WARNING: Running pip as the 'root' user can result in broken permissions
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# WARNING: Running pip as the 'root' user can result in broken permissions
Use the --root-user-action=ignore option to ignore the "Running pip as the
'root' user can result in broken permissions" warning.
Alternatively, you can create a virtual environment or run the pip install
command with the --user option.
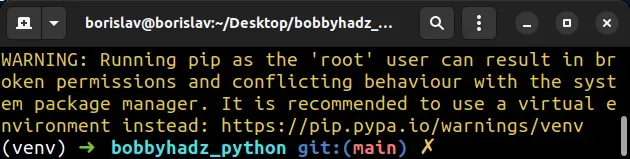
WARNING: Running pip as the 'root' user can result in broken permissions and conflicting behaviour with the system package manager. It is recommended to use a virtual environment instead: https://pip.pypa.io/warnings/venv
The warning is often shown when pip installing a package with sudo or in a
Docker container that doesn't have a user added.
# Using the --root-user-action option to ignore the warning
One way to ignore the warning is to use the --root-user-action option.
pip install --upgrade pip pip install --root-user-action=ignore requests # 👇️ Or with pip3 pip3 install --upgrade pip pip3 install --root-user-action=ignore requests
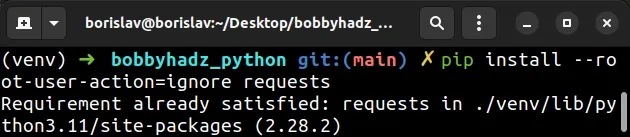
Make sure to replace requests in the example with the name of the package you
are installing.
The --root-user-action option is available as of pip v22.1.
Update your version of pip if you have an
older version.
# 👇️ Check pip version pip --version # 👇️ Upgrade pip version pip install --upgrade pip pip3 install --upgrade pip
# Setting the PIP_ROOT_USER_ACTION environment variable
Alternatively, you can set the PIP_ROOT_USER_ACTION environment variable to
ignore.
Here is an example of how to do that in a Docker file.
# 👇️ Upgrade pip RUN pip install --upgrade pip ENV PIP_ROOT_USER_ACTION=ignore
And here is how to set the environment variable on Linux, MacOS and Windows.
# Linux and MacOS export PIP_ROOT_USER_ACTION=ignore # Windows Command Prompt setx PIP_ROOT_USER_ACTION ignore # PowerShell $Env:PIP_ROOT_USER_ACTION="ignore"
Make sure to run the correct command depending on your operating system and shell type.
# If you don't add a user to a Docker container, the root user is used
If you don't add a user to a docker container, all commands are run as root.
You can add a user before running a pip install command to get rid of the
warning when using Docker.
FROM python:3.10.10-alpine3.17 RUN pip install pip --upgrade RUN adduser -D newuser USER newuser WORKDIR /home/newuser COPY --chown=newuser:newuser requirements.txt requirements.txt RUN pip install --user -r requirements.txt ENV PATH="/home/newuser/.local/bin:${PATH}" COPY --chown=newuser:newuser . . CMD ["python", "manage.py", "runserver", "0.0.0.0:8000"]
We used the adduser command to add a new user before we ran the pip install
command.
If no user is added, all commands are run as root which causes the issue.
# Using the --user option instead of sudo
Note that using sudo pip install is not a good practice.
Installing third-party packages with root privileges is dangerous and should be avoided.
One alternative is to use the --user option.
pip install requests --user pip3 install requests --user python -m pip install requests --user python3 -m pip install requests --user
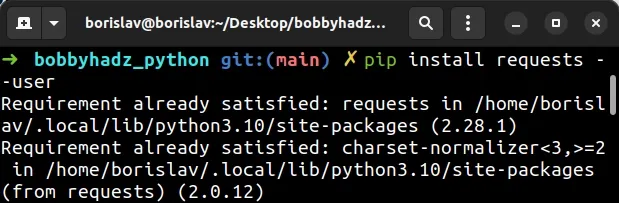
The --user option installs the package in the user's home directory.
If you decide to use this approach inside a Docker container, make sure to add a user first.
Any command you run in a container that doesn't have a user added is run as root.
# The --user option doesn't work in a virtual environment
However, the --user option wouldn't work if you are inside a virtual
environment.
A best practice is to create a virtual environment and install packages in it.
# 👇️ Use the correct version of Python when creating VENV python -m venv venv # 👇️ Activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ Activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ Activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 # 👇️ install the specific package in the virtual environment pip install requests
If the python -m venv venv command doesn't work, try the following 2 commands:
python3 -m venv venvpy -m venv venv
Your virtual environment will use the version of Python that was used to create it.
Make sure to use the correct command to activate your virtual environment depending on your operating system and your shell.
Your virtual environment will use the version of Python that was used to create it.
sudo, try changing its permissions or recreate it without sudo.sudo chmod -R 777 venv
The command above assumes that your virtual environment is in a folder called
venv.
777 means granting all users full access to the contents of the directory.
Creating a virtual environment and installing the package inside it helps because the virtual environment is an isolated Python installation.
You won't get permission issues because you aren't installing any packages globally.
Rather the packages are installed in the lib folder of your virtual
environment.
Make sure your versions of pip, setuptools and wheel are up-to-date:

