Get the Second to Last Element in Array in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Get the Second to Last Element in an Array in JavaScript
To get the second to last element in an array, use bracket notation to access
the element at index array.length - 2.
The last element in an array has an index of array.length - 1 and the second
to last has an index of array.length - 2.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; const secondToLast = arr[arr.length - 2]; console.log(secondToLast); // 👉️ "c"
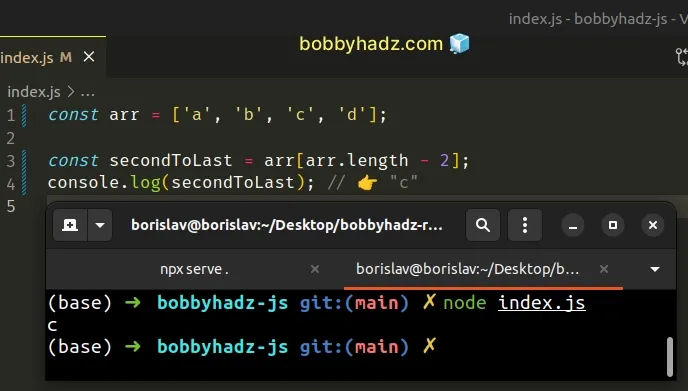
We accessed the array at index array.length - 2 to get the second to last
array element.
0 and the last element has an index of array.length - 1.By subtracting 1 from the last index, we get the index of the second to last
array element.
If the array contains less than 2 elements, we would get an undefined value.
const arr = []; const secondToLast = arr[arr.length - 2]; console.log(secondToLast); // 👉️ undefined
You can use the logical OR (||) operator to provide a fallback value.
const arr = []; const secondToLast = arr[arr.length - 2] || ''; console.dir(secondToLast); // 👉️ ''
We used a fallback value of an empty string, but you can use any other value that suits your use case
# Get the Second to Last Element in an Array using Array.at()
An alternative approach is to use the Array.at() method.
The Array.at() method counts backward when supplied with a negative index.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; const secondToLast = arr.at(-2); console.log(secondToLast); // 👉️ "c"
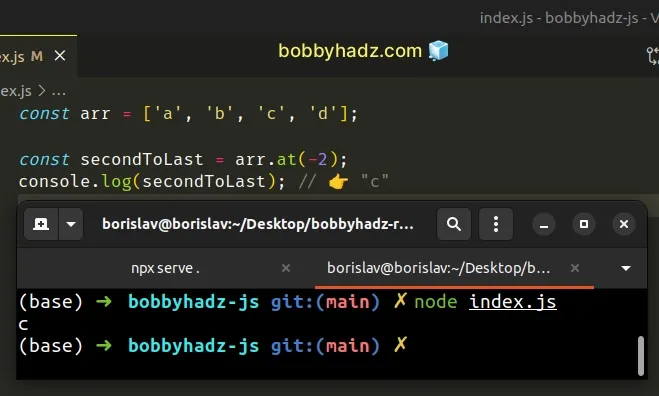
The Array.at() method takes an integer and returns the item at that index.
The method allows for positive and negative integers.
You can use negative integers to count back from the end of the array.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; console.log(arr.at(-1)); // 👉️ d console.log(arr.at(-2)); // 👉️ c
A negative index of -1 returns the last element and a negative index of -2
returns the second to last array element.
We would get an undefined value if the array contains only a single element or
is empty.
const arr = []; const secondToLast = arr.at(-2); console.log(secondToLast); // 👉️ undefined
# Get the Second to Last Element in an Array using Array.slice()
You can also get the second to last element in an array using Array.slice().
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; const secondToLast = arr.slice(-2, -1)[0]; console.log(secondToLast); // 👉️ 'c'
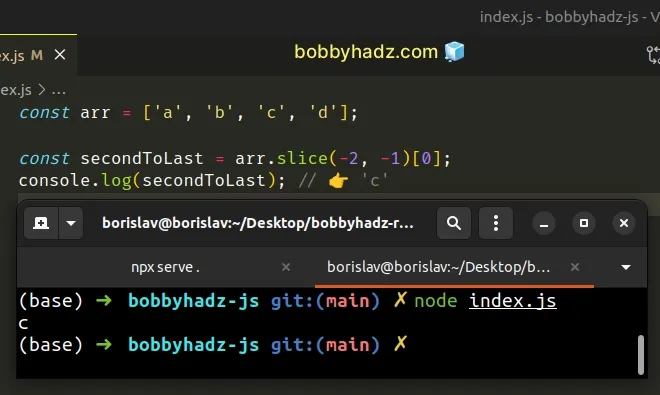
The Array.slice() method returns a copy of a portion of an array.
The method takes the following 2 arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start index | The index of the first element to include in the returned array |
| end index | The index of the first element to exclude from the returned array |
The Array.slice() method can be passed negative indexes to count backward.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; // 👇️ [ 'c' ] console.log(arr.slice(-2, -1));
A negative start index of -2 means "start at the second to last character".
A negative end index of -1 means "go up to, but not including the last
character".
The Array.slice() method returns an array, so we had to access the array
element at index 0 to get the second to last element of the original array.
# Get the Second to Last Element in an Array using reverse
You can also use the Array.reverse() method to reverse the array and access
the reversed array at index 1 to get the second to last array element.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; const secondToLast = [...arr].reverse()[1]; console.log(secondToLast); // 👉️ 'c'
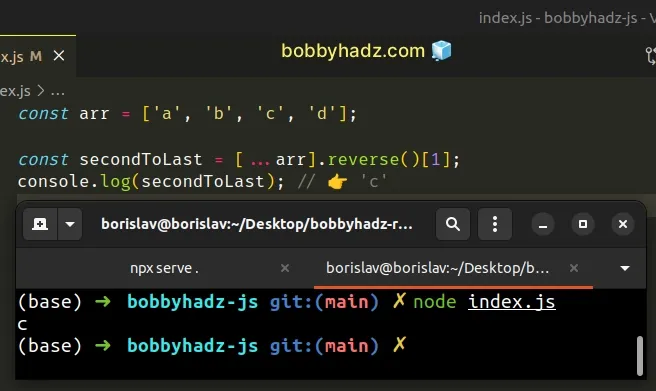
The Array.reverse() method reverses an array in place.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; console.log(arr.reverse()); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 'd', 'c', 'b', 'a' ]
We had to use the spread syntax (...) to create a shallow copy of the array to not mutate the original.
The last step is to access the reversed array at index 1.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use square
bracket notation to access the element at index array.length - 2 or the
Array.at() method with a negative index of -2.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Split a String and get First or Last Array Element in JS
- Get one or Multiple Random Elements from an Array in JS
- Get the last N elements of an Array in JavaScript
- Get the first N elements of an Array in JavaScript
- Get the First and Last Elements of an Array in JavaScript
- Get every Nth Element of Array using JavaScript

