IndexError: index 0 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 0
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# IndexError: index 0 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 0
The Python "IndexError: index 0 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 0" occurs when we try to access the first item in the first dimension of an empty numpy array.
To solve the error, use a try/except block or check if the array's size is
not equal to 0 before accessing it at an index.
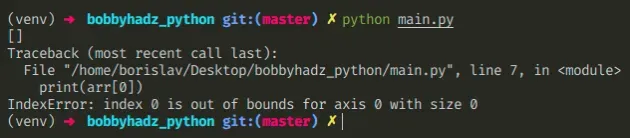
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (0,) print(arr.size) # 👉️ 0 # ⛔️ IndexError: index 0 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 0 print(arr[0])
Here is another example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np # 👇️ Array of 0 rows and 0 columns arr = np.zeros((0, ), int) print(arr) # [] # ⛔️ IndexError: index 0 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 0 print(arr[0])
We tried to access the first element in an empty array which caused the error.
# Using the shape or size properties on the array
You can use the shape property to print the shape of the array - a tuple of the array's dimensions.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3,) print(arr.size) # 👉️ 3
The size property can be used to print the array's size (the number of elements in the array).
Note that NumPy uses zero-based indexing - the first element in an array has an
index of 0.
# Checking if the array's size is greater than 0
One way to solve the error is to check if the array's size is greater than 0
before accessing its first item.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([]) if arr.size > 0: print(arr[0]) else: print('The array has a size of 0')
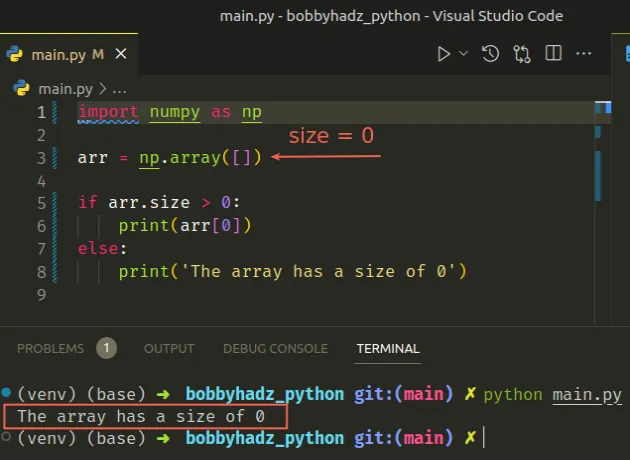
The if block is only run if the size of the array is greater than 0,
otherwise, the else block runs.
# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except statement to handle the error.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([]) try: print(arr[0]) except IndexError: print('The array is empty')
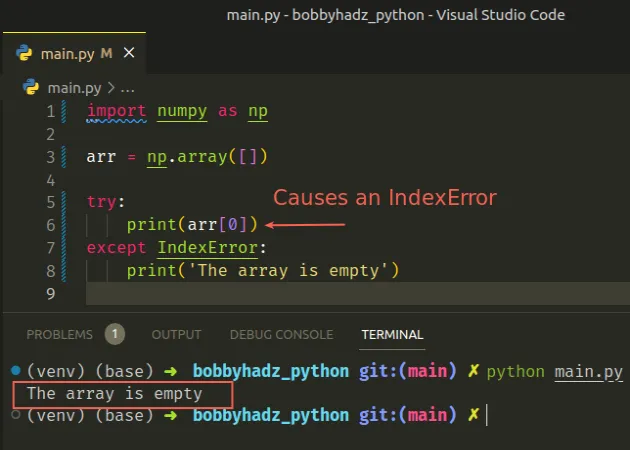
We tried accessing the array element at index 0 which raised an IndexError
exception.
You can handle the error or use the pass keyword in the except block.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([]) try: print(arr[0]) except IndexError: pass
The pass statement does nothing and is used when a statement is required syntactically but the program requires no action.
# Make sure the array has the correct dimensions
When declaring a NumPy array, make sure it has the correct dimensions.
import numpy as np arr_1 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) print(arr_1.shape) # 👉️ (3,) print(arr_1.size) # 👉️ 3 print(arr_1[0]) # 👉️ 1 # ----------------------------------------- # 👇️ Array with 2 rows and 3 columns # [[0 0 0] # [0 0 0]] arr_2 = np.zeros((2, 3), dtype=int) print(arr_2.shape) # (2, 3) print(arr_2[0]) # 👉️ [0 0 0] print(arr_2[0][0]) # 👉️ 0 print(arr_2.size) # 👉️ 6
Axis 0 is the first dimension of an array and the size property can be used
to get the number of elements in the array.
# Creating an array with 0 rows and N columns
Make sure you aren't creating an array with 0 rows and N columns.
import numpy as np arr = np.zeros((0, 3), dtype=int) print(arr) # 👉️ [] print(arr.shape) # (0, 3) # ⛔️ IndexError: index 0 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 0 print(arr[0])
The array in the example has a size 0 for its first dimension, so trying to
access any element at index would cause an IndexError.
Instead, specify a non-zero value for the rows.
import numpy as np # 👇️ array with 2 rows and 3 columns arr = np.zeros((2, 3), dtype=int) # [[0 0 0] # [0 0 0]] print(arr) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (2, 3) print(arr[0]) # 👉️ [0 0 0]
The code sample creates an array with 2 rows and 3 columns.
# Accessing a non-empty array at an index that doesn't exist
The error also occurs if you access a non-empty array at an index that doesn't exist.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([0]) print(arr[0]) # 👉️ 0 print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (1, ) print(arr.size) # 1 # ⛔️ IndexError: index 1 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 1 print(arr[1])
The array in the example has a single element.
NumPy indices are zero-based, so accessing the array at index 1 causes an
error.
The first element in a NumPy array has an index of 0 and the last element has
an index of -1 or len(array) - 1.
You can use a try/except statement to handle the error.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([0]) try: print(arr[1]) except IndexError: # 👇️ this runs print('The specified index does NOT exist')
If the index doesn't exist, an IndexError is raised and is then handled by the
except block.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable in Python
- IndexError: list assignment index out of range in Python
- Only integers, slices (
:), ellipsis (...), numpy.newaxis (None) and integer or boolean arrays are valid indices - IndexError: pop from empty list in Python [Solved]
- Replacement index 1 out of range for positional args tuple
- IndexError: too many indices for array in Python [Solved]
- IndexError: tuple index out of range in Python [Solved]
- IndexError: single positional indexer is out-of-bounds [Fix]

