SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON [Solved]
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON
The "SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON" error occurs when we
try to JSON.parse a value that is not a valid JSON string, e.g. a native
JavaScript object.
To solve the error, use the JSON.stringify() method if you need to convert a
value to JSON.
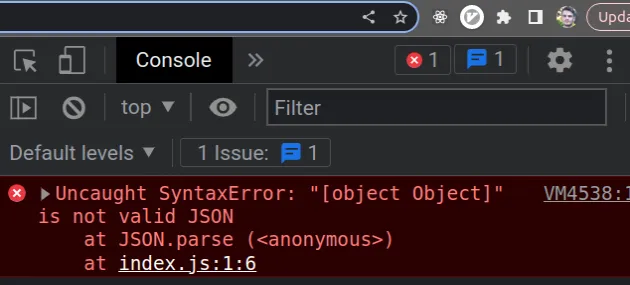
You might also get the error named "SyntaxError: Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1" depending on your browser or version of Node.js.
SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON Uncaught SyntaxError:️ Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1
# Examples of how the error occurs
Here are some examples of how the error occurs.
// ⛔️ SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON // Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1 JSON.parse({}); // 👈️ parsing a JS object // ✅ If you meant to convert a value to JSON const jsonStr = JSON.stringify({site: 'bobbyhadz.com'}); // -------------------------------------------------- // ⛔️ SyntaxError: // Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1 JSON.parse({a: 'b'}); // 👈️ parsing a JS object // -------------------------------------------------- // ⛔️ (if using jQuery) // ⛔️ SyntaxError: // Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1 $.parseJSON({}) // 👈️ parsing a JS object
We passed a native JavaScript object to the JSON.parse method.
# If the value is already a JS object, you don't have to parse it
If the value is already a native JavaScript value (not JSON), you don't have to
use the JSON.parse or $.parseJSON methods.
You can use the value in your code as is.
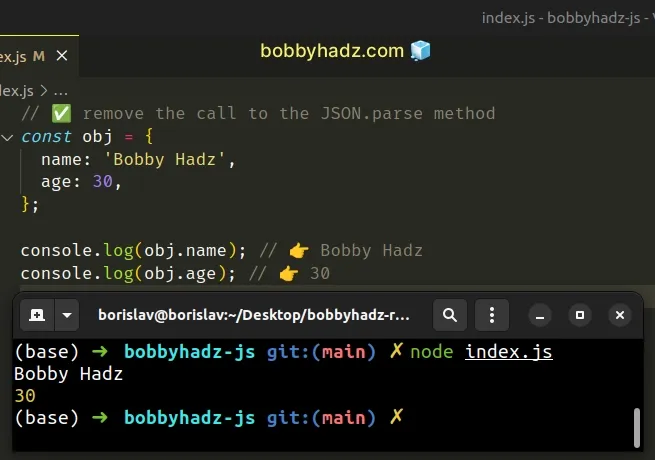
In this case, you can remove the call to the JSON.parse() method and use the
object as is.
// ✅ remove the call to the JSON.parse method const obj = { name: 'Bobby Hadz', age: 30, }; console.log(obj.name); // 👉️ Bobby Hadz console.log(obj.age); // 👉️ 30
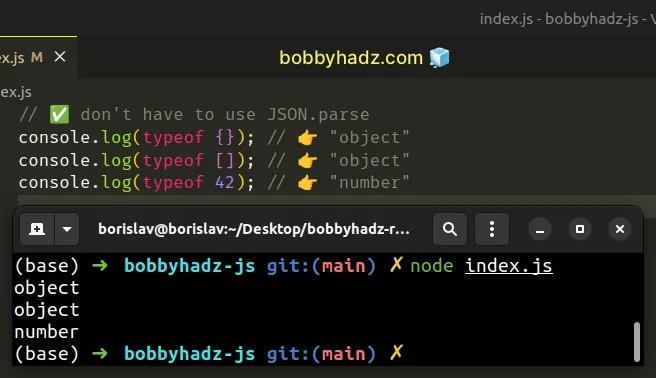
You can check the type of a value by using the typeof operator.
// ✅ don't have to use JSON.parse console.log(typeof {}); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof []); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof 42); // 👉️ "number"
string. If the type of the value is not string, then it is not JSON and is a native JavaScript value that you can use directly in your code.Libraries like jQuery and axios
automatically parse the JSON response to a native JavaScript value, so you don't
have to use the JSON.parse() method as the value is already parsed.
# Use JSON.stringify() to convert a value to JSON
If you're trying to convert a value to JSON, use the JSON.stringify() method
instead:
// ✅ is now valid JSON string const json = JSON.stringify({name: 'Bobby'}); console.log(json); // 👉️ {"name":"Bobby"} console.log(typeof json); // 👉️ string
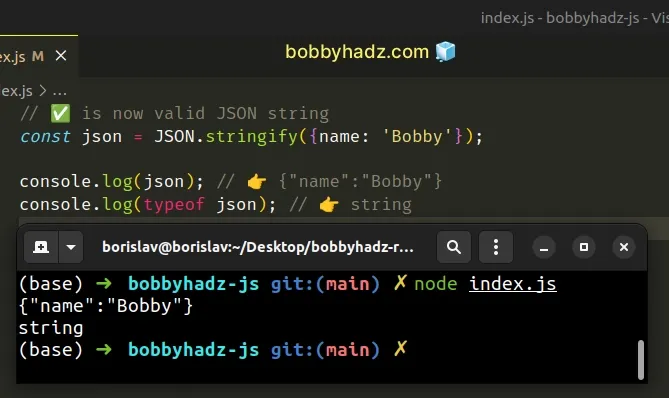
The JSON.stringify() method converts a native JavaScript value to a JSON string.
try/catch block to handle any errors.If for some reason, you have to use the JSON.parse() method with a native
JavaScript object, you can first stringify the object and then parse the JSON.
const parsed = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify({name: 'Bobby'})); console.log(parsed); // 👉️ { name: 'Bobby' } console.log(typeof parsed); // 👉️ object
The code sample first converts the object to a JSON string using
JSON.stringify().
Then, the JSON.parse() method is used to parse the JSON string into a native
JavaScript object.
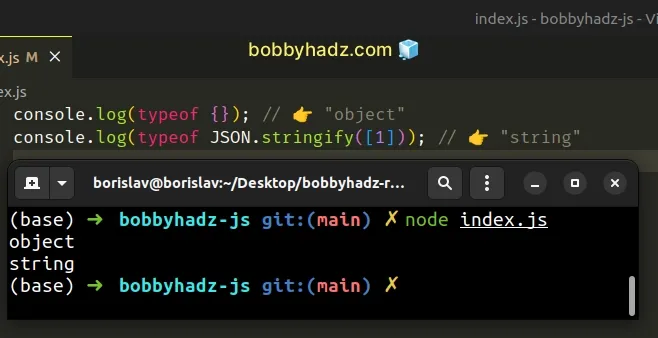
# All JSON values have a type of string
If the value is JSON, then it must be of type string.
console.log(typeof {}); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof JSON.stringify([1])); // 👉️ "string"
# Using a try/catch statement to handle a possible error
Here's an example of how to use a try/catch block to handle a possible error
when parsing a value.
try { const parsed = JSON.parse({}); } catch (err) { // ⛔️ SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON console.log(err.message); }
We call the JSON.parse() method inside a try/catch block. If passed an
invalid JSON value, the method will throw an error which will get passed to the
catch() function.
You can handle the error in the catch function as you see fit.
# Awaiting a Promise before you parse the JSON
Another common cause of the error is forgetting to await a Promise.
Make sure to await the Promises
async function fetchData() { // Awaiting the fetch() Promise ✅ const res = await fetch( 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', ); // Parsing the JSON data (must await again) ✅ const json = await res.json(); console.log(json); } fetchData();
Notice that we await the Promise that is returned from fetch and then await
the method that parses the JSON into native JavaScript.
# Make sure your server sends the correct response
If you are expecting valid JSON from your server, you can console.log the
response from your server and its type using the typeof operator.
If your server is not sending valid JSON, make sure to set the Content-Type
header to application/json on your server side.
If the value is malformed or not valid JSON, you have to format it correctly
before passing it to the JSON.parse method.
# Parsing a JSON string
The JSON.parse method parses a JSON string into a native JavaScript value.
const jsonStr = ` { "id": 1, "name": "Alice" } `; // ✅ parse JSON string into JS value const result = JSON.parse(jsonStr); console.log(result); // 👉️ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' } console.log(typeof result); // 👉️ object // ------------------------------------------------- // ✅ convert JS value to JSON string const jsonStr2 = JSON.stringify({id: 1, name: 'Bobby'}); console.log(jsonStr2); // 👉️ '{"id":1,"name":"Bobby"}' console.log(typeof jsonStr2); // 👉️ string
The JSON.stringify method converts a native JavaScript value to a JSON string.
Trying to parse a native JavaScript value causes the error.
// ⛔️ SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON JSON.parse({site: 'bobbyhadz.com'});
When you aren't sure about the type of a value, use the typeof operator.
JSON values always are of type string. If the value isn't of type string,
then it isn't JSON.
If you get the error "SyntaxError: JSON.parse unexpected character", click on the following article.
# Common reasons the error occurs
The "SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON" error occurs for multiple reasons:
- Trying to parse a native JavaScript object using
JSON.parse(). Note that you don't have to callJSON.parseif the value is already an object. - Mistakenly using
JSON.parse()when trying to convert a value to a JSON string. Instead, use theJSON.stringify()method to convert a JS value to JSON. - Your server sending back an incorrect response, with a possibly wrong
Content-Typeheader.

