UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0x92 in position
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0x92 in position
The Python "UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0x92 in position: invalid start byte" occurs when we specify an incorrect encoding when decoding a bytes object.
To solve the error, specify the correct encoding, e.g. cp1252.
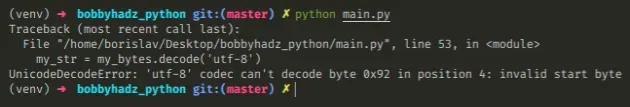
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_bytes = 'abc ’ def'.encode('cp1252') # ⛔️ UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0x92 in position 4: invalid start byte my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8')
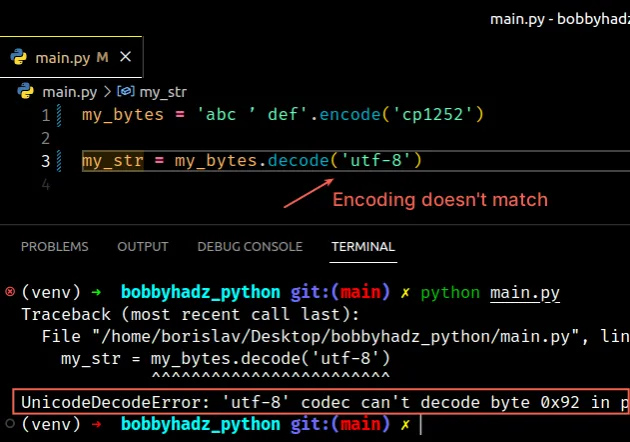
Notice that the string was encoded using the cp1252 encoding and then we tried
to decode the bytes object using the utf-8 encoding.
The two encodings don't match.
The 0x92 byte can be decoded using the cp1252 encoding.
string to a bytes object and decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string.# Use the same encoding that was used to encode the string to bytes
When decoding a bytes object, we have to use the same encoding that was used to encode the string to a bytes object.
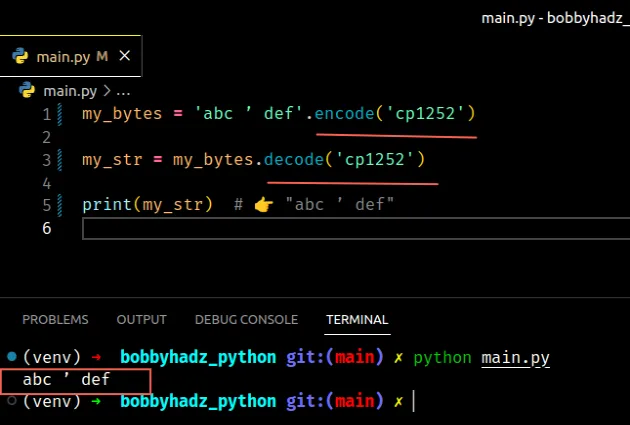
In the example, we can set the encoding to cp1252.
my_bytes = 'abc ’ def'.encode('cp1252') my_str = my_bytes.decode('cp1252') print(my_str) # 👉️ "abc ’ def"
Windows-1252 or cp1252 is a
single-byte character encoding of the Latin alphabet.
If that doesn't work, try using the latin-1 encoding and see if the data is
legible.
my_bytes = 'abc ’ def'.encode('cp1252') my_str = my_bytes.decode('latin-1') print(my_str) # 👉️ "abc def"
Notice that the character that cannot be decoded got stripped when using the
latin-1 encoding.
You can also try using the mac_roman encoding if the file or string was
created on a macOS machine.
my_bytes = 'abc ’ def'.encode('cp1252') my_str = my_bytes.decode('mac_roman') print(my_str) # 👉️ "abc í def"
# Specify the correct encoding when reading from a file using pandas
If you got the error when reading from a file using
pandas, try setting the encoding to
cp1252 or latin-1.
import pandas as pd # 👇️ set encoding to cp1252 df = pd.read_csv('employees.csv', sep='|', encoding='cp1252') print(df)
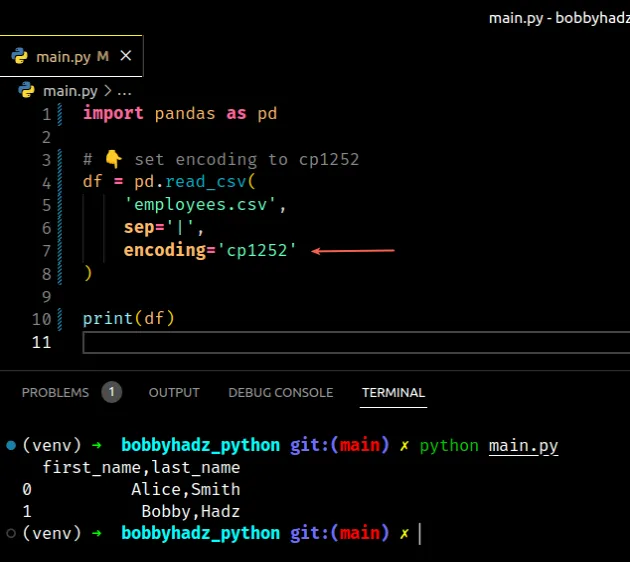
The code sample assumes that you have an employees.csv file in the same
directory as your Python script.
first_name,last_name Alice,Smith Bobby,Hadz
You can try doing the same if using the native open() function.
import csv with open('employees.csv', newline='', encoding='cp1252') as csvfile: csv_reader = list(csv.reader(csvfile, delimiter=',')) print(csv_reader)
# Setting the errors keyword argument to ignore
If the error persists, you could set the
errors` keyword argument
to ignore to ignore the characters that cannot be decoded.
Note that ignoring characters that cannot be decoded can lead to data loss.
import csv # 👇️ Set errors to ignore with open('employees.csv', newline='', encoding='utf-8', errors='ignore') as csvfile: csv_reader = list(csv.reader(csvfile, delimiter=',')) print(csv_reader)
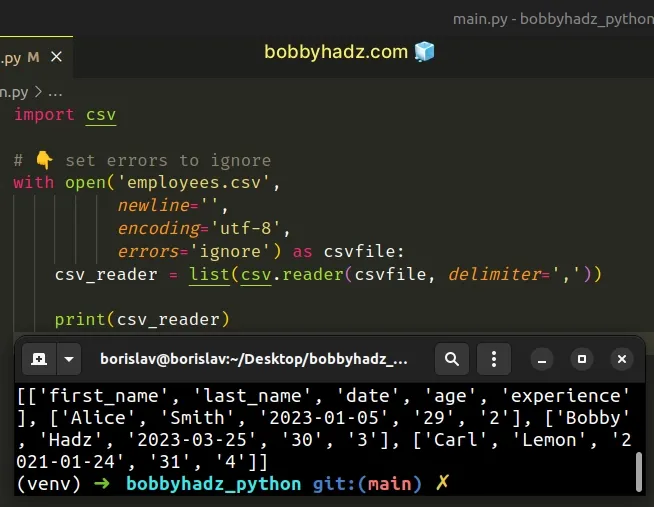
errors set to ignore won't raise a UnicodeDecodeError.Make sure you didn't open a file in rb (read binary) mode if you have to read
from it.
# Open the file in binary mode if you don't need to interact with it
If you don't need to interact with the contents of the file, you can open it in binary mode without decoding it.
with open('example.txt', 'rb') as f: data = f.read() print(data)
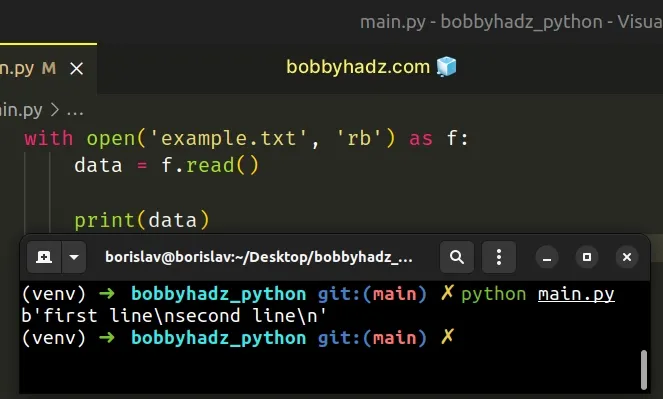
We opened the file in binary mode (using the rb mode), so the data variable
contains a bytes object.
You shouldn't specify encoding when opening a file in binary mode.
You can use this approach if you need to upload the file to a remote server and don't need to decode it.
# How the error occurs
Encoding is the process of converting a string to a bytes object and
decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string.
When decoding a bytes object, we have to use the same encoding that was used to encode the string to a bytes object.
Here is an example that shows how using a different encoding to encode a string to bytes than the one used to decode the bytes object causes the error.
my_text = 'a ’ b' my_binary_data = my_text.encode('cp1252') # ⛔️ UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0x92 in position 2: invalid start byte my_text_again = my_binary_data.decode('utf-8')
We can solve the error by using the cp1252 encoding to decode the bytes
object.
my_text = 'a ’ b' my_binary_data = my_text.encode('cp1252') my_text_again = my_binary_data.decode('cp1252') print(my_text_again) # 👉️ "a ’ b"

