Missing initializer in const declaration Error in JS and TS
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Missing initializer in const declaration Error in JS
- 'Const' declarations must be initialized in TypeScript
If you got the error when using TypeScript, click on the second subheading.
# Missing initializer in const declaration Error in JS
The "Missing initializer in const declaration" error occurs when a variable is
declared using const, but its value is not initialized on the same line.
To solve the error, initialize the variable on the same line you declare it,
e.g. const num = 30;.
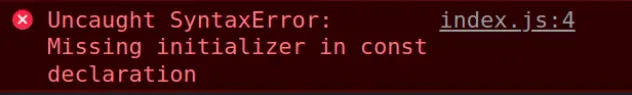
Here's an example of how the error occurs.
// ⛔️ Missing initializer in const declaration const country; // ⛔️ Missing initializer in const declaration const age; age = 30;
We declared a variable using the const keyword, however, we didn't initialize its value on the same line.
const cannot be reassigned, so we have to set their value upon declaration.const name = 'bobby'; const age = 30; const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'];
# Use let to declare variables that can be reassigned
If you need to declare a variable that can be reassigned, use the let statement instead.
// ✅ let = can be reassigned let country; country = 'Chile'; // ✅ const = Set value upon declaration const age = 30;
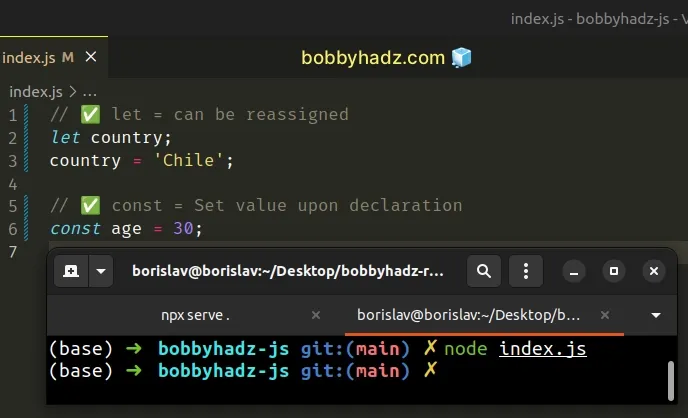
Variables declared using let can be reassigned later on in your code.
Console tab or your Node.js terminal.The error message should display the file in which the error occurred and the specific line.
# Variables declared using let cannot be redeclared
Variables declared using the let statement can be reassigned. However, they
cannot be redeclared.
let country; // ⛔️ Identifier 'country' has already been declared let country = 'Chile';
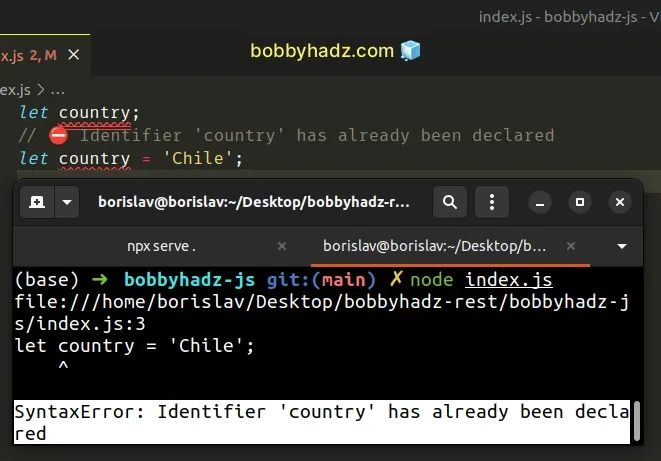
We tried to redeclare the country variable and got an error. Instead, omit the
let keyword when reassigning a variable declared using let.
let age; age = 30; console.log(age); // 👉️ 30 age = 31; console.log(age); // 👉️ 31
# Set the value on the same line when using const
If you don't need to reassign the variable, use the const keyword and set its
value when declaring the variable.
// ✅ Works const country = 'Chile'; // ⛔️ Error: Assignment to constant variable country = 'Brazil';
const keyword cannot be reassigned.Using const lets the reader of your code know that this variable will not be
reassigned at a later point.
# The const keyword doesn't make objects and arrays immutable
Note that the const keyword doesn't make objects or arrays immutable, it just
prevents you from reassigning the variable.
// 👇️ can change the contents of an array declared using const const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz']; arr[0] = 'xyz'; console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 'xyz', 'hadz' ] // --------------------------------------------- // 👇️ can change the contents of an object declared using const const obj = {name: 'bobby'}; obj['name'] = 'alice'; console.log(obj); // 👉️ { name: 'alice' }
We are still able to change the contents of an array or an object declared using
const, however, we can't redeclare or reassign the variables.
# 'Const' declarations must be initialized in TypeScript
The error "const declarations must be initialized" occurs when we declare a
variable using const but don't assign a value to it.
To solve the error, specify a value in the same statement in which the
variable is declared or use the let keyword instead.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
// ⛔️ 'const' declarations must be initialized.ts(1155) const arr: string[];
We declared the arr variable using the
const
keyword but didn't assign a value to it.
To solve the error, we have to assign a value to the const variable in the
same statement in which it was declared.
const arr: string[] = [];
What value you assign to the variable will depend on its type.
# Using the let keyword to solve the error
An alternative solution is to use the let keyword to declare your variable.
let arr: string[]; arr = ['bobby', 'hadz']; arr = ['.', 'com']; console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['.', 'com']
When you use the let keyword, you can reassign the variable as many times as
necessary.
const cannot be reassigned, which is why the "const declarations must be initialized" error occurs.If you declare a const variable without a value, you are effectively declaring
an empty variable that cannot be reassigned and given a value later on, which
must be a mistake.
We use a colon to give the variable a type and an equal sign to assign a value to it.
const obj: { name: string } = { name: 'Bobby Hadz' };
Note that variables declared using const cannot be reassigned, but they are
not immutable.
const obj: { name: string } = { name: 'Bobby Hadz' }; obj['name'] = 'Carl'; console.log(obj); // 👉️ {name: 'Carl'} // ⛔️ Error: Assignment to constant variable. obj = { name: 'Alan' };
The code sample shows that we are able to change the value of an object declared
using const, however, trying to reassign the const variable causes an error.
This is because you aren't allowed to reassign or redeclare a variable declared
using the const keyword.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

