Enable tracemalloc to get the object allocation traceback
Last updated: Apr 13, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Enable tracemalloc to get the object allocation traceback
The Python "RuntimeWarning: Enable tracemalloc to get the object allocation
traceback" occurs when you forget to await a coroutine.
To resolve the issue, make sure to await all coroutines in your Python script.
Here is an example of when the warning is shown.
import asyncio async def my_coroutine(): print('bobby') # ⛔️ RuntimeWarning: coroutine 'sleep' was never awaited # asyncio.sleep(0.5) # RuntimeWarning: Enable tracemalloc to get the object allocation traceback asyncio.sleep(0.5) # 👈️ Forgot to await asyncio.sleep() print('hadz.com') loop = asyncio.new_event_loop() asyncio.set_event_loop(loop) async def main(): tasks = [] asyncio.create_task(my_coroutine()) tasks.append(asyncio.create_task(my_coroutine())) await asyncio.wait(tasks) loop.run_until_complete(main()) loop.close()
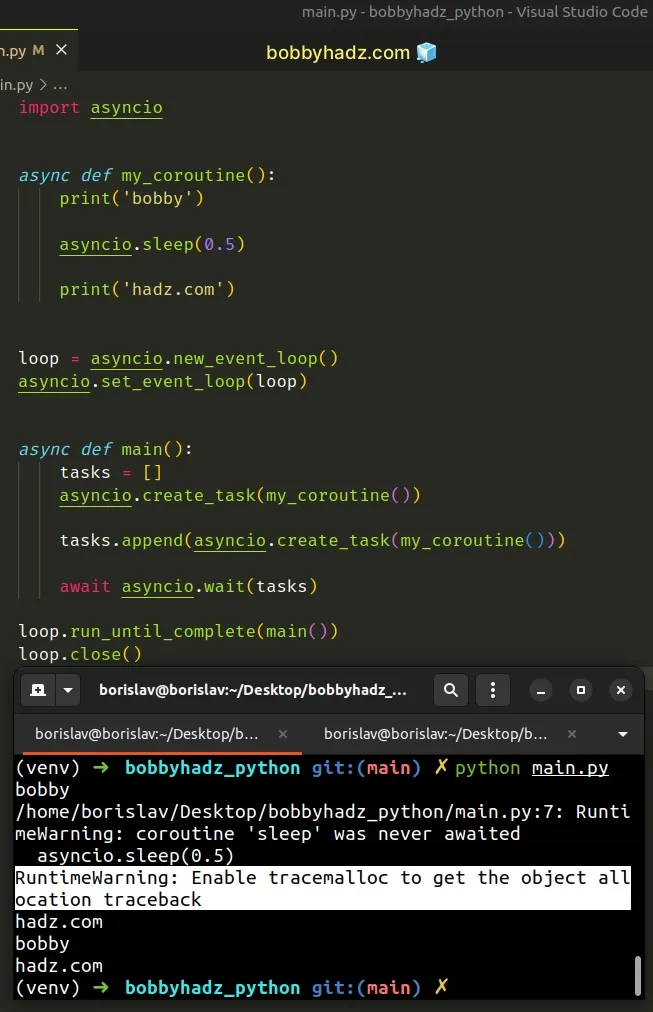
The issue occurred because I forgot to await the coroutine that is returned from
asyncio.sleep().
# Make sure to await all coroutines to resolve the issue
I just have to add the await keyword to await the coroutine to resolve the
issue.
In other words, this:
# ⛔️ Incorrect asyncio.sleep(0.5)
Becomes this:
# ✅ Correct await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
Here is the complete example.
import asyncio async def my_coroutine(): print('bobby') asyncio.sleep(0.5) print('hadz.com') loop = asyncio.new_event_loop() asyncio.set_event_loop(loop) async def main(): tasks = [] asyncio.create_task(my_coroutine()) tasks.append(asyncio.create_task(my_coroutine())) await asyncio.wait(tasks) loop.run_until_complete(main()) loop.close()
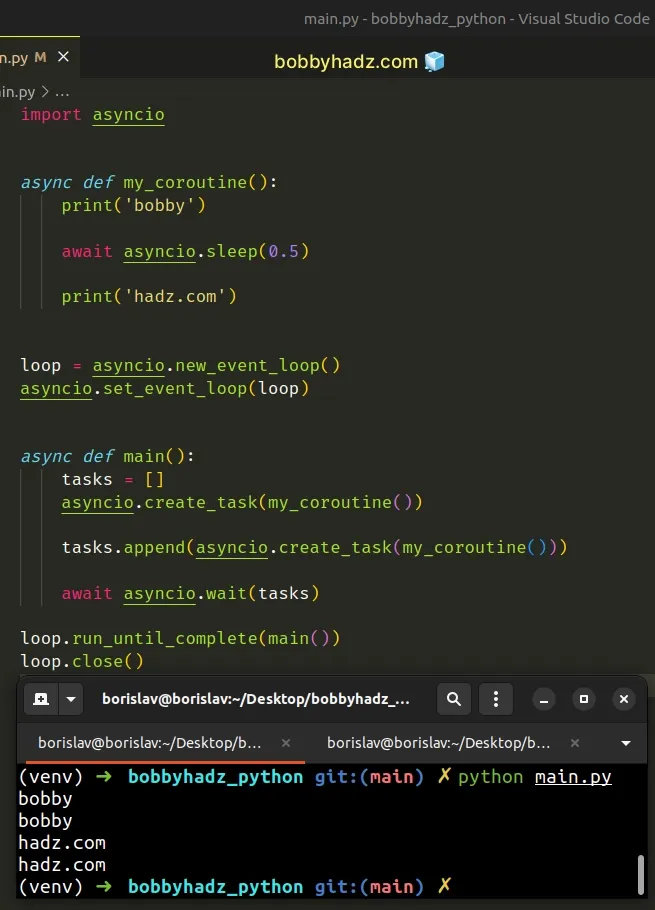
You have to await all
coroutines in
your code.
For example, coroutines are returned from calls to asyncio.sleep() and
asyncio.wait().
You can hover over a method in your IDE to see if it returns a coroutine.
Here is an example that does that in VS Code.
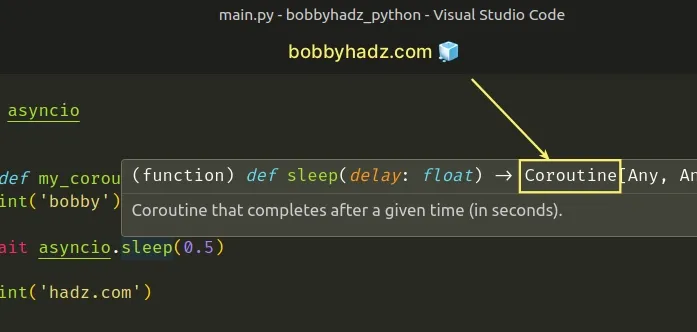
# You also need to await async functions
Note that async functions are also awaitable.
For example, the following code sample shows the warning.
import asyncio async def greet(name): return f'hello {name}' async def main(): # ⛔️ RuntimeWarning: Enable tracemalloc to get the object allocation traceback greet('bobby hadz') # 👈️ Forgot to await greet() asyncio.run(main())
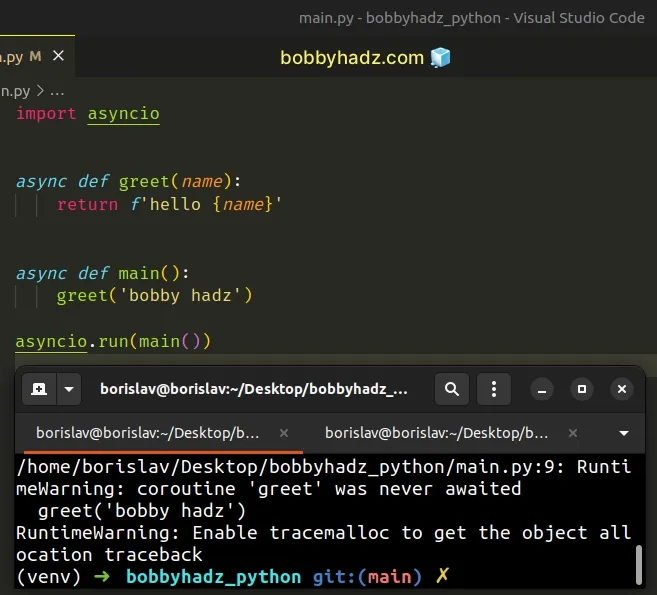
The warning is shown because I forgot to await the greet async function.
Here is the corrected version of the code.
import asyncio async def greet(name): return f'hello {name}' async def main(): print(await greet('bobby hadz')) asyncio.run(main())
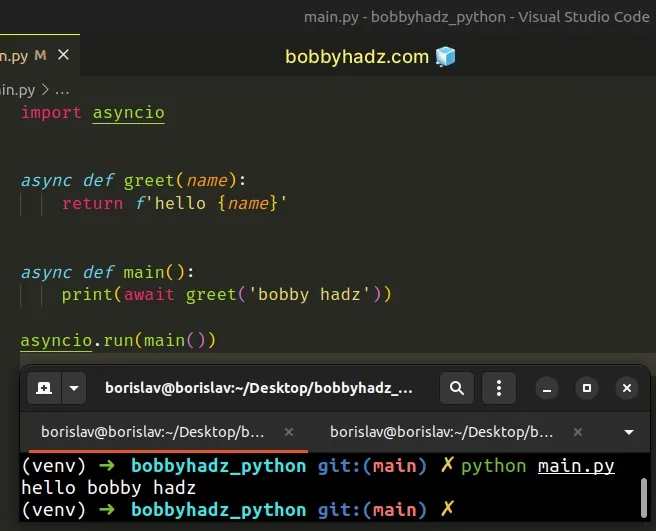
Python coroutines are awaitable so they can be awaited from other coroutines.
A coroutine is considered to be:
- a coroutine function: an
async deffunction. - a coroutine object: an object that is returned by calling a coroutine function.
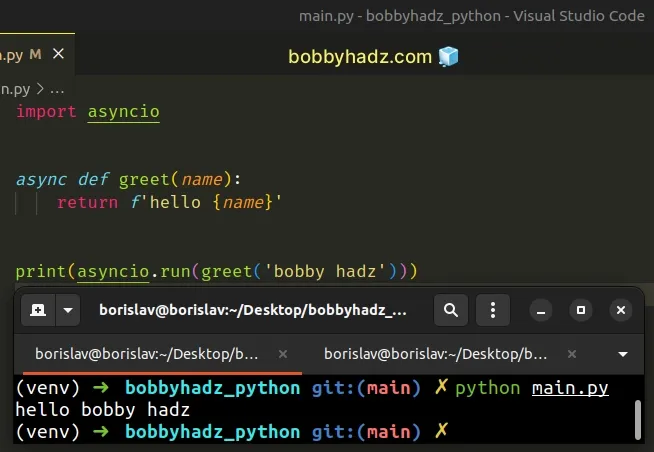
If you need to call an async function outside an event loop, use the
asyncio.run()
method.
import asyncio async def greet(name): return f'hello {name}' print(asyncio.run(greet('bobby hadz')))
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

