PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·5 min
# PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error solved
The "PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error" occurs for multiple reasons:
- Trying to open a file, but the specified path is a folder.
- Not having the necessary permissions to open a file.
- Trying to open a file that is already opened in another application (e.g. excel).
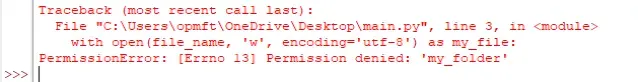
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
# ⛔️ PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/path/to/folder' # 👇️ Notice that this is a path to a folder file_name = r'C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz_python' with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write('first line' + '\n')
Make sure to specify the name of the file and its extension in the path.
# ⛔️ Points to a directory file_name = r'C:\Users\Public' # ✅ Points to a file file_name = r'C:\Users\Public\example.txt'
Notice that the path to the file is prefixed with an r. This is necessary to
treat backslashes as literal characters.
# Specify the complete (absolute) path to the file
One way to solve the error is to specify the complete path to the file.
import os file_name = r'C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz_python\example.txt' print(os.path.isfile(file_name)) # 👉️ True print(os.path.isdir(file_name)) # 👉️ False with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write('first line' + '\n')
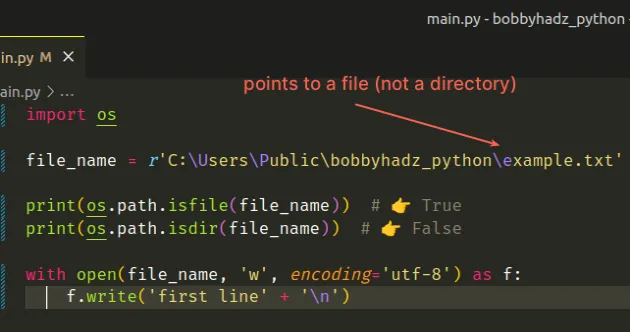
Now the code sample opens an example.txt file and writes to it.
Make sure to specify the entire path to the file, including the extension.
On most operating systems, you can find the absolute path to a file by:
- Right-clicking on the file.
- Click on "Properties".
The path that is shown will likely not include the name of the file, but will point to the directory that contains the file.
Make sure to specify the name of the file and the extension at the end.
You can also open the file in Finder and look at the path.
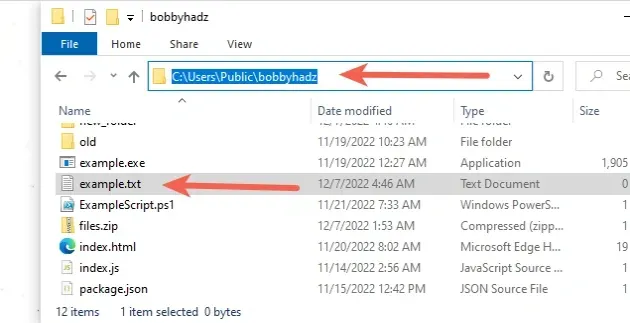
Make sure to add the filename and the extension at the end of the absolute path.
Notice that the string is prefixed with r to mark it as a
raw string.
file_name = r'C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz_python\example.txt'
r are called raw strings and treat backslashes as literal characters.This is necessary because path components are separated by backslashes on
Windows and have a special meaning in Python - they are used as Escape
characters (e.g. \n or \t).
# Using a local path when the file is located in the same directory
If you are trying to open a file that is located in the same directory as your Python script, you don't have to specify an absolute path.
with open(r'example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
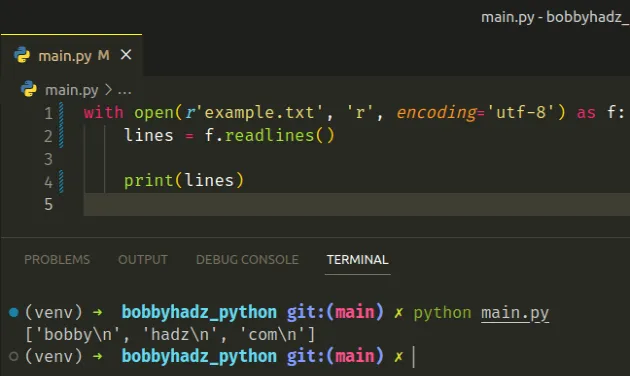
The example.txt file has the following contents:
bobby hadz com
The code sample above assumes that there is a file called example.txt in the
same directory as the Python script (main.py).
my_project/ main.py example.txt
When only the name of the file is specified in the call to open(), the file is assumed to be in the same directory as the Python script.
If you have issues opening the file:
- Move the file to the same directory as your Python script.
- Use a local path, e.g.
example.txtas shown in the code sample above.
# Using an if statement to check if the path points to a filter or a folder
Alternatively, you can use an if statement to check if the path points to a
file or a folder before opening it.
import os file_name = r'C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz_python' print(os.path.isfile(file_name)) # 👉️ False print(os.path.isdir(file_name)) # 👉️ True if os.path.isfile(file_name): with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines) else: # 👇️ this runs print('The specified path is a folder')
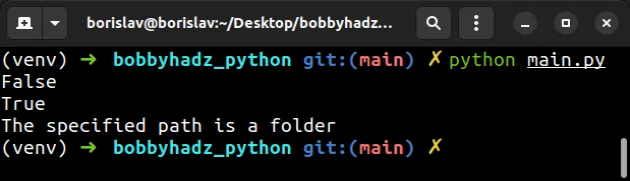
The
os.path.isfile
method returns True if the path is an existing, regular file.
The if block is only run if the supplied path points to a file, in which case
we call the open() function with the path.
# Make sure the files you are interacting with are closed
The error error often occurs when the file you are trying to read from or write to is opened by a different application, e.g. excel.

The screenshot shows how trying to open a file that is already used by another application causes the error.
Make sure to close the file before you try to interact with it with your Python script.
# Opening all files in a directory
If you meant to open all files in a directory, use a list comprehension to select the names of the files.
import os dir_name = r'C:\Users\Public\my_folder' files_in_dir = [f for f in os.listdir(dir_name) if os.path.isfile(f)] print(files_in_dir) for file_name in files_in_dir: with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element, or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
The os.listdir() method takes the path as an argument and returns a list containing the names of the entries in the directory for the specified path.
Another common cause of the error is not having the necessary permissions to open a file.
If none of the suggestions helped, try opening CMD or PowerShell as an administrator before running your Python script.
# Run CMD as an administrator
If you created the file using elevated permissions, you need to have elevated permissions to interact with the file.
If the file can only be read from and written to by an administrator user, you have to open your shell as an administrator.
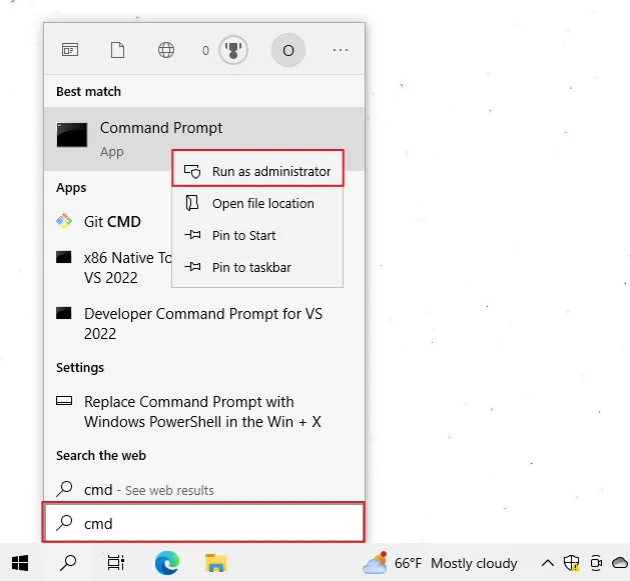
To run CMD as an administrator:
- Click on the search bar and type "cmd".
- Right-click on "Command Prompt".
- Click on "Run as administrator".
- Navigate to your Python script and run it.
You can also run PowerShell as an administrator to be able to run the script.
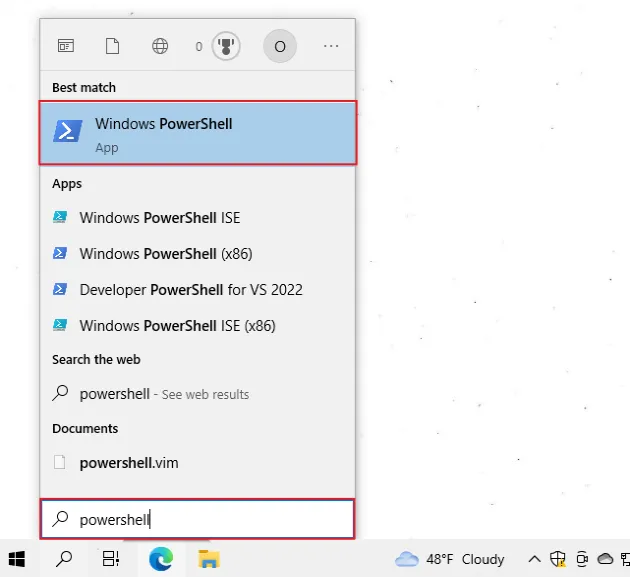
To run PowerShell as an administrator:
- Click on the search bar and type "PowerShell".
- Right-click on "Windows PowerShell".
- Click on "Run as administrator".
# Conclusion
To solve the "PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error", make sure:
- You haven't specified a path to a folder instead of a file.
- You have the necessary permissions to open the file.
- The file isn't opened in another application (e.g. excel).

