AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'
The Python "AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'" occurs
when we call the replace() method on a list instead of a string.
To solve the error, call replace() on a string, e.g. by accessing the list
at a specific index or by iterating over the list.

Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz'] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace' my_list.replace('b', '_')
We created a list with 2 elements and tried to call the replace() method on
the list which caused the error.
replace() method is string-specific, so we have to call it on a string, and not on a list object.# Accessing the list at a specific index
One way to solve the error is to access the list at a specific index before
calling replace().
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz'] result = my_list[0].replace('b', '_') print(result) # 👉️ "_o__y"
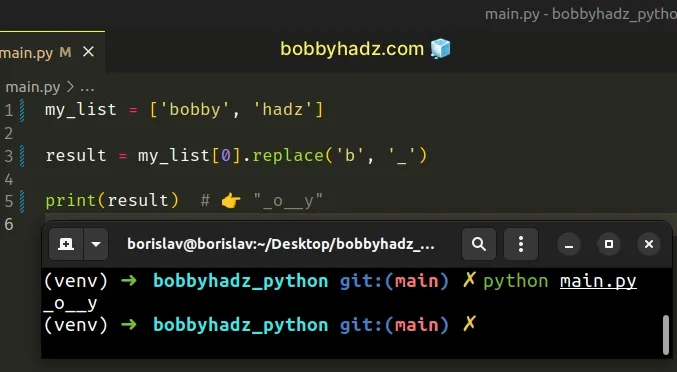
We accessed the list element at index 0 and called the replace() method on
the string.
Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a list has an index of 0,
and the last item has an index of -1 or len(a_list) - 1.
# Calling the replace() method on each string in the list
If you need to call the replace() method on each string in a list, use a list
comprehension.
my_list = ['hello', 'world'] new_list = [element.replace('l', '_') for element in my_list] print(new_list) # 👉️ ['he__o', 'wor_d']
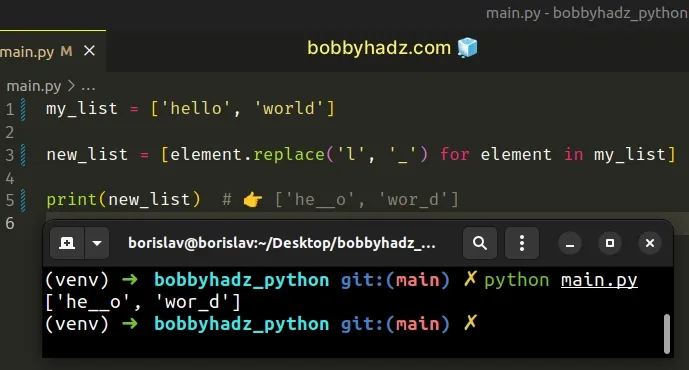
Alternatively, you can use a for loop to call
the replace method on each string in the list.
my_list = ['hello', 'world'] for word in my_list: result = word.replace('l', '_') print(result) # 👉️ "he__o", "wor_d"
We used a for loop to iterate over the list and called the replace() method
on each string.
The str.replace() method returns a copy of the string with all occurrences of a substring replaced by the provided replacement.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| old | The substring we want to replace in the string |
| new | The replacement for each occurrence of old |
| count | Only the first count occurrences are replaced (optional) |
replace() method on a list instead of a string.# Converting the list to a string before calling join()
You can also use the String.join() method to convert the list to a string
before calling the replace() method.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz'] a_str = ' '.join(my_list) result = a_str.replace('b', '_') print(result) # 👉️ _o__y hadz
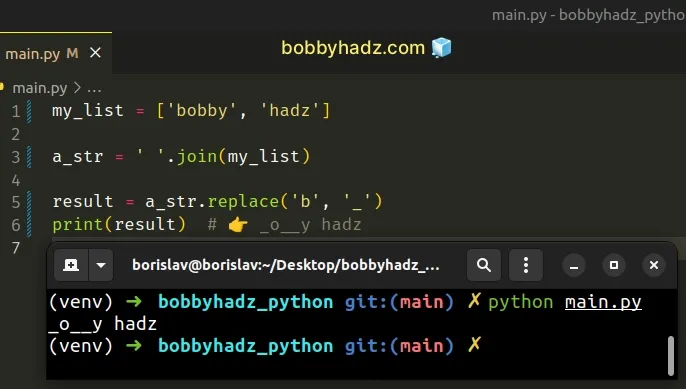
We called the str.join() method with a space separator, but you can use any
other value.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz'] a_str = '@'.join(my_list) result = a_str.replace('b', '_') print(result) # 👉️ _o__y@hadz
If you want to join the list without a separator, call the method on an empty string.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz'] a_str = ''.join(my_list) result = a_str.replace('b', '_') print(result) # 👉️ _o__yhadz
The str.join() method takes an iterable as an argument and returns a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable.
Note that the method raises a TypeError if there are any non-string values in
the iterable.
If your iterable contains numbers or other types, convert all of the values to
strings before calling join().
my_list = ['bobby', 1, 'hadz', 2] list_of_strings = list(map(str, my_list)) a_str = ''.join(list_of_strings) result = a_str.replace('b', '_') print(result) # 👉️ _o__y1hadz2
We used the map() function to convert the integers in the list to strings
before calling the join() method.
# Make sure to call the replace() method on a string
To solve the error, you either have to correct the assignment of the variable
and make sure to call replace() on a string, or call replace() on an element
in the list that is of type string.
You can either access the list at a specific index, e.g. my_list[0] or use a
for loop to iterate over the list if you have to call replace() on each
element.
You can view all the attributes an object has by using the dir() function.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # 👉️ [... 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', # 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort' ...] print(dir(my_list))
If you pass a class to the dir() function, it returns a list of names of the class's attributes, and recursively of the attributes of its bases.
If you try to access any attribute that is not in this list, you will get the "AttributeError: list object has no attribute" error.
Since replace() is not a method implemented by lists, the error is caused.

