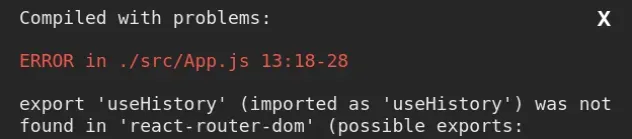
Export 'useHistory' was not found in react-router-dom
Last updated: Apr 6, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Export 'useHistory' was not found in react-router-dom
To solve the error "export 'useHistory' (imported as 'useHistory') was not
found in 'react-router-dom'", use the useNavigate hook instead, e.g.
const navigate = useNavigate().
The hook returns a function that lets you navigate programmatically.
// 👇️ import useNavigate import {useNavigate} from 'react-router-dom'; export default function App() { const navigate = useNavigate(); const handleClick = () => { // 👇️ Navigate programmatically navigate('/about'); }; return ( <div> <button onClick={handleClick}>Navigate to About</button> </div> ); }
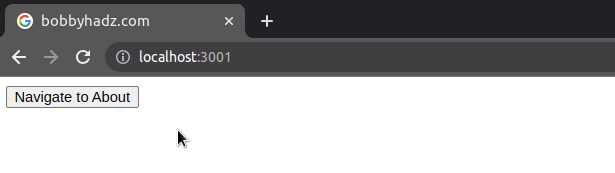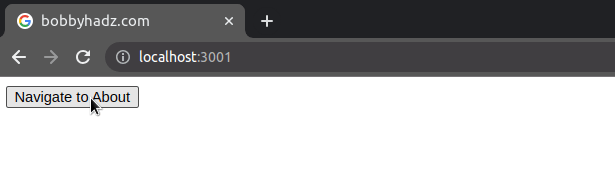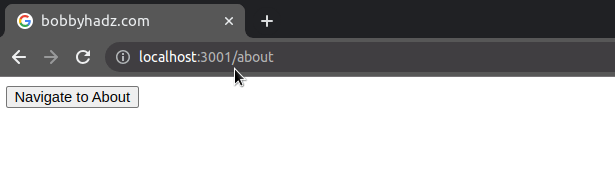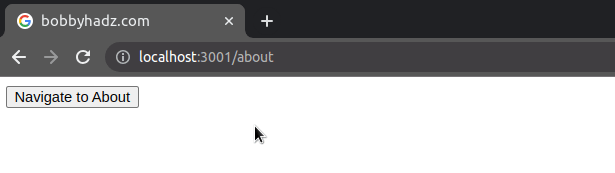
In version 6 of React Router, the useHistory() hook is replaced with
useNavigate().
useNavigate hook returns a function that lets us navigate programmatically, e.g. after a form is submitted.The parameter we passed to the navigate function is the same as the to prop
on a <Link to="/about"> component.
If you want to use the equivalent of the history.replace() method, pass an
options parameter to the navigate function.
import {useNavigate} from 'react-router-dom'; export default function App() { const navigate = useNavigate(); const handleClick = () => { // 👇️ Replace set to true navigate('/about', {replace: true}); }; return ( <div> <button onClick={handleClick}>Navigate to About</button> </div> ); }
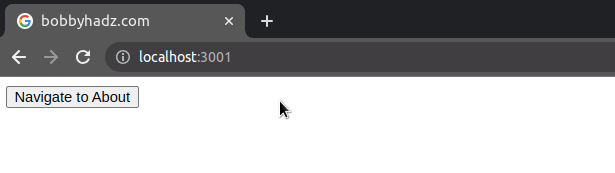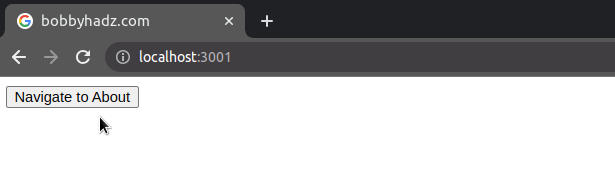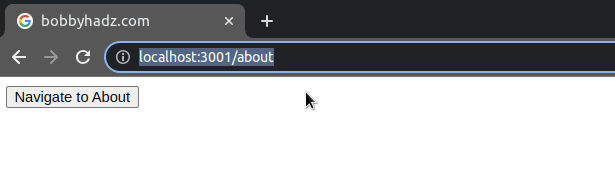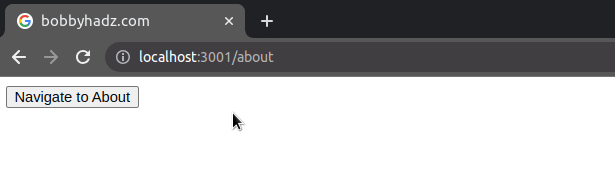
When the replace property is set to true on the options object, the current
entry in the history stack gets replaced with the new one.
This is useful, for example, when a user logs in - you don't want them to be able to click the back button and get back to the login page.
Or if you have a route that redirects to a different page. Then you don't want users to click the back button and get redirected again.
You can also call the navigate function with a delta to go back in the history
stack, e.g. navigate(-1) is the same as
hitting the back button.

