How to Initialize an Array of Objects in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Initialize an Array of Objects in JavaScript
To initialize an array of objects:
- Use the
Array()constructor to create an array of N empty elements. - Pass the array and a
map()function to theArray.from()method. - Return an object on each iteration of the
map()function.
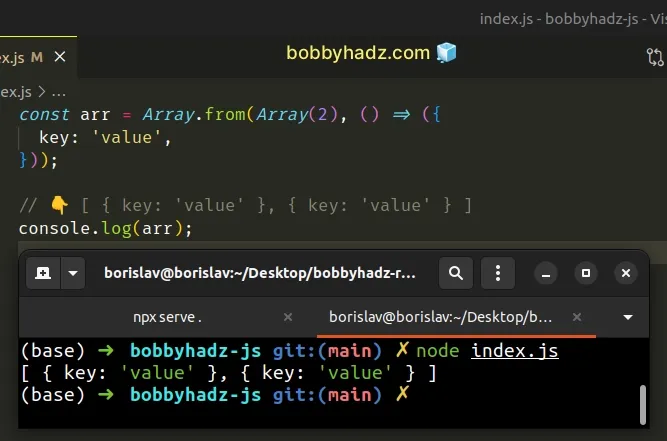
const arr = Array.from(Array(2), () => ({ key: 'value', })); // 👇️ [ { key: 'value' }, { key: 'value' } ] console.log(arr);
You also have access to the index in the map() function.
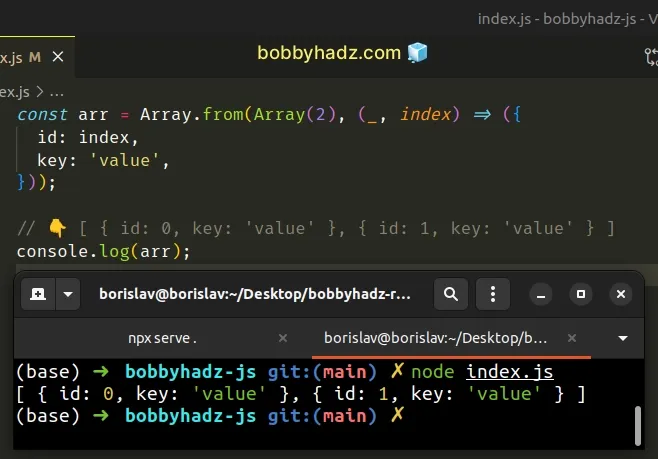
const arr = Array.from(Array(2), (_, index) => ({ id: index, key: 'value', })); // 👇️ [ { id: 0, key: 'value' }, { id: 1, key: 'value' } ] console.log(arr);
The Array.from() method creates a new array from the provided iterable.
The second argument we passed to the method is a map() function.
The function gets invoked with each element in the array.
On each iteration, we return an object.
The Array.from() method returns a new array containing the elements that the
map function returned.
# Initialize an Array of Objects using fill()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array()constructor to create an array of N empty elements. - Use the
Array.fill()method to fill the array withundefinedvalues. - Use the
map()method to fill the array with objects.
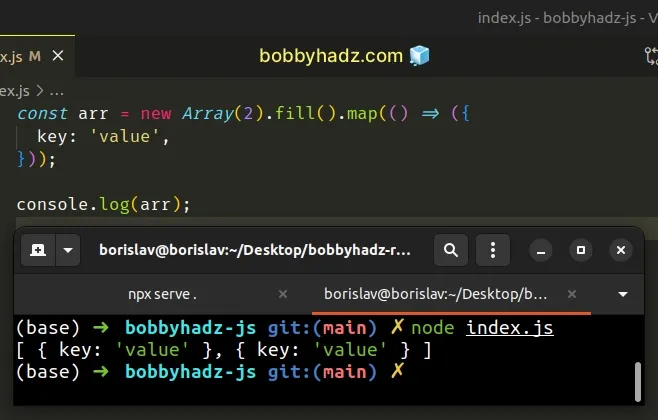
const arr = new Array(2).fill().map(() => ({ key: 'value', })); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ { key: 'value' }, { key: 'value' } ]
You can also access the index when using the Array.map() method.
const arr1 = new Array(2).fill().map((_, index) => ({ id: index, })); console.log(arr1); // 👉️ [ { id: 0 }, { id: 1 } ]
The argument we passed to the Array() constructor is the number of empty elements the array should contain.
console.log(new Array(2)); // 👉️ [ , ]
The Array() constructor sets the array's length to the provided value.
const arr = []; arr.length = 2; console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ , ]
We used the Array.fill()
method to fill the array with undefined values.
// 👇️ [ undefined, undefined ] console.log(new Array(2).fill());
This is necessary because the map() function doesn't iterate over empty
elements.
We could have passed an object directly to the Array.fill() method to fill the
array with objects.
However, note that the objects in the array would store the same reference.
const arr = new Array(2).fill({key: 'value'}); // 👇️ [{key: 'value'}, {key: 'value'}] console.log(arr); arr[0].anotherKey = 'another value'; // [ // { key: 'value', anotherKey: 'another value' }, // { key: 'value', anotherKey: 'another value' } // ] console.log(arr);
This is why we used the Array.map() method to iterate over the array and fill
it with objects stored in different locations in memory.
Alternatively, you can use a simple for loop.
# Initialize an Array of Objects using for loop
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array()constructor to create an array of N empty elements. - Use a
forloop to iterate over the array. - Assign an object to each element.
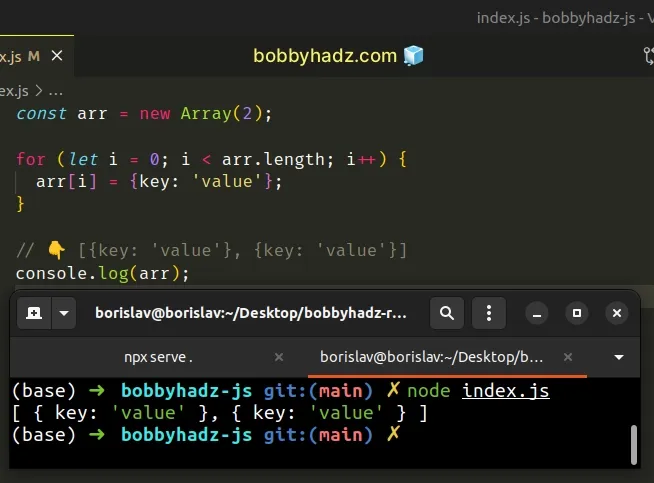
const arr = new Array(2); for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = {key: 'value'}; } // 👇️ [{key: 'value'}, {key: 'value'}] console.log(arr);
We used the Array() constructor to create an array of 2 empty elements.
The for loop allows us to iterate over the array and assign an object to each
empty element.
We can't use the Array.forEach() method to iterate over the array because it
skips empty elements.
Instead, we used the array's length in a basic for loop.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

