How to Convert an Object to an Array in TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Convert an object to an Array in TypeScript
There are three ways to convert an object to an array in TypeScript:
Object.keys()- returns an array containing the object's keys.Object.values()- returns an array containing the object's values.Object.entries()- returns an array containing key-value pair arrays.
const obj = { name: 'Bobby', country: 'Chile' }; const keys = Object.keys(obj); console.log(keys); // 👉️ ['name', 'country'] const values = Object.values(obj); console.log(values); // 👉️ ['Bobby', 'Chile'] const entries = Object.entries(obj); console.log(entries); // 👉️ [['name', 'Bobby'], ['country', 'Chile']]
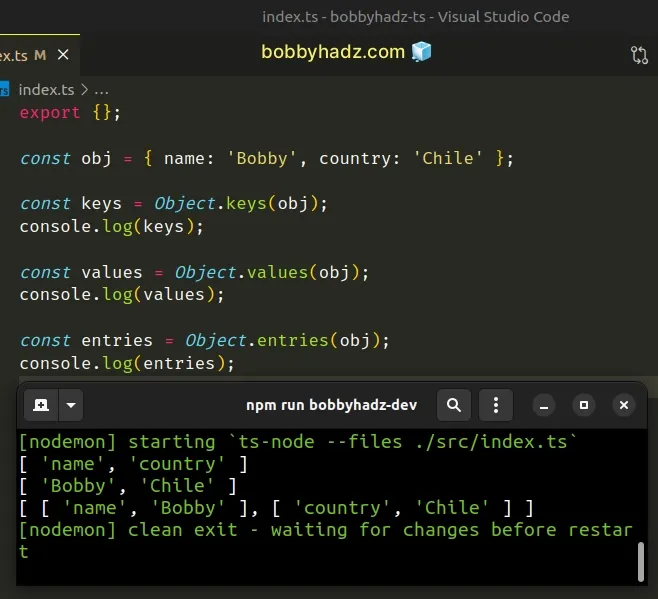
The first example uses the Object.keys method to get an array of the object's keys.
The method returns an array of strings where the keys of the object are in the
same order as provided by a for...in loop.
// 👇️️ ['one', 'two'] console.log(Object.keys({one: 1, two: 2}));
You can then iterate over the array of keys as follows.
const obj = { name: 'Bobby', country: 'Chile' }; const keys = Object.keys(obj) as (keyof typeof obj)[]; console.log(keys); // 👉️ ['name', 'country'] keys.forEach((key) => { // 👇️ name Bobby, country Chile console.log(key, obj[key]); });
# Convert an Object's values to an Array in TypeScript
You can use Object.values method to convert an object's values to an array.
const obj = { name: 'Bobby Hadz', country: 'Chile' }; const values = Object.values(obj); console.log(values); // 👉️ ['Bobby Hadz', 'Chile']
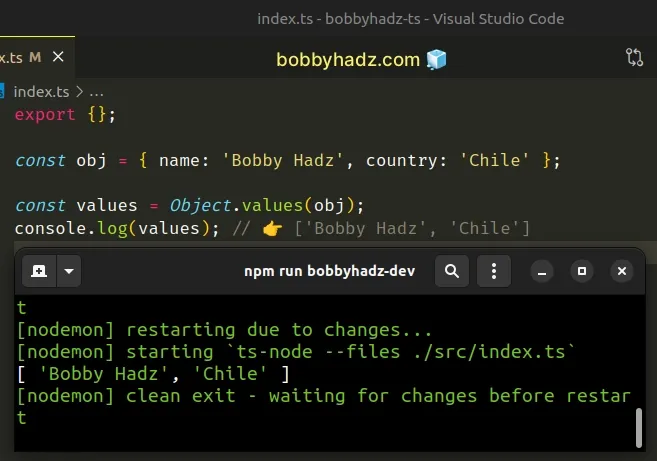
Similarly to the keys method, the values are added to the array in the same
order as that provided by a for...in loop.
# Convert an Object's entries to an Array in TypeScript
Use the Object.entries method to convert an object to an array of key-value pair arrays.
const obj = { name: 'Bobby Hadz', country: 'Chile' }; // 👇️ const entries: [string, string][] const entries = Object.entries(obj); console.log(entries); // 👉️ [['name', 'Bobby Hadz'], ['country', 'Chile']]
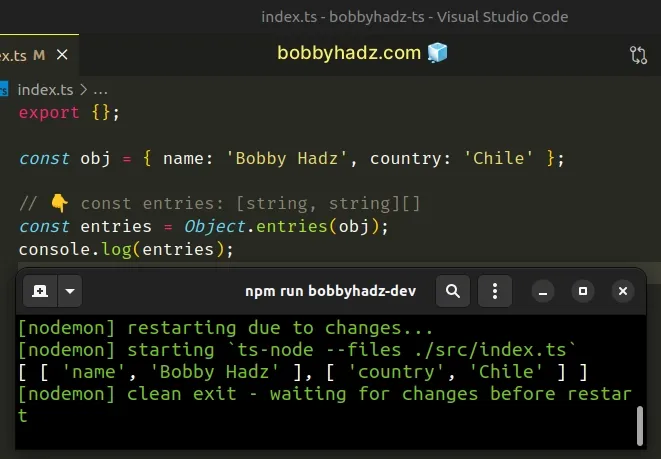
The nested arrays consist of 2 elements - the key and the value.
You can iterate over the array of key-value pairs by using the forEach()
method.
const obj = { name: 'Bobby', country: 'Chile' }; // 👇️ const entries: [string, string][] const entries = Object.entries(obj); console.log(entries); // 👉️ [['name', 'Bobby'], ['country', 'Chile']] entries.forEach(([key, value]) => { // 👇️ name Bobby, country Chile console.log(key, value); });
Notice that we used array destructuring to destructure the key and value from the array.
Here is an example of how array destructuring works.
const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz']; const [a, b] = arr; console.log(a); // 👉️ "bobby" console.log(b); // 👉️ "hadz"
We're basically unpacking the array's elements into variables. Note that the order is preserved.
I've also written an article on how to convert an object to a JSON string.

