OverflowError: math range error in Python [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- OverflowError: math range error in Python
- OverflowError: integer division result too large for a float
# OverflowError: math range error in Python
The Python "OverflowError: math range error" occurs when the result of a mathematical calculation is too large.
Use a try/except statement to handle the error or use the NumPy module if
you have to manipulate larger numbers.
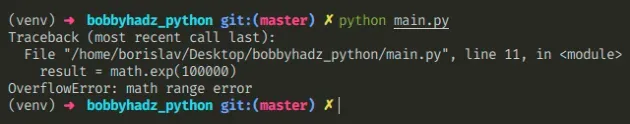
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import math # ⛔️ OverflowError: math range error result = math.exp(100000)
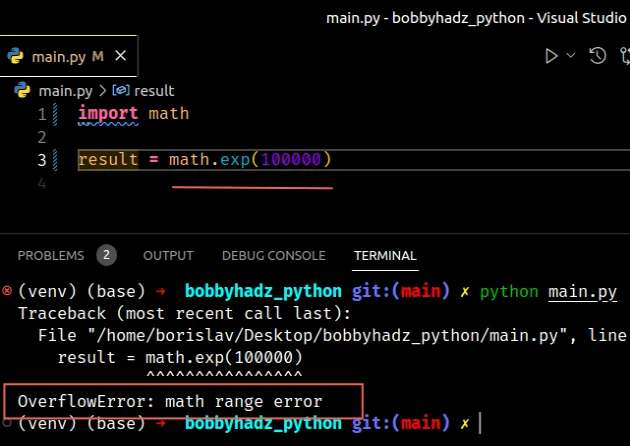
The number we are trying to calculate is too large and it would take quite a
while for the operation to complete, so an OverflowError is raised.
# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
One way to handle the error is to use a try/except statement.
import math try: result = math.exp(100000) except OverflowError: result = math.inf print(result) # 👉️ inf
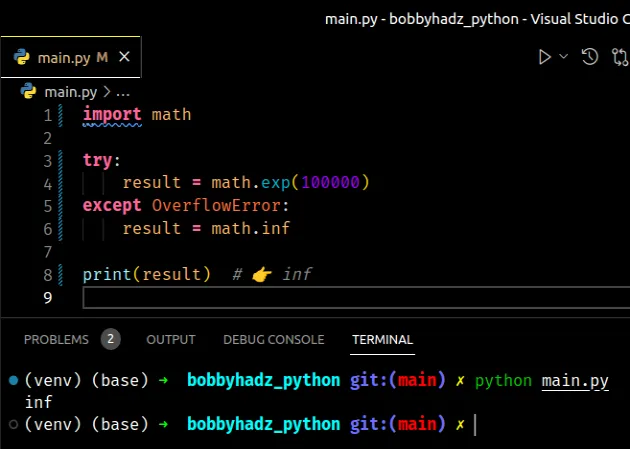
If calling the math.exp() method with the specified number raises an
OverflowError, the except block runs.
In the except block, we set the result variable to positive infinity.
The math.inf property returns a floating-point positive infinity.
It is equivalent to using float('inf').
None or handle it in any other way that suits your use case.# Using the NumPy module to solve the error
An alternative approach is to install and use the NumPy module.
Open your terminal in your project's root directory and install the NumPy module.
pip install numpy pip3 install numpy
Now you can import and use the NumPy module.
import numpy as np result = np.exp(100000) print(result) # 👉️ inf
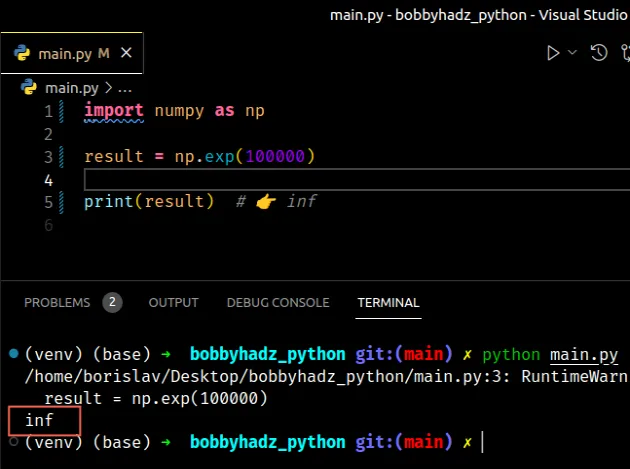
You might get a runtime warning when running the code sample, however, an error isn't raised.
You can view the methods that are supported by the NumPy package in the sidebar of the official docs.
# Getting the error when converting to float
You might also get the error when converting a large integer to a float.
Here is an example of using the exponentiation operator between two integers.
print(4000**400) # ✅ works
The result is a very large number, however, Python doesn't have any issues computing it.
However, if you try to convert the result to a float, you'll get an error.
# ⛔️ OverflowError: int too large to convert to float print(float(4000**400))
This is because Python cannot handle as large numbers when working with floats.
# OverflowError: integer division result too large for a float
The Python "OverflowError: integer division result too large for a float" occurs when the result of a division is too large.
Use the floor division // operator to solve the error, e.g.
result = large_num // 5.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
large_num = 5**1000 # ⛔️ OverflowError: integer division result too large for a float result = large_num / 5
The division operator / always produces a float value, however, floating-point
numbers always take the same amount of space.
To solve the error, we can use
floor division //.
large_num = 5**1000 # ✅ Using floor division result = large_num // 5 print(result) # very large number
Division / of integers yields a float, while floor division // of integers
results in an integer.
floor() function applied to the result.Integers can store a variable amount of space as long as we have the required memory available.
A good way to illustrate the difference is to use the sys.getsizeof() method
with integers and floats.
import sys print(sys.getsizeof(1000)) # 👉️ 28 print(sys.getsizeof(10000000000)) # 👉️ 32 print(sys.getsizeof(3.0)) # 👉️ 24 print(sys.getsizeof(3.00000000000)) # 👉️ 24
The sys.getsizeof() method returns the size of an object in bytes.
Notice that the size of the integer grows with the number of digits, whereas floating-point numbers take the same amount of space regardless of how many digits the number consists of.

