Python: 'list' object attribute 'append' is read-only [Fix]
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Python: 'list' object attribute 'append' is read-only
The Python "AttributeError: 'list' object attribute 'append' is read-only"
occurs when you try to set the append attribute on a list object.
To solve the error, call the append() method on the list instead of setting
it as an attribute.
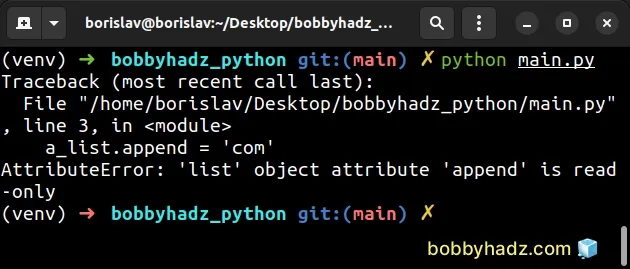
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
a_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'list' object attribute 'append' is read-only a_list.append = 'com'
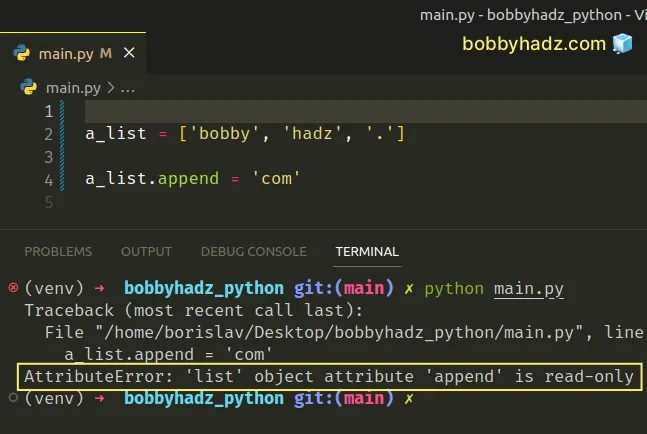
The error occurs because we are trying to set the append attribute on the list
object.
Instead, we should call the list.append() method to add an item to the list.
a_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] # ✅ Correctly using list.append() a_list.append('com') a_list.append('xyz') # ['bobby', 'hadz', '.', 'com', 'xyz'] print(a_list)
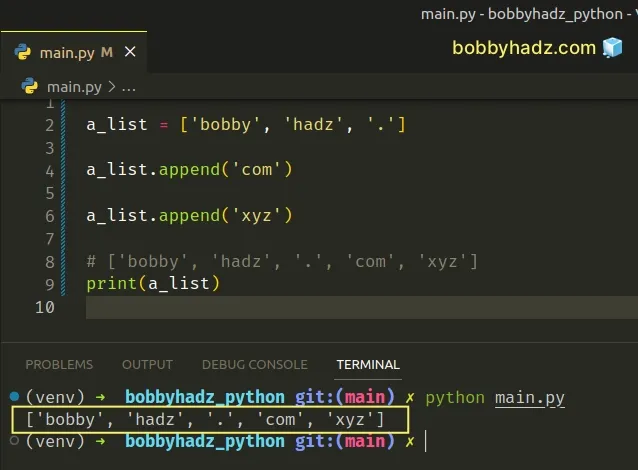
The list.append() method adds the supplied value to the end of the list.
Note that the method returns None as it mutates the original list in place.
() when calling the method and specified the item we want to add to the list between the parentheses.If you need to add elements to a list in a loop, click on the following article.
# Modifying the value of a list item at a given index
If you are trying to change the value of a list item at a specific index, use square brackets.
a_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] a_list[0] = 'new' print(a_list) # 👉️ ['new', 'hadz', '.']
0, and the last item has an index of -1 or len(a_list) - 1.You can use the list.index() method if you need to get the index of a value in
a list.
a_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] print(a_list.index('bobby')) # 👉️ 0
The method returns the index of the first item whose value is equal to the provided argument.
Notice that we called the method with parentheses () in the same way we called
the list.append() method.
If you need to append multiple values to a list, follow the instructions in the next subheading.
# AttributeError: 'list' object attribute 'extend' is read-only
The "AttributeError: 'list' object attribute 'extend' is read-only" error is
raised when you try to use the list.extend() method as an attribute.
To solve the error, call the method with parentheses, passing it the values you want to add to the list.
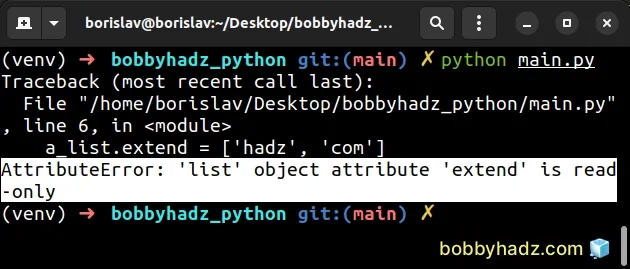
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
a_list = ['bobby'] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'list' object attribute 'extend' is read-only a_list.extend = ['hadz', 'com']
We tried to access the list.extend() method as an attribute which caused the
error.
The list.extend() method should be called using parentheses () and not
accessed as an attribute.
a_list = ['bobby'] a_list.extend(['hadz', 'com']) print(a_list) # 👉️ ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']
The list.extend() method takes an iterable and extends the list by appending
the items from the iterable.
Note that the method returns None, so don't try to store the result of calling it in a variable.
# Conclusion
The Python "AttributeError: 'list' object attribute 'X' is read-only" occurs when you try to access a method as an attribute.
To solve the error, call the method using parentheses () instead of setting it
as an attribute using dot . notation.
Here is an example of incorrectly using list.append().
# 🚨 Incorrect code a_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'list' object attribute 'append' is read-only a_list.append = 'com'
And here is how you would correct the code sample by calling the list.append()
method with parentheses.
# ✅ Correct code a_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] a_list.append('com') a_list.append('xyz') # ['bobby', 'hadz', '.', 'com', 'xyz'] print(a_list)
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

