What is the npm init test command in a package.json file?
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- The purpose of the npm test command in a package.json file
- Updating the
testcommand in yourpackage.jsonfile
# The purpose of the npm test command in a package.json file
The test command in the scripts section of your package.json file is the
command that is run when you issue the npm test command from your terminal.
When you generate a new package.json file, with the npm init -y command,
the test command gets set to a placeholder value.
npm init -y
Here are the contents of a newly created package.json file.
{ "name": "my-project", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, "keywords": [], "author": "", "license": "ISC" }
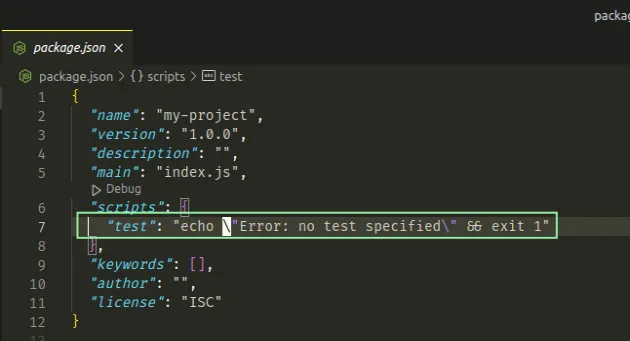
The test script from your package.json file is run whenever you issue the
npm test command.
npm test
> my-project@1.0.0 test > echo "Error: no test specified" && exit 1 Error: no test specified
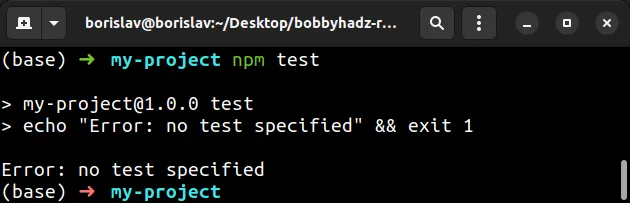
By default, the test command is set to print a message as a reminder that you
haven't set up a test command yet.
You can also issue the command with npm run test.
npm run test
The test command is usually used to run your project's tests when testing
locally or when deploying to a remote server.
The tests are usually run before you push changes to production.
The flow is as follows:
- You make changes to your project, e.g. implement new features or update existing functionality.
- You write tests that verify these features work as expected.
- You automatically run the tests with the
npm testcommand before deploying to a production environment. - If the tests fail, the deployment gets canceled, so that broken code doesn't get pushed to production.
# Updating the test command in your package.json file
Let's look at an example of updating the test command in the package.json
file.
Let's first create an index.js file that we will test.
export function sum(a, b) { return a + b; }
The index.js file exports a single sum function.
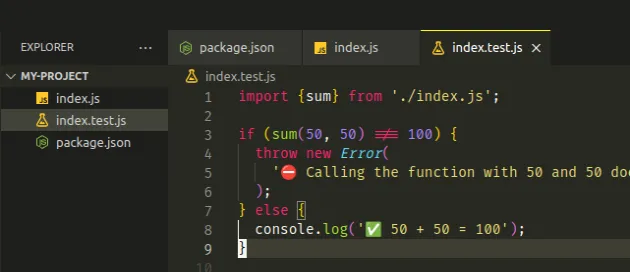
Now create an index.test.js file in the same directory, right next to your
index.test.js file.
import {sum} from './index.js'; if (sum(50, 50) !== 100) { throw new Error( '⛔️ Calling the function with 50 and 50 does NOT return 100', ); } else { console.log('✅ 50 + 50 = 100'); }
The index.test.js file imports the sum function and tests its output.
The file structure of the project looks as follows.
index.js index.test.js package.json
Now update the test command in your package.json file.
{ "type": "module", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "test": "node index.test.js" } }
Notice that the type attribute is set to module, so we are able to use the
ES6 import/export syntax.
We set the test command to node index.test.js, so when we issue
npm run test, the index.test.js file is run.
npm test
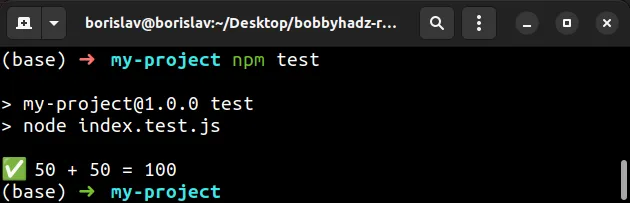
The npm test command ran the index.test.js file and as shown in the
screenshot, the test passed.
Instead of writing the tests manually, you will most likely use a test runner package such as jest.
The purpose of a test runner is to detect changes to your code and rerun your tests automatically.
Any time you make changes to your code, your tests are rerun, so you instantly know if something breaks.
This allows you to iterate quickly and shortens the feedback loop.

