Call a class method from another Class in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Call a class method from another class in Python
To call a class method from another class:
- Instantiate the class in the other class.
- Call the method on the instance of the class.
- Pass all of the required arguments in the call to the method.
class A: def method_a(self, a, b): return a + b class B: def method_b(self, a, b): return A().method_a(a, b) b1 = B() print(b1.method_b(10, 15)) # 👉️ 25
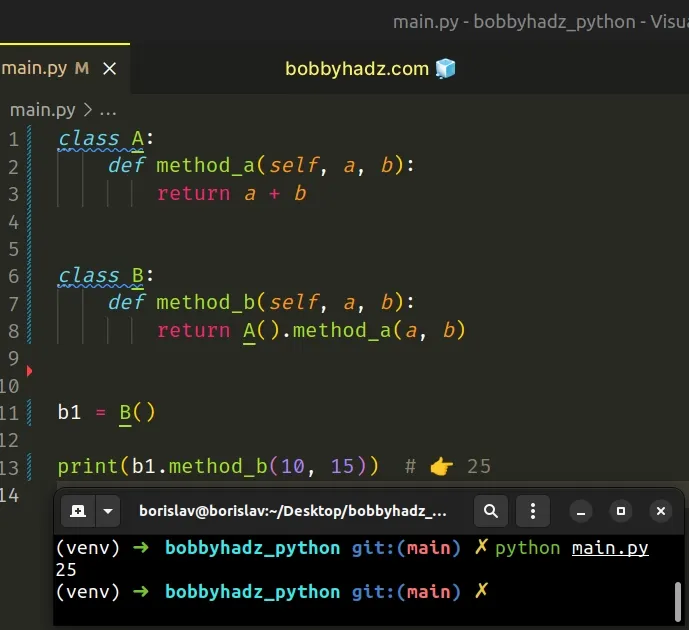
We instantiated class A in class B in order to call method_a in
method_b.
The classes don't take any arguments because they don't define an __init__()
method.
__init__ method, make sure to supply all of the required arguments when instantiating them.The methods in the example are accessed on instances of the classes.
# Calling a static class method from another class
If you defined a static method, you don't have to instantiate the class to call the method from another class.
class A: @staticmethod def method_a(a, b): return a + b class B: def method_b(self, a, b): return A.method_a(a, b) b1 = B() print(b1.method_b(10, 15)) # 👉️ 25
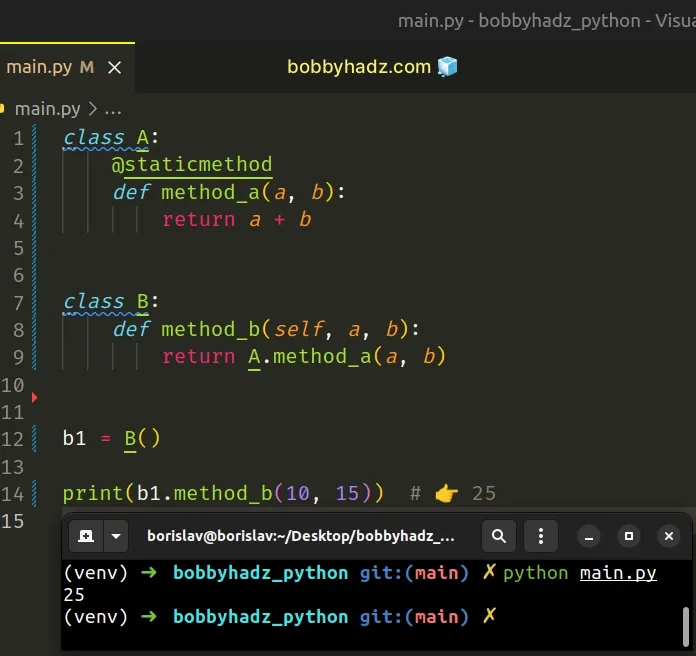
We used the @staticmethod decorator to define a static method in the class.
self) and can be invoked on the class or an instance of the class.Notice that we didn't have to create an instance of class A to be able to call
method_a.
You can also call method_a and store the result in a class variable in the
other class.
class A: def method_a(self, a, b): return a + b class B: result = A().method_a(15, 20) print(B.result)
The result class variable is shared by all instances of class B.
# Instantiating classes that have an __init__ method
Here is an example of instantiating classes that also define an __init__()
method.
class A: def __init__(self, name, age): self.name = name self.age = age def method_a(self, a, b): return a + b class B: def __init__(self, name, age): self.name = name self.age = age def method_b(self, a, b): return A(self.name, self.age).method_a(a, b) b1 = B('bobby', 30) print(b1.method_b(10, 15))
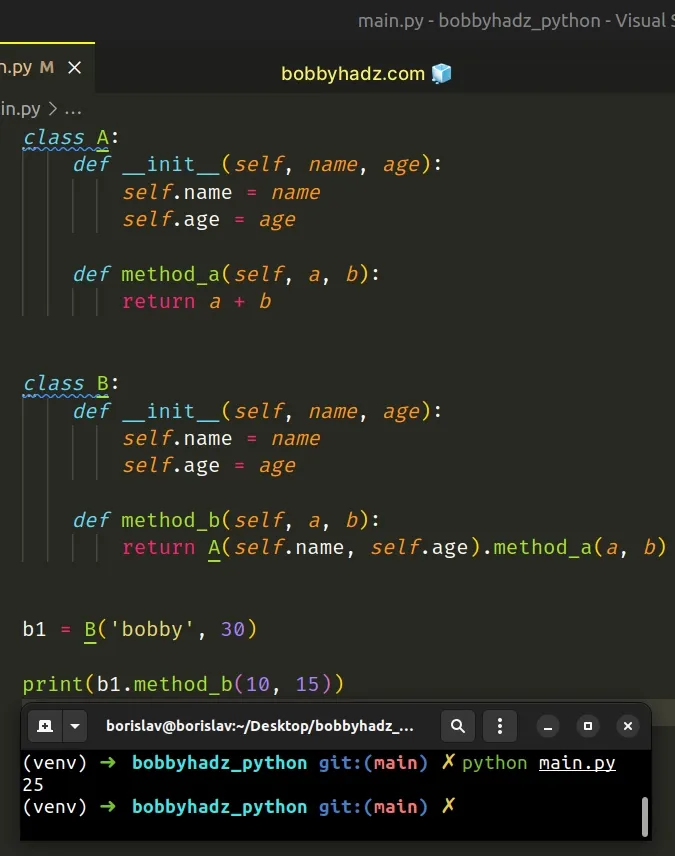
We had to pass the necessary arguments when instantiating class A in class
B.
You can also pass an instance of class A as an argument when instantiating
class B.
class A: def method_a(self, a, b): return a + b class B: def __init__(self, instanceA): self.instanceA = instanceA def method_b(self, a, b): return self.instanceA.method_a(a, b) a1 = A() b1 = B(a1) print(b1.method_b(10, 15)) # 👉️ 25
Class B takes an instance of class A as an argument in its __init__()
method.
Now we are able to access the instance in method_b to call method_a.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Purpose of 'return self' from a class method in Python
- Convert a string to a Class object in Python
- Creating class instances from a Dictionary in Python
- How to Update or access Class variables in Python
- How to Create an incremental ID in a Class in Python
- How to get the File path of a Class in Python
- TypeError: Class() takes no arguments in Python [Solved]

