Module not found: Can't resolve 'path', zlib, buffer, http
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024
Reading time·13 min

# Table of Contents
- Module not found: Can't resolve 'path'
- Module not found: Can't resolve 'zlib'
- Module not found: Can't resolve 'buffer'
- Module not found: Can't resolve 'http'
# Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'path'
The error "Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'path'" occurs because there has been a breaking change in Webpack version 5.
To solve the error, set the browser.path property to false in your
package.json file.
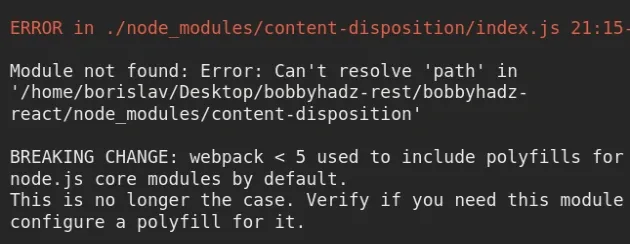
⛔️ Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'path' in '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz-rest/bobbyhadz-react/node_modules/content-disposition' BREAKING CHANGE: webpack < 5 used to include polyfills for node.js core modules by default. This is no longer the case. Verify if you need this module and configure a polyfill for it. If you want to include a polyfill, you need to: - add a fallback 'resolve.fallback: { "path": require.resolve("path-browserify") }' - install 'path-browserify' If you don't want to include a polyfill, you can use an empty module like this: resolve.fallback: { "path": false }
The first thing you should try is to set the browser.path property to false
in your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ add this to package.json 👇️ "browser": { "path": false, "stream": false } }
browser object to your package.json file as shown in the code sample.Path is a Node.js core module and should most likely not be bundled with your client-side code.
By setting path to false, we use an empty module instead of including a
polyfill for the path module.
If the error persists, try to run the following 2 commands.
# with NPM npm install path npm install stream # with YARN yarn add path yarn add stream
If the error persists, you have to edit your webpack.config.js file:
- Make sure you have path-browserify installed.
npm install path-browserify npm install stream-browserify yarn add path-browserify yarn add stream-browserify
- Open your
webpack.config.jsand add a fallback to yourresolve.fallbackproperty.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ path: require.resolve("path-browserify"), stream: require.resolve("stream-browserify"), } } } }
CTRL + F for resolve: if your webpack.config.js file is cluttered and long.Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.path
property from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE this from package.json "browser": { "path": false, "stream": false } }
If you use "Create React App", you might have to edit your
node_modules/react-scripts/config/webpack.config.json file.
Alternatively, you can run the npm run eject command, but it is a one-way
operation.
Once you run the command, you can't go back.
The command removes the single-build dependency from your project and copies the
configuration files into your project as dependencies in package.json.
npm run eject
Once you run the npm run eject command, a config directory is created.
The config directory contains a webpack.config.js file that you should edit.
Open your config/webpack.config.js file and add a fallback to your
resolve.fallback property.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ path: require.resolve("path-browserify"), stream: require.resolve("stream-browserify"), } } } }
Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.path
property from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE this from package.json "browser": { "path": false, "stream": false } }
If the error is not resolved and you use Next.js, you might be trying to use the
path module in code that is run on the browser.
# Module not found: Can't resolve 'path' in Next.js
If you use the Node.js built-in path module in your Next.js application, you
have to be sure to only use it on the server.
You can use path in your
getStaticProps
and
getServerSideProps.
If you use the Node.js (server-side) path module outside of the
getStaticProps, getStaticPaths and getServerSideProps methods, the error
occurs.
import {join} from 'path'; // ⛔️ CAN'T use path here ⛔️ export const getServerSideProps = async () => { // ✅ Can use path here (runs only on the server) console.log(join); return { props: {}, // will be passed to the page component as props } };
If you use the path module in your code, remove the browser.path property
from your package.json file if you've set it to false.
If you don't use the path module in your code, create a next.config.js file
in your project's root directory (next to your package.json file) and add the
following code.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 5 module.exports = { webpack5: true, webpack: config => { config.resolve.fallback = { path: false, }; return config; }, };
If you have an existing next.config.js file and still use Webpack version 4,
edit your config to look as follows.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 4 module.exports = { webpack: (config, {isServer}) => { if (!isServer) { config.node = { path: 'empty', }; } return config; }, };
If you get an error such as "Module not found: Can't resolve 'zlib'" or "Module
not found: Can't resolve 'buffer'", you would have to add a zlib or a buffer
property to your config object just like we did for the path property.
# Module not found: Can't resolve 'zlib' error
The error "Module not found: Can't resolve 'zlib'" most commonly occurs when you import a Node.js-specific function in your frontend (e.g. React.js) application.
To solve the error, make sure to ignore or remove all Node.js imports from your frontend code.
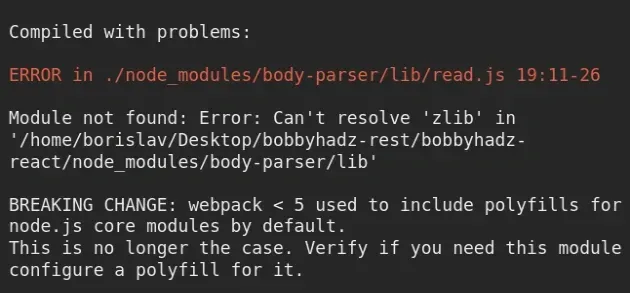
Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'zlib' in '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz-rest/bobbyhadz-react/node_modules/body-parser/lib' BREAKING CHANGE: webpack < 5 used to include polyfills for node.js core modules by default. This is no longer the case. Verify if you need this module and configure a polyfill for it. If you want to include a polyfill, you need to: - add a fallback 'resolve.fallback: { "zlib": require.resolve("browserify-zlib") }' - install 'browserify-zlib' If you don't want to include a polyfill, you can use an empty module like this: resolve.fallback: { "zlib": false }
The following imports are the most common cause of the error.
import { response } from 'express'; import { json } from 'express'; import e from 'express';
You can press CTRL + F and search for express imports in your frontend
code (e.g. React.js codebase).
Once you remove these imports the error will be resolved.
Then your browser tries to import Node-specific code that it can't parse and the error occurs.
If the error persists, try to set the browser.zlib property to false in your
package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ add this to package.json 👇️ "browser": { "zlib": false, "stream": false } }
browser object to your package.json file as shown in the code sample.Zlib is a Node.js core module and should most likely not be bundled with your client-side code.
By setting zlib and stream to false, we use an empty module instead of
including a polyfill for the zlib module.
If you want to include a polyfill for the zlib module and you use TypeScript:
- Install the following modules.
# 👇️ with NPM npm install browserify-zlib npm install stream-browserify # 👇️ with YARN yarn add browserify-zlib yarn add stream-browserify
Open your tsconfig.json file and resolve browserify-zlib and stream to the
installed node_modules paths in your paths object.
{ // ... rest "paths": { "zlib": ["node_modules/browserify-zlib"], "stream": ["node_modules/stream-browserify"] } }
If you add the paths object in your tsconfig.json file, make sure to remove
the zlib and stream properties from package.json.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE these from package.json "browser": { "zlib": false, "stream": false } }
If the error persists, you have to edit your webpack.config.js file:
- Make sure you have
browserify-zlibinstalled.
# 👇️ with NPM npm install browserify-zlib npm install stream-browserify # 👇️ with YARN yarn add browserify-zlib yarn add stream-browserify
- Open your
webpack.config.jsand add a fallback to yourresolve.fallbackproperty.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ zlib: require.resolve("browserify-zlib"), stream: require.resolve("stream-browserify"), } } } }
CTRL + F for resolve: if your webpack.config.js file is cluttered and long.Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.zlib and
browser.stream properties from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE these from package.json "browser": { "zlib": false, "stream": false } }
If you use "Create React App", you might have to edit your
node_modules/react-scripts/config/webpack.config.json file.
Alternatively, you can run the npm run eject command, but it is a one-way
operation.
Once you run the command, you can't go back.
The command removes the single-build dependency from your project and copies the
configuration files into your project as dependencies in package.json.
npm run eject
Once you run the npm run eject command, a config directory is created.
The config directory contains a webpack.config.js file that you should edit.
Open your config/webpack.config.js file and add a fallback to your
resolve.fallback property.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ zlib: require.resolve("browserify-zlib"), stream: require.resolve("stream-browserify"), } } } }
Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.zlib and
browser.stream properties from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE these from package.json "browser": { "zlib": false, "stream": false } }
If the error is not resolved and you use Next.js, you might be trying to use the
zlib module in code that is run on the browser.
# Module not found: Can't resolve 'zlib' in Next.js
If you use the Node.js built-in zlib module in your Next.js application, you
have to be sure to only use it on the server.
You can use zlib in your
getStaticProps
and
getServerSideProps.
If you use the Node.js (server-side) zlib module outside of the
getStaticProps, getStaticPaths and getServerSideProps methods, the error
occurs.
import zlib from 'zlib'; // ⛔️ CAN'T use zlib here ⛔️ export const getServerSideProps = async () => { // ✅ Can use zlib here (runs only on the server) console.log(zlib) return { props: {}, // will be passed to the page component as props } };
If you use the zlib module in your code, remove the browser.zlib property
from your package.json file if you've set it to false.
If you don't use the zlib module in your code, create a next.config.js file
in your project's root directory (next to your package.json file) and add the
following code.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 5 module.exports = { webpack5: true, webpack: config => { config.resolve.fallback = { zlib: false, }; return config; }, };
If you have an existing next.config.js file and still use Webpack version 4,
edit your config to look as follows.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 4 module.exports = { webpack: (config, {isServer}) => { if (!isServer) { config.node = { zlib: 'empty', }; } return config; }, };
If you get an error such as "Module not found: Can't resolve 'path'" or "Module
not found: Can't resolve 'buffer'", you would have to add a path or a buffer
property to your config object just like we did for the zlib property.
# Module not found: Can't resolve 'buffer'
The error "Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'buffer'" occurs because there has been a breaking change in Webpack version 5.
To solve the error, set the browser.buffer property to false in your
package.json file.

Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'buffer' in '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz-rest/bobbyhadz-react/node_modules/safe-buffer' BREAKING CHANGE: webpack < 5 used to include polyfills for node.js core modules by default. This is no longer the case. Verify if you need this module and configure a polyfill for it. If you want to include a polyfill, you need to: - add a fallback 'resolve.fallback: { "buffer": require.resolve("buffer/") }' - install 'buffer' If you don't want to include a polyfill, you can use an empty module like this: resolve.fallback: { "buffer": false }
The first thing you should try is to set the browser.buffer property to
false in your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ add this to package.json 👇️ "browser": { "buffer": false, } }
browser object to your package.json file as shown in the code sample.Buffer is a Node.js core module and should most likely not be bundled with your client-side code.
By setting buffer to false, we use an empty module instead of including a
polyfill for the buffer module.
If the error persists, you have to edit your webpack.config.js file:
- Make sure you have buffer installed.
# 👇️ with NPM npm install buffer # 👇️ with YARN yarn add buffer
- Open your
webpack.config.jsand add a fallback to yourresolve.fallbackproperty.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ "buffer": require.resolve("buffer/"), } } } }
CTRL + F for resolve: if your webpack.config.js file is cluttered and long.Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.buffer
property from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE this from package.json "browser": { "buffer": false, } }
If you use "Create React App", you might have to edit your
node_modules/react-scripts/config/webpack.config.json file.
Alternatively, you can run the npm run eject command, but it is a one-way
operation.
Once you run the command, you can't go back.
The command removes the single-build dependency from your project and copies the
configuration files into your project as dependencies in package.json.
npm run eject
Once you run the npm run eject command, a config directory is created.
The config directory contains a webpack.config.js file that you should edit.
Open your config/webpack.config.js file and add a fallback to your
resolve.fallback property.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ "buffer": require.resolve("buffer/"), } } } }
Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.buffer
property from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE this from package.json "browser": { "buffer": false, } }
If the error is not resolved and you use Next.js, you might be trying to use the
buffer module in code that is run on the browser.
# Module not found: Can't resolve 'buffer' in Next.js
If you use the Node.js built-in buffer module in your Next.js application,
you have to be sure to only use it on the server.
You can use buffer in your
getStaticProps
and
getServerSideProps.
If you use the Node.js (server-side) buffer module outside of the
getStaticProps, getStaticPaths and getServerSideProps methods, the error
occurs.
import {Buffer} from 'buffer'; // ⛔️ CAN'T use buffer here ⛔️ export const getServerSideProps = async () => { // ✅ Can use buffer here (runs only on the server) console.log(Buffer); return { props: {}, // will be passed to the page component as props } };
If you use the buffer module in your code, remove the browser.buffer
property from your package.json file if you've set it to false.
If you don't use the buffer module in your code, create a next.config.js
file in your project's root directory (next to your package.json file) and add
the following code.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 5 module.exports = { webpack5: true, webpack: config => { config.resolve.fallback = { buffer: false, }; return config; }, };
If you have an existing next.config.js file and still use Webpack version 4,
edit your config to look as follows.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 4 module.exports = { webpack: (config, {isServer}) => { if (!isServer) { config.node = { buffer: 'empty', }; } return config; }, };
If you get an error such as "Module not found: Can't resolve 'path'" or "Module
not found: Can't resolve 'zlib'", you would have to add a path or a zlib
property to your config object just like we did for the buffer property.
# Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'http'
The error "Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'http'" occurs because there has been a breaking change in Webpack version 5.
To solve the error, set the browser.http property to false in your
package.json file.
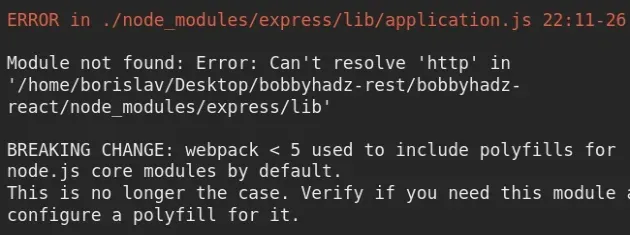
⛔️ Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'http' in '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz-rest/bobbyhadz-react/node_modules/express/lib' BREAKING CHANGE: webpack < 5 used to include polyfills for node.js core modules by default. This is no longer the case. Verify if you need this module and configure a polyfill for it. If you want to include a polyfill, you need to: - add a fallback 'resolve.fallback: { "http": require.resolve("stream-http") }' - install 'stream-http' If you don't want to include a polyfill, you can use an empty module like this: resolve.fallback: { "http": false }
The first thing you should try is to set the browser.http property to false
in your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ add this to package.json 👇️ "browser": { "http": false, "https": false, } }
browser object to your package.json file as shown in the code sample.Http is a Node.js core module and should most likely not be bundled with your client-side code.
By setting http to false, we use an empty module instead of including a
polyfill for the http module.
If the error persists, you have to edit your webpack.config.js file:
- Make sure you have stream-http installed.
npm install stream-http npm install https-browserify yarn add stream-http yarn add https-browserify
- Open your
webpack.config.jsand add a fallback to yourresolve.fallbackproperty.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ http: require.resolve('stream-http'), https: require.resolve('https-browserify'), } } } }
CTRL + F for resolve: if your webpack.config.js file is cluttered and long.Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.http
property from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE this from package.json "browser": { "http": false, "https": false, } }
If you use "Create React App", you might have to edit your
node_modules/react-scripts/config/webpack.config.json file.
Alternatively, you can run the npm run eject command, but it is a one-way
operation.
Once you run the command, you can't go back.
The command removes the single-build dependency from your project and copies the
configuration files into your project as dependencies in package.json.
npm run eject
Once you run the npm run eject command, a config directory is created.
The config directory contains a webpack.config.js file that you should edit.
Open your config/webpack.config.js file and add a fallback to your
resolve.fallback property.
module.exports = function (webpackEnv) { // ... return { // ... resolve: { // ... fallback: { // 👇️👇️👇️ add this 👇️👇️👇️ http: require.resolve('stream-http'), https: require.resolve('https-browserify'), } } } }
Note that if you include a polyfill, you should remove the browser.https
property from your package.json file.
{ "dependencies": {}, "devDependencies": {}, // 👇️ REMOVE this from package.json "browser": { "http": false, "https": false, } }
If the error is not resolved and you use Next.js, you might be trying to use the
http module in code that is run on the browser.
# Module not found: Can't resolve 'http' in Next.js
If you use the Node.js built-in http module in your Next.js application, you
have to be sure to only use it on the server.
You can use http in your
getStaticProps
and
getServerSideProps.
If you use the Node.js (server-side) http module outside of the
getStaticProps, getStaticPaths and getServerSideProps methods, the error
occurs.
import {get} from 'http'; // ⛔️ CAN'T use http here ⛔️ export const getServerSideProps = async () => { // ✅ Can use http here (runs only on the server) console.log(get); return { props: {}, // will be passed to the page component as props } };
If you use the http module in your code, remove the browser.http property
from your package.json file if you've set it to false.
If you don't use the http module in your code, create a next.config.js file
in your project's root directory (next to your package.json file) and add the
following code.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 5 module.exports = { webpack5: true, webpack: config => { config.resolve.fallback = { http: false, }; return config; }, };
If you have an existing next.config.js file and still use Webpack version 4,
edit your config to look as follows.
// 👇️ assumes you use Webpack 4 module.exports = { webpack: (config, {isServer}) => { if (!isServer) { config.node = { http: 'empty', }; } return config; }, };
If you get an error such as "Module not found: Can't resolve 'path'" or "Module
not found: Can't resolve 'zlib'", you would have to add a path or a zlib
property to your config object just like we did for the http property.

