JsonWebTokenError: jwt malformed error in Node.js [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# JsonWebTokenError: jwt malformed error in Node.js [Solved]
The Node.js "JsonWebTokenError: jwt malformed" error occurs when you pass a
null value or a value that is not a JSON web token to the jwt.verify()
method.
To solve the error, make sure to pass a valid JSON web token to jwt.verify().
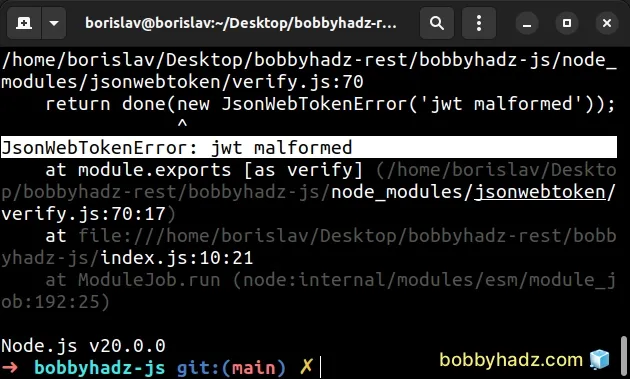
Here is the complete error message.
/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz-rest/bobbyhadz-js/node_modules/jsonwebtoken/verify.js:70 return done(new JsonWebTokenError('jwt malformed')); ^ JsonWebTokenError: jwt malformed at module.exports [as verify] (/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz-rest/bobbyhadz-js/node_modules/jsonwebtoken/verify.js:70:17)
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken'; const secret = 'my_secret'; const token = 'bobbyhadz.com'; // ⛔️ JsonWebTokenError: jwt malformed const decoded = jwt.verify(token, secret);
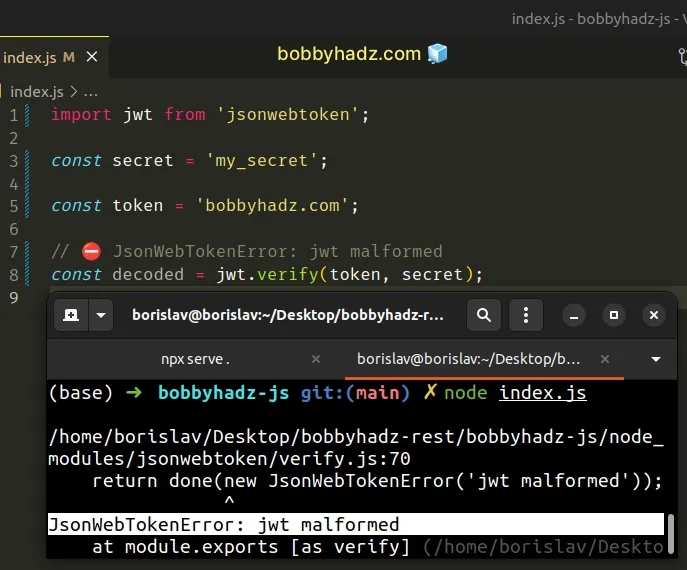
The value we passed to the jwt.verify() method is not a valid JSON web token
which caused the error.
jwt.verify() with is not null or undefined and is a valid JSON web token.The first argument you pass to
jwt.verify()must be a valid JSON web token string.
If you need to sign a JSON web token, use the jwt.sign() method.
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken'; const secret = 'my_secret'; const token = jwt.sign({foo: 'bar'}, secret); console.log(token); const decoded = jwt.verify(token, secret); console.log(decoded.foo);
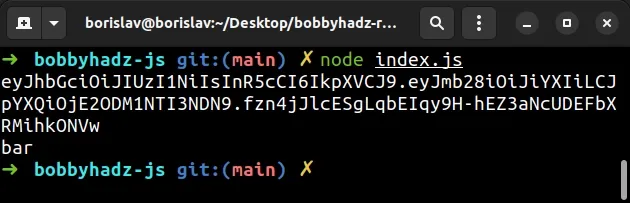
Your JSON web token should look similar to the following string.
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJmb28iOiJiYXIiLCJpYXQiOjE2ODM1NTI3NDN9.fzn4jJlcESgLqbEIqy9H-hEZ3aNcUDEFbXRMihkONVw
Notice that there are 2 dots in the JWT string.
- The part before the first period is the header.
- The part after the first period is the payload (the encoded data).
- The part after the second period is the signature.
# Specify the Authorization header when making an HTTP request
Once you sign the payload into a JSON web token string with the jwt.sign()
method, you can specify the token using the Authorization header.
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken'; const secret = 'my_secret'; // 👇️ sign the payload into a JSON web token const token = jwt.sign({foo: 'bar'}, secret); console.log(token); async function getUser() { try { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/', { method: 'GET', // 👇️ specify Authorization header headers: { Authorization: token, }, }); if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`Error! status: ${response.status}`); } const result = await response.json(); return result; } catch (err) { console.log(err); } } getUser().then(data => { console.log(data); });
Notice that we set the Authorization header when issuing the HTTP request.
headers: { Authorization: token, },
Depending on how your server is set up, you might also have to include the
Bearer prefix when making the request.
headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${token}`, },
If your browser needs to make an authorized request to your server, then:
- Your browser has to initiate the login process by filling in a login form with the correct credentials.
- Your server has to use the
jwt.sign()method to sign the payload (e.g. the user's ID) into a JSON web token string. - The server has to respond with the generated JSON web token string.
- The browser has to store the JSON web token string (most commonly in local storage) and use it when making HTTP requests that require authorization.
If your server needs to access the JSON web token string that was sent from your
browser, use the req.headers object.
// In your Route handler (Express.js) const token = req.headers.authorization.split(' ')[1];
The example above assumes that your Authorization header contains the Bearer
prefix.
If it does not, then you don't have to split the string.
// In your Route handler (Express.js) const token = req.headers.authorization;
The req object will be accessible in your route handler functions in an
Express.js application.
The req.headers object gives you access to the request headers (including
authorization).
If at any point in time, the value of the JSON web token string gets corrupted, the "JsonWebTokenError: jwt malformed" error is raised.
You can console.log() the value of your JSON web token string and debug it.
Your JSON web token should look similar to the following string.
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJmb28iOiJiYXIiLCJpYXQiOjE2ODM1NTI3NDN9.fzn4jJlcESgLqbEIqy9H-hEZ3aNcUDEFbXRMihkONVw
You can view more examples of using the jsonwebtoken package in
the package's NPM page.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

