ParseError: not well-formed (invalid token) [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# ParseError: not well-formed (invalid token) [Solved]
The error "xml.etree.ElementTree.ParseError: not well-formed (invalid token)" occurs when the string you are trying to parse contains an invalid character.
To solve the error, ignore the errors by using the XMLParser class from the
lxml module and setting recover to True.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET data = """ <body> <p>bobbyhadz.com \x08</p> </body>""" # ⛔️ xml.etree.ElementTree.ParseError: not well-formed (invalid token): line 3, column 19 print(ET.XML(data))
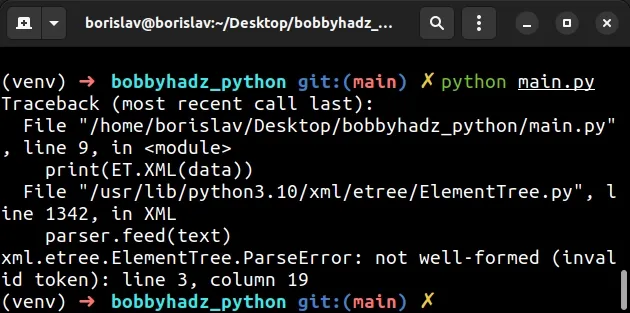
The \x08 character is invalid which caused the error.
One way to get around this is to use the XMLParser class from the lxml
module.
First, install the lxml module by issuing the following command.
pip install lxml # or with pip3 pip3 install lxml
Now, import and use the module as follows.
from lxml import etree data = """ <body> <p>bobbyhadz.com \x08</p> </body>""" parser = etree.XMLParser(recover=True) root = etree.fromstring(data, parser=parser) print(root.tag) # 👉️ body # b'<body>\n <p>bobbyhadz.com </p>\n</body>' print(etree.tostring(root)) print(root.find('p').tag) # 👉️ p
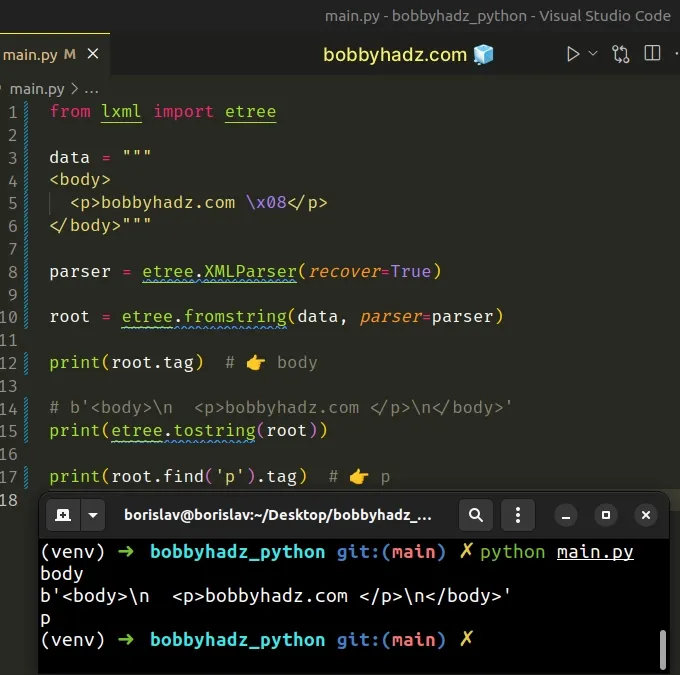
Make sure to set the recover argument to True, so the parser ignores the
errors that were caused by trying to parse invalid characters.
# Removing the invalid characters to solve the error
You can also solve the error by removing the invalid characters.
First, use the repr() method to print the string and make note of the invalid
characters.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET data = """ <body> <p>bobbyhadz.com \x08</p> </body>""" # '\n<body>\n <p>bobbyhadz.com \x08</p>\n</body>' print(repr(data))
The string contains a \x08 that we have to remove.
We can use the str.replace() method to remove the character from the string.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET data = """ <body> <p>bobbyhadz.com \x08</p> </body>""" data = data.replace('\x08', '') root = ET.XML(data) print(root.tag) # b'<body>\n <p>bobbyhadz.com </p>\n</body>' print(ET.tostring(root)) print(root.find('p').tag) # 👉️ p
The str.replace() method returns a copy of the string with all occurrences of
a substring replaced by the provided replacement.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| old | The substring we want to replace in the string |
| new | The replacement for each occurrence of old |
| count | Only the first count occurrences are replaced (optional) |
We remove all occurrences of the character by replacing them with empty strings.
You might have to call the replace() method multiple times if your string
contains multiple invalid characters.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET data = """ <body> <p>\x0c bobbyhadz.com \x08</p> </body>""" data = data.replace('\x08', '').replace('\x0c', '') root = ET.XML(data) print(root.tag) # b'<body>\n <p>bobbyhadz.com </p>\n</body>' print(ET.tostring(root)) print(root.find('p').tag) # 👉️ p
The first call to the str.replace() method removes the \x08 character and
the second removes the \x0c character.
The str.replace() method returns a new string with the matches replaced, so
you can chain as many calls to the method as necessary.
Once you remove all invalid characters, you can safely use the ET.XML()
method.
The method parses an XML document from a string constant.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

