NameError: name 'df' or 'pd' is not defined in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
Note: if you got the error NameError: name 'pd' is not defined, click on the second subheading.
# NameError: name 'df' is not defined in Python
The Python "NameError: name 'df' is not defined" occurs when we try to access
the df (DataFrame) variable before it is defined.
To solve the error, make sure to declare the df variable before accessing
it.
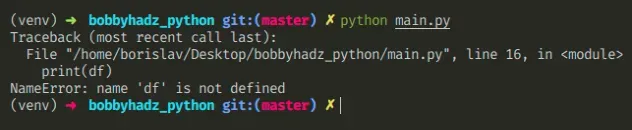
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import pandas as pd # ⛔️ NameError: name 'df' is not defined print(df) # 👇️ The definition is below df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } )
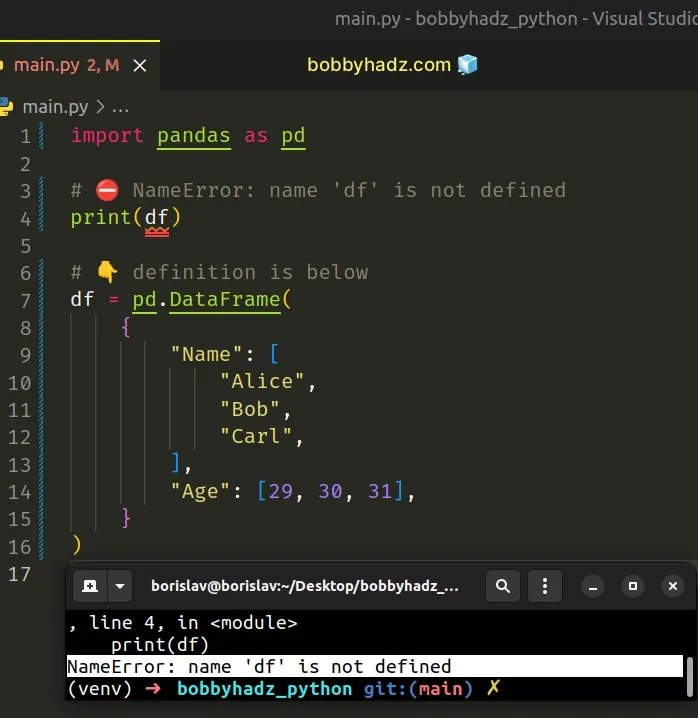
The issue is that we are trying to access the df variable before it was
defined.
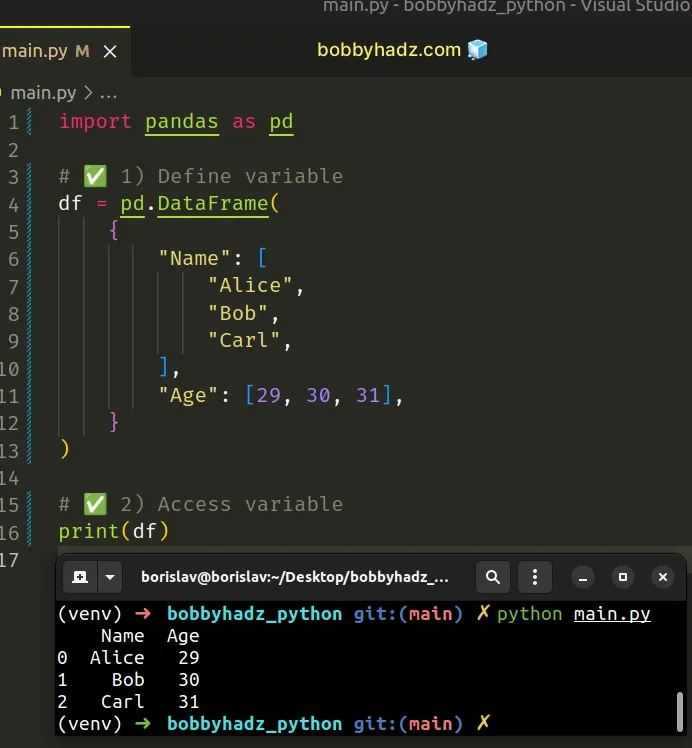
# Access the variable after it has been declared
To solve the error, make sure to access the variable after it has been defined.
import pandas as pd # ✅ 1) Define the variable df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) # ✅ 2) Access the variable print(df)
Make sure to import the pandas module before using it as shown in the code sample.
The error is also raised if you use the pandas module without having imported
it.
# Common causes of the error
The error occurs for multiple reasons:
- Accessing a
dfvariable that doesn't exist. - Accessing a
dfvariable before it is declared. - Accessing a scoped variable from outside. For example, declaring a
dfvariable in a function and trying to access it from outside.
Note: if you got the error NameError: name 'pd' is not defined, click on the following subheading.
# Trying to access a scoped variable from outside
Here is an example of trying to access a scoped variable from outside.
import pandas as pd def my_func(): # 👇️ df exists only in this function df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) my_func() # ⛔️ NameError: name 'df' is not defined print(df)
We declared the df variable in a function, but we are trying to access it from
the outer scope.
One way to solve the error would be to mark the variable as global.
import pandas as pd def my_func(): global df df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) my_func() # ✅ works print(df)
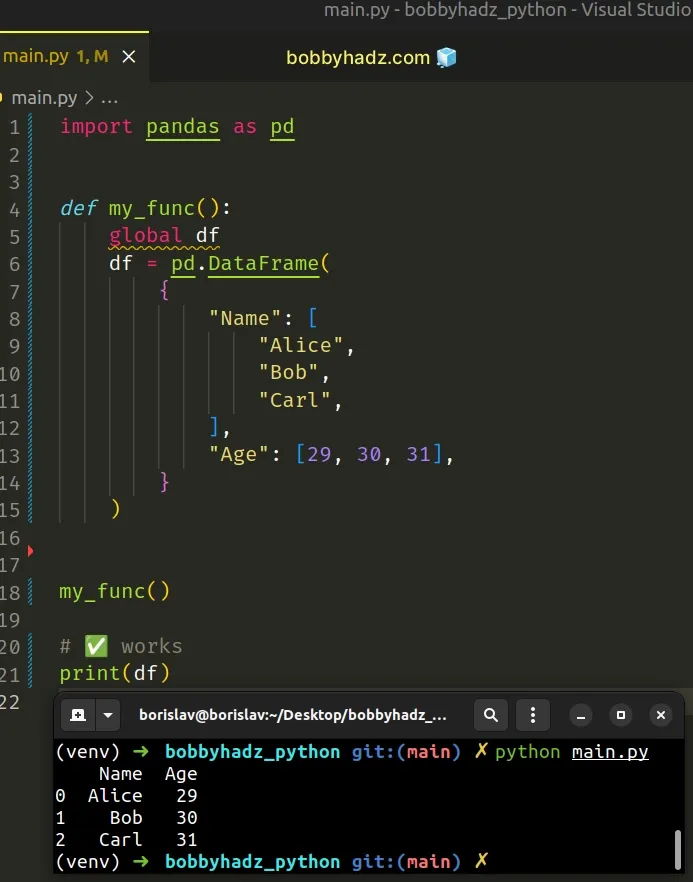
global keyword should generally be avoided as it makes our code harder to read and reason about.An alternative approach would be to return the df variable from the function
and store the result.
import pandas as pd def my_func(): df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) return df result = my_func() print(result)
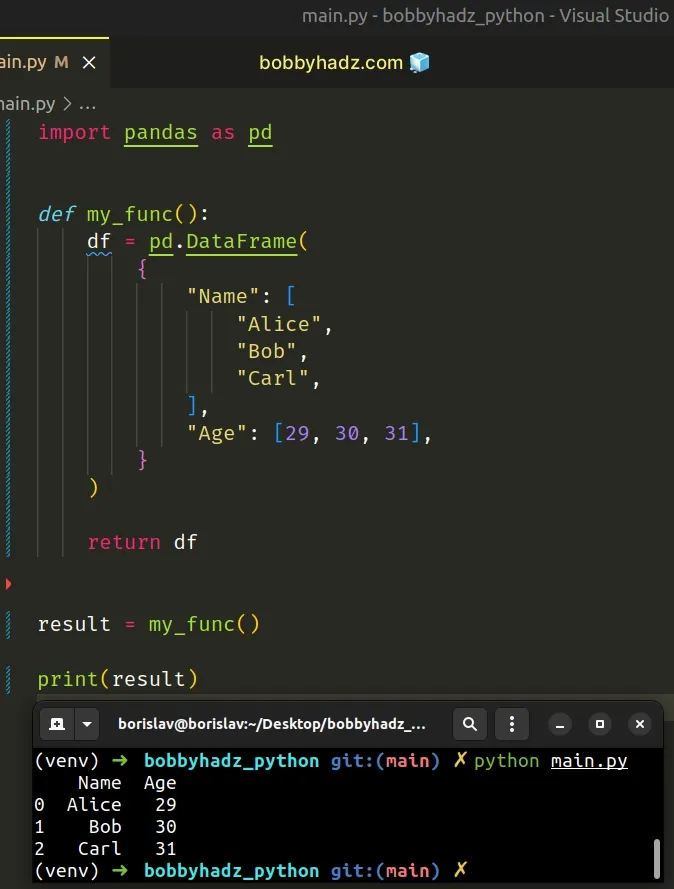
Whichever approach you pick, make sure the df variable is available in the
scope in which you're trying to access it.
# Make sure to not import the pandas module in a nested scope
Also, make sure you haven't imported pandas in a nested scope, e.g. a
function.
def my_func(): import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) return df # ⛔️ NameError: name 'pd' is not defined. Did you mean: 'id'? df2 = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } )
We imported the pandas module in a function, so we can't use it outside of the
function.
Import the module at the top level to be able to use it throughout your code.
# ✅ Import at the top level of your file import pandas as pd def my_func(): df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) return df df2 = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } )
The import statement for the pandas module has to come at the top of the file
before any code that makes use of it.
# Make sure to not import the pandas module in a try/except statement
You also should be importing the pandas module in a
try/except statement.
try: # 👉️ Code here could raise an error import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) except ImportError: print(pd) print(pd)
The code sample works, however, if the code in the try statement raises an
error, the pandas module won't get imported successfully.
This would cause the error because we are trying to access properties on the
pandas module in the outer scope and the except block.
Instead, move the import statement to the top level of the file.
import pandas as pd try: df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) except ImportError: print(pd) print(pd)
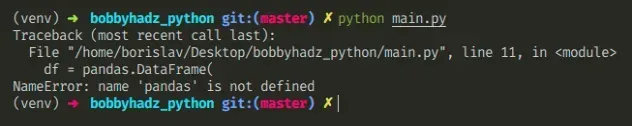
# NameError: name 'pd' is not defined in Python
The Python "NameError: name 'pd' is not defined" occurs when we use the
pandas module without importing it first.
To solve the error, install the module and import it (import pandas as pd)
before using it.
NameError: name 'pd' is not defined in Python NameError: name 'pandas' is not defined in Python
Open your terminal in your project's root directory and install the pandas module.
# 👇️ In a virtual environment or using Python 2 pip install pandas # 👇️ For python 3 (could also be pip3.10 depending on your version) pip3 install pandas # 👇️ If you get a permissions error sudo pip3 install pandas # 👇️ If you don't have pip in your PATH environment variable python -m pip install pandas # 👇️ For python 3 (could also be pip3.10 depending on your version) python3 -m pip install pandas # 👇️ For Anaconda conda install -c anaconda pandas
# Import the pandas module before using it
After you install the pandas module, make sure to import it before using it.
# ✅ Import pandas and alias it as pd import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) print(df)
The import statement imports the pandas module and aliases it to pd, so we
access the module's classes as pd.DataFrame,
pd.Series,
etc.
# Misspelling the name of the module
Make sure you haven't misspelled pandas and are using all lowercase letters
because module names are case-sensitive.
# Importing the module in a nested scope
Also, make sure you haven't imported pandas in a nested scope, e.g. a
function. Import the module at the top level to be able to use it throughout
your code.
# Make sure to use the correct import statement
If you got the error "NameError: name 'pandas' is not defined in Python", then
you haven't aliased pandas as pd in your code and you should update the
import statement.
import pandas df = pandas.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) print(df)
However, note that importing pandas and aliasing it as pd is much more
common in modern code bases.
# 👇️ pandas aliased as pd import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame( { "Name": [ "Alice", "Bob", "Carl", ], "Age": [29, 30, 31], } ) print(df)
The import statement imports the pandas module and aliases it to pd, so we
access the module's classes as pd.DataFrame, pd.Series, etc.
If the error persists after importing pandas as pd, restart your IDE and
development server.

