How to extend Array.prototype in TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Extend Array.prototype in TypeScript
To extend Array.prototype in TypeScript:
- Create a
.d.tsfile and add an interface that extendsArray. - Add types for the methods you intend to use on array objects.
- Add the methods to the
Array.prototypeobject.
In the src directory of your project, create a types directory containing
the following index.d.ts file.
export {}; declare global { interface Array<T> { removeLast(): T[]; } }
The example shows how to extend the Array
interface with a method named
removeLast() that returns an array containing elements of the same type.
Now in your index.ts file, add the method to the Array.prototype object.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']; if (!Array.prototype.removeLast) { Array.prototype.removeLast = function () { this.pop(); return this; }; } // 👇️ const result: string[] const result = arr.removeLast(); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
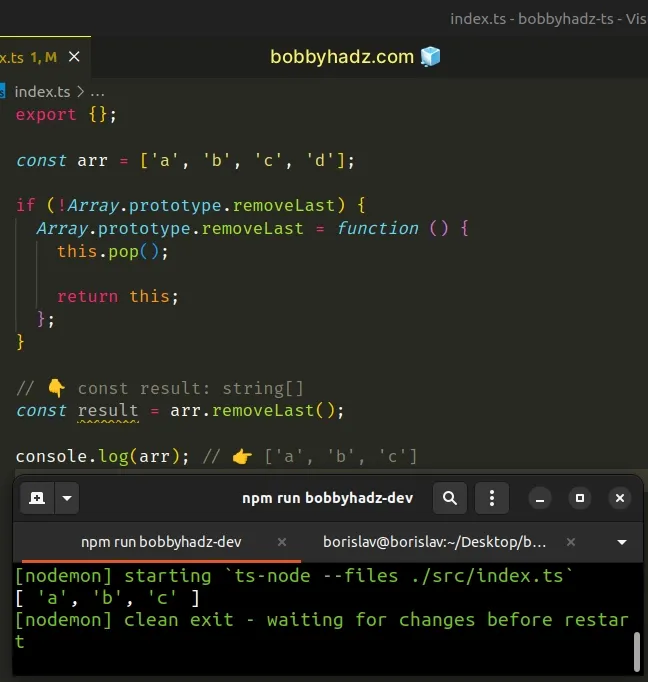
We added the removeLast method to the Array.prototype and used it.
Array.prototype object in a file that runs before all other files, e.g. an index.ts file.If you try to use the method before it was added to the prototype you'd get an error.
# Add the path to your types directory to your tsconfig.json file
If you are getting an error in your IDE, try adding the path to your types
directory to your tsconfig.json file.
{ "compilerOptions": { // ... rest "typeRoots": ["./node_modules/@types", "./src/types"] } }
We used the export {} line in our index.d.ts file to mark it as an external
module.
A module is a file that contains at least 1 import or export statement. We
are required to do that to be able to augment the global scope.
index.d.ts file according to your use case.You should add the names (and types) of all of the methods you intend to access on arrays.
export {}; declare global { interface Array<T> { removeLast(): T[]; } }
The provided file simply adds a removeLast method with a return type of T[],
which is most likely not what you need.
We used a generic in the method type. Generics are like variables but for types.
removeLast method takes no parameters and returns an array containing elements of the same type.TypeScript looks for .d.ts files in the same places it looks for your regular
.ts files.
The location is determined by the include and exclude settings in your
tsconfig.json file.
TypeScript will merge the declared from you Array interface with the original
Array interface, so when you use the arrays, you will be able to access
methods and properties from both interfaces.
I've also written an article on how to get the type of the array elements from an array type.
If you need to extend String.prototype, Object.prototype, Date.prototype or Number.prototype, click on the link and follow the instructions.

