sqlalchemy.exc.NoSuchModuleError: Can't load plugin: sqlalchemy.dialects:postgres
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·2 min
# sqlalchemy.exc.NoSuchModuleError: Can't load plugin: sqlalchemy.dialects:postgres
The error "sqlalchemy.exc.NoSuchModuleError: Can't load plugin:
sqlalchemy.dialects:postgres" occurs when we use the outdated postgres dialect
in a connection URL.
To solve the error, use the dialect postgresql in your connection URL
instead.
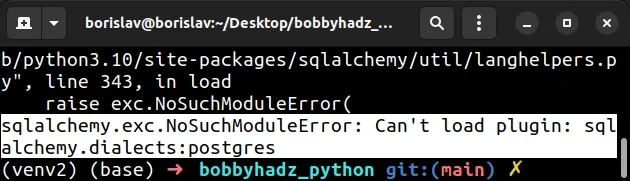
File "/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv2/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sqlalchemy/util/langhelpers.py", line 343, in load raise exc.NoSuchModuleError( sqlalchemy.exc.NoSuchModuleError: Can't load plugin: sqlalchemy.dialects:postgres
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
from flask import Flask from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy app = Flask(__name__) # ⛔️ Using postgres:// dialect app.config["SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI"] = "postgres://username@localhost:5432/exampledb" db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# Use the postgresql dialect instead
To solve the error, use the postgresql dialect instead.
from flask import Flask from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy app = Flask(__name__) # ✅ Using postgresql:// dialect app.config["SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI"] = "postgresql://username@localhost:5432/exampledb" db = SQLAlchemy(app) print(db)
Make sure you don't have 2 s characters next to one another in the string
postgresql.
Database URLs use the following format.
dialect://username:password@host:port/database
Username, password, host and port are optional depending on the database type and configuration.
Your connection string for PostgreSQL might look something like this.
postgresql://bobbyhadz:password@localhost:5432/mydatabase
The database URL should start with postgresql://, not with postgres:// as
SQLAlchemy v1.4 has removed support
for the deprecated postgres dialect.
If you get the error ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'flask', click on the link and follow the instructions.
# Using the str.replace() method to correct the string
If you have the URL stored in a string or if you get the URL using an
environment variable, you can use the str.replace() method to make sure you
specify the postgresql dialect instead of postgres.
# ⛔️ Incorrect URL (postgres dialect) DATABASE_URL = "postgres://username@localhost:5432/exampledb" # ✅ Correct URL (postgresql dialect) DATABASE_URL = DATABASE_URL.replace( 'postgres://', 'postgresql://', 1 ) # 👇️ postgresql://username@localhost:5432/exampledb print(DATABASE_URL)
This approach would work if you get the database URL via an environment variable (e.g. on Heroku).
str.replace() method after os.getenv("DATABASE_URL") to replace the incorrect postgres dialect with postgresql.If the string postgres:// is not contained in your database URL, then nothing
is replaced.
Here is an example that loads the DATABASE_URL from an environment variable
and replaces the substring.
import os uri = os.getenv("DATABASE_URL") if uri.startswith("postgres://"): uri = uri.replace("postgres://", "postgresql://", 1) # The rest of the connection code
The code sample is suitable for a Heroku environment and assumes that you have a
DATABASE_URL environment variable.
The str.replace method returns a copy of the string with all occurrences of a substring replaced by the provided replacement.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| old | The substring we want to replace in the string |
| new | The replacement for each occurrence of old |
| count | Only the first count occurrences are replaced (optional) |
The method doesn't change the original string. Strings are immutable in Python.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

