second set of parentheses.
def is_subscribed(): return True print(is_subscribed()) # 👉️ True
# Having a function and a variable that share the same name
Another common cause of the error is having a function and a variable that share the same name.
def example(): return 'bobbyhadz.com' example = True # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable example()
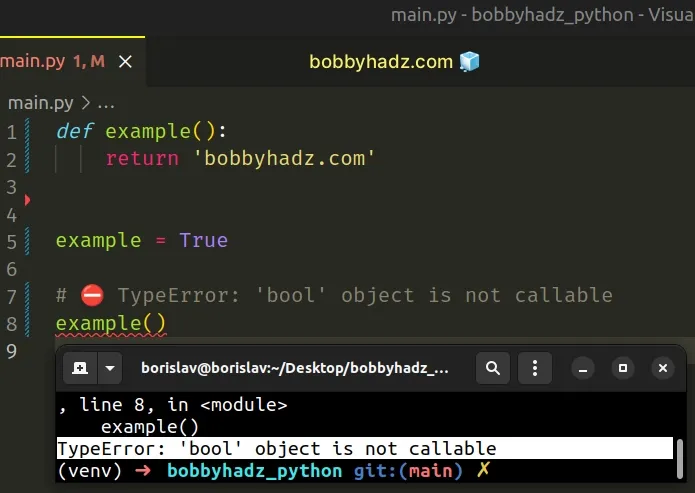
The example variable shadows the function with the same name, so when we try
to call the function, we actually end up calling the variable.
Renaming the variable or the function solves the error.
def example(): return 'bobbyhadz.com' my_bool = True print(example()) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
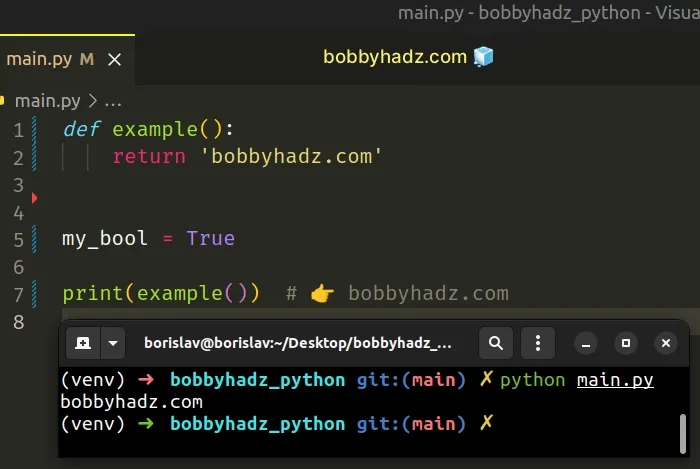
The variable has a different name, so it no longer clashes with the function and the error is resolved.
# Having a class method and a class property with the same name
The error is also caused when we have a class method and a class property with the same name.
class Employee(): def __init__(self, is_subscribed): self.is_subscribed = is_subscribed # 👇️ Same name as the class variable def is_subscribed(self): return self.is_subscribed emp = Employee(False) # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable print(emp.is_subscribed())
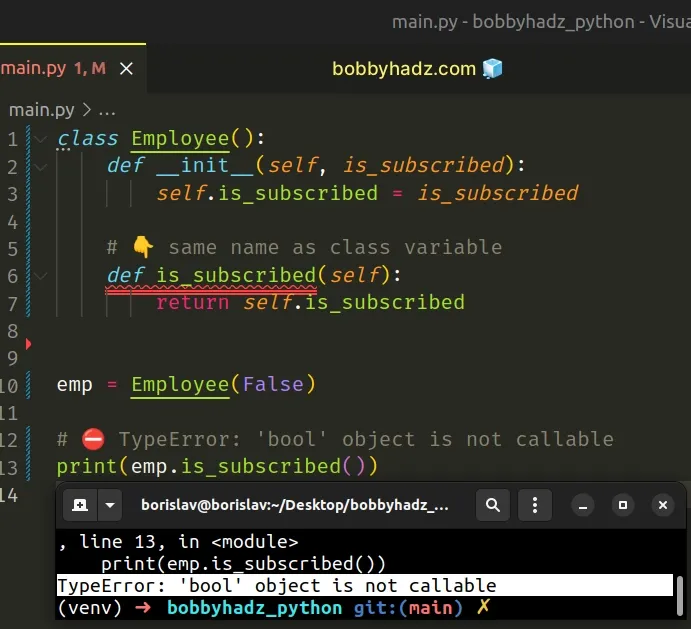
The Employee class has a method and an attribute with the same name.
To solve the error, rename the class method.
class Employee(): def __init__(self, is_subscribed): self.is_subscribed = is_subscribed def get_is_subscribed(self): return self.is_subscribed emp = Employee(False) print(emp.get_is_subscribed()) # 👉️ False
Now the method and the class property have different names, so they no longer clash.
Calling the method now invokes the actual method and not the boolean class property.
# Conclusion
To solve the "TypeError: 'bool' object is not callable" error, make sure:
- You aren't trying to call a boolean value (
TrueorFalse) with parentheses. - You aren't calling a function that returns a boolean value twice.
- You don't have a function and a variable with the same name.
- You aren't overriding a built-in function and setting it to a boolean.
- You don't have a class method and a property with the same name.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

