Increment the Values in an Array using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- Increment the Values in an Array in JavaScript
- Creating an incrementing array in JavaScript
- Increment specific values in an array in JavaScript
- Increment the values in an array using
forEach() - Increment the values in an array using a
forloop
# Increment the Values in an Array in JavaScript
To increment the values in an array:
- Use the
Array.map()method to iterate over the array. - Increment each value and return the result.
- The
map()method will return a new array containing the incremented values.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; const newArr = arr.map(num => num + 1); console.log(newArr); // 👉️ [2, 3, 4]
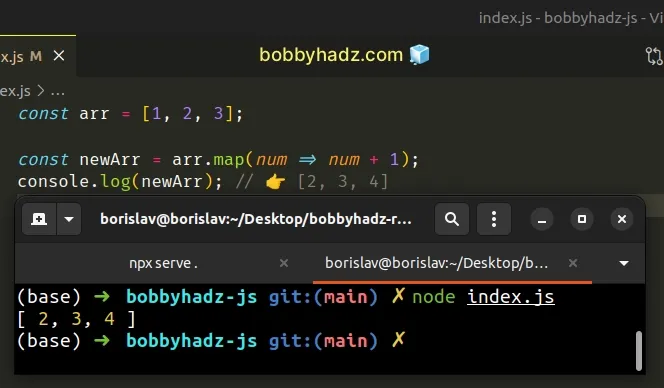
The function we passed to the Array.map() method gets called with each element in the array.
On each iteration, we add 1 to the current number and return the result.
The map() method returns a new array containing the values returned from the
callback function.
Array.map() method doesn't mutate the original array, it returns a new array.# Creating an incrementing array in JavaScript
If you need to create an incrementing array, use the Array.from() method.
const arr1 = Array.from(Array(5), (_, index) => index); console.log(arr1); // 👉️ [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 ] const arr2 = Array.from(Array(5), (_, index) => index + 1); console.log(arr2); // 👉️ [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
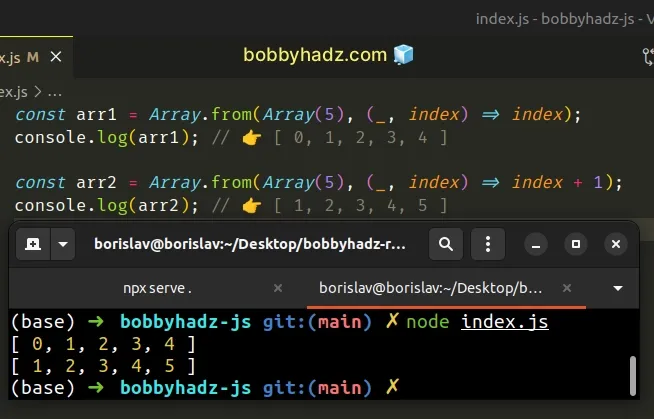
The function we passed to the Array.from() method is a map() function, just
like in the previous example.
You can use the index to create an incrementing array.
# Increment specific values in an array in JavaScript
If you need to increment a specific value, access the array at an index and increment the value.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; arr[0] += 1; console.log(arr[0]); // 👉️ 2 arr[0] = arr[0] + 1; console.log(arr[0]); // 👉️ 3
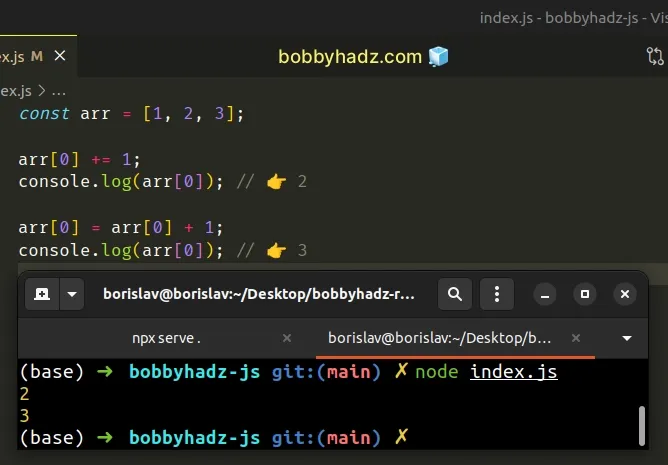
The
addition assignment (+=)
operator is a shorthand for myVariable = myVariable + value.
0, and the last element has an index of array.length - 1.When you access the array at the specific index and assign a new value to it, you mutate the original array and change its value in place.
Note that when using the addition assignment (+=) operator with primitives like
strings or numbers, the variable has to be declared using the let keyword.
let a = 1; a += 5; console.log(a); // 👉️ 6 // 👇️ same as above a = a + 5; console.log(a) // 👉️ 11 const b = 1; // ⛔️ SyntaxError b ++ 5;
When using the addition assignment (+=) operator with primitives, we reassign the variable.
This is not the case with arrays or objects, where we change the value of a specific element without reassigning the actual variable.
Alternatively, you can use the Array.forEach() method.
# Increment the values in an array using forEach()
This is a two-step process:
- Use the
Array.forEach()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, increment the element at the current index by
1.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; arr.forEach((num, index) => { arr[index] = num + 1; }); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [2, 3, 4]
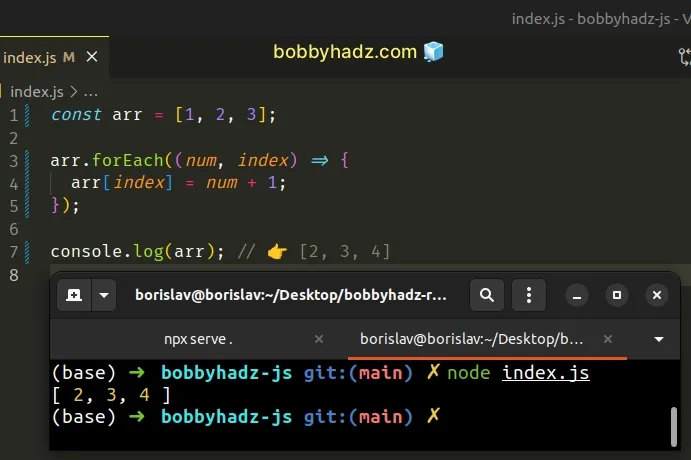
The function we passed to the Array.forEach() method gets called with each element in the array.
We access the element at the current index and increment its value by 1.
The forEach() method returns undefined, so we have to perform some kind of
mutation to persist the state.
You can also use a basic for loop.
# Increment the values in an array using a for loop
This is a two-step process:
- Use a
forloop to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, increment the element at the current index by
1.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) { arr[index] = arr[index] + 1; } console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 2, 3, 4 ]
The code sample is very similar to the previous one.
However, instead of using the Array.forEach() method, we used a basic for
loop to iterate over the array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

