TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable in Python [Fix]
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable in Python
The Python "TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable" occurs when we try
to call a None value as if it were a function.
To solve the error, track down where the None value comes from and correct
the assignment or remove the parenthesis.
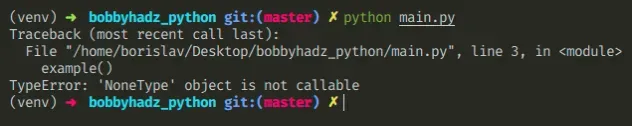
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
value = None # ⛔️ TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable value()
You have to track down where the variable got assigned a None value and either
correct the assignment to a function or class or remove the parentheses.
# Calling a function twice causes the error
Make sure you aren't calling a function twice.
# 👇️ this function returns None def do_math(a, b): print(a + b) # ⛔️ TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable do_math(10, 15)() # 👈️ Remove the extra set of parentheses
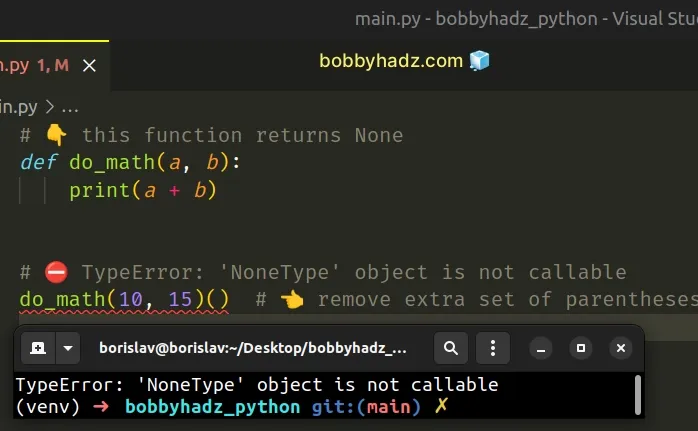
The function in the example returns None, so the
second set of parentheses tries to invoke the None value.
If we remove the second set of parentheses, everything works as expected.
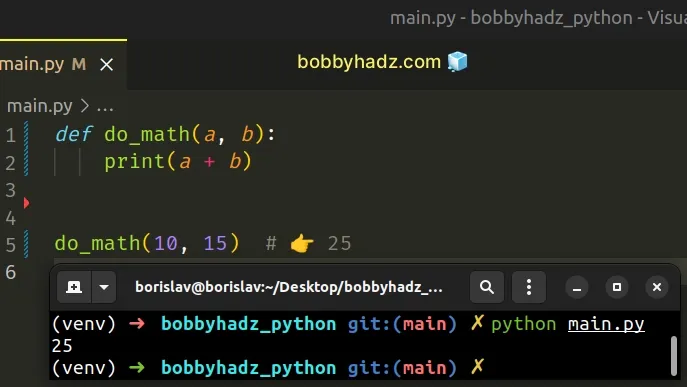
def do_math(a, b): print(a + b) do_math(10, 15) # 👉️ 25
# Common causes on None values in Python
The most common sources of None values are:
- Having a function that doesn't return anything (returns
Noneimplicitly). - Explicitly setting a variable to
None. - Assigning a variable to the result of calling a built-in function that doesn't return anything.
- Having a function that only returns a value if a certain condition is met.
# Common causes of the error
The error occurs for multiple reasons:
- Trying to call a
Nonevalue as a function with parentheses(). - Having a function and a variable with the same name.
- Overriding a built-in function by mistake and setting it to a
None. - Having a class method and a class property with the same name.
- Calling a function that returns
Nonetwice.
# Having a function and a variable with the same name
Make sure you don't have a function and a variable that share the same name.
def example(): return 'bobbyhadz.com' example = None # ⛔️ TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable example()
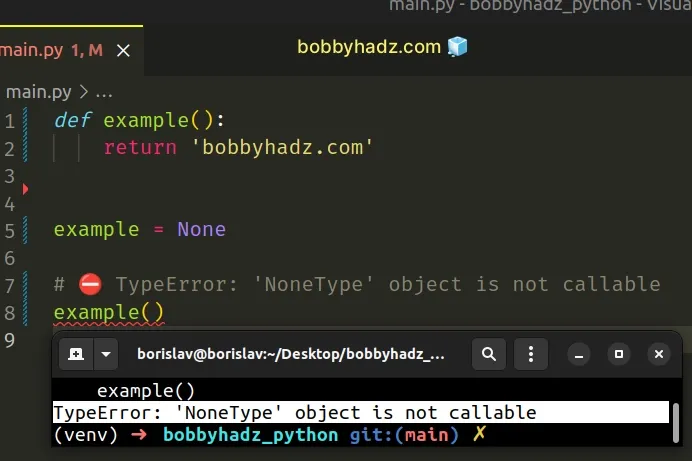
The function and the variable share the same name, so the variable that we set
to None shadows the function.
When we try to call the function, we end up calling the variable.
To solve the error, either rename the function or rename the variable.
def example(): return 'bobbyhadz.com' my_variable = None print(example()) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
The variable now has a different name, so the error is no longer caused.
# Having a class method and a class property with the same name
The error is also caused when we have a class method and a class property with the same name.
class Employee(): def __init__(self): self.name = None def name(self): return self.name emp1 = Employee() # ⛔️ TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable print(emp1.name())
The Employee class has a method and an attribute with the same name.
To solve the error, make sure to rename the method in the class.
class Employee(): def __init__(self): self.name = None def get_name(self): return self.name emp1 = Employee() print(emp1.get_name()) # 👉️ None
Once you rename the method, you will be able to call it without any issues.
# Calling a None value as a function causes the error
The error is also caused if you call a None value as a function.
my_variable = None # ⛔️ TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable print(my_variable())
You have to track down where the variable got assigned a None value and
correct the assignment to a function or remove the parentheses.
my_variable = None print(my_variable) # 👉️ None
You can use an if statement if you need to
check if the variable is not None before calling
it as a function.
my_variable = None if my_variable is not None: my_variable() else: print('the variable is None')
The if block is only run if the variable doesn't store a None value.
Otherwise, the else block runs.
# Having an extra set of parentheses
Here is another example of how the error occurs.
def greet(f): f() def another_func(): print('hello') # ⛔️ TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable greet(another_func())
The greet function takes another function as an argument and calls it.
However, notice that we called the other function when passing it to greet.
The function returns None, so the greet function got called with a None
value.
To solve the error, remove the parentheses in the call to the greet function.
def greet(f): f() def another_func(): print('hello') greet(another_func) # 👉️ hello
We passed the function and not the result of calling it to the greet function,
so the error is resolved.
Now the greet function gets called with a function, invokes it and prints the
message.
# Conclusion
To solve the "TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable" error, make sure:
- You aren't trying to call a
Nonevalue with parentheses(). - You don't have a function and a variable with the same name.
- You aren't overriding a built-in function and setting it to
None. - You don't have a class method and a property with the same name.
- You aren't calling a function that returns
Nonetwice.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Return a default value if None in Python
- Why does my function print None in Python [Solved]
- Join multiple Strings with possibly None values in Python
- Why does list.reverse() return None in Python
- Check if a Variable is or is not None in Python
- Convert None to Empty string or an Integer in Python
- How to Convert JSON NULL values to None using Python

