Python: locale.Error: unsupported locale setting [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Python: locale.Error: unsupported locale setting
- Setting the LC_ALL environment variable to C
- Setting the LC_ALL environment variable to en_US
- Setting the environment variables in your profile file
- Setting an incorrect locale causes the error
- Solving the error in Docker
# Python: locale.Error: unsupported locale setting
The Python error "locale.Error: unsupported locale setting" occurs when the
LC_ALL environment variable is not set or is set to an invalid value.
To solve the error, set the environment variable to one of the supported locales and make sure you have the locale installed.
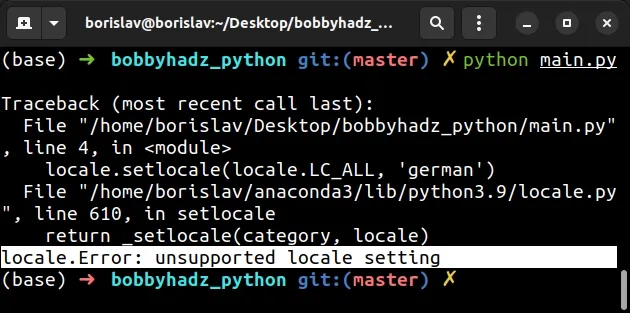
Here is the complete stack trace.
Traceback (most recent call last): File "/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py", line 4, in <module> locale.setlocale(locale.LC_ALL, 'german') File "/home/borislav/anaconda3/lib/python3.9/locale.py", line 610, in setlocale return _setlocale(category, locale) locale.Error: unsupported locale setting
The error is usually caused when you try to pip install a module, create a
virtual environment or use the locale.setlocale() method.
Here is an example of how the error occurs when using the locale.setlocale
method.
import locale # ⛔️ locale.Error: unsupported locale setting locale.setlocale(locale.LC_ALL, 'abc')
The LC_ALL environment variable is used to specify a language environment with
one variable without having to set each LC_* variable.
# Setting the LC_ALL environment variable to C
The first thing you should try is to set the LC_ALL environment variable to
C.
LC_ALL can be set to C to configure an English environment with the ANSI C
locale.
Open your terminal and issue the following command.
export LC_ALL=C
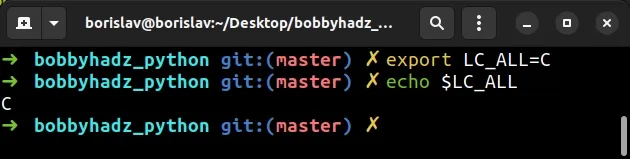
Check if the error is resolved after issuing the command.
When the LC_ALL environment variable is set, it overrides the LANGUAGE,
LC_CTYPE, LC_NUMERIC and all other LC_* variables.
The environment variable is most often set when you need to make sure that the code that is run won't behave differently based on the locale.
Check if the error persists after setting the LC_ALL environment variable to
C.
# Setting the LC_ALL environment variable to en_US
If the error persists, issue the following command.
locale -a
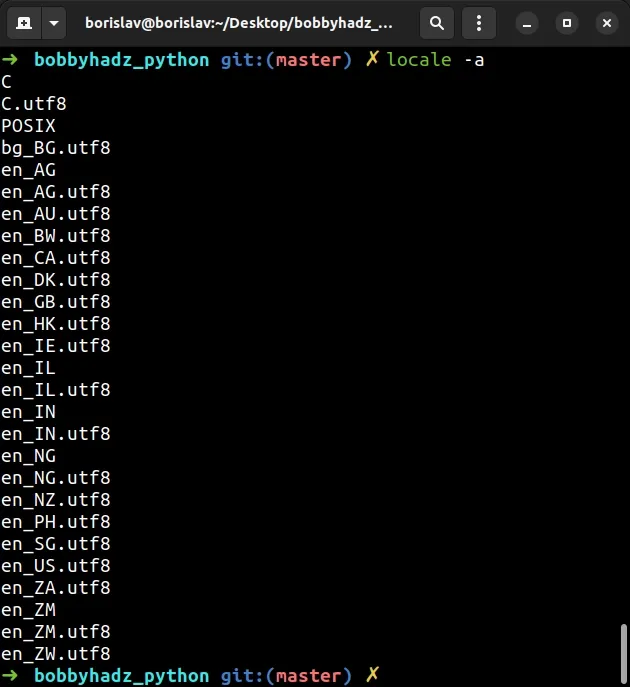
The command outputs the environment variables that are set by the LC_ALL
environment variable.
Notice that on some lines the locale and the encoding are separated by a period.
On some machines, the encoding is utf-8 and on other machines, the encoding is
utf8 (without the hyphen).
If the encoding in the output on your machine has a hyphen (utf-8), issue the
following commands.
export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8" export LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
If the encoding doesn't have a hyphen (utf8), issue the following commands
instead.
export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF8" export LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF8"
Check if the error has been resolved after issuing the commands.
If the error persists, run the following command.
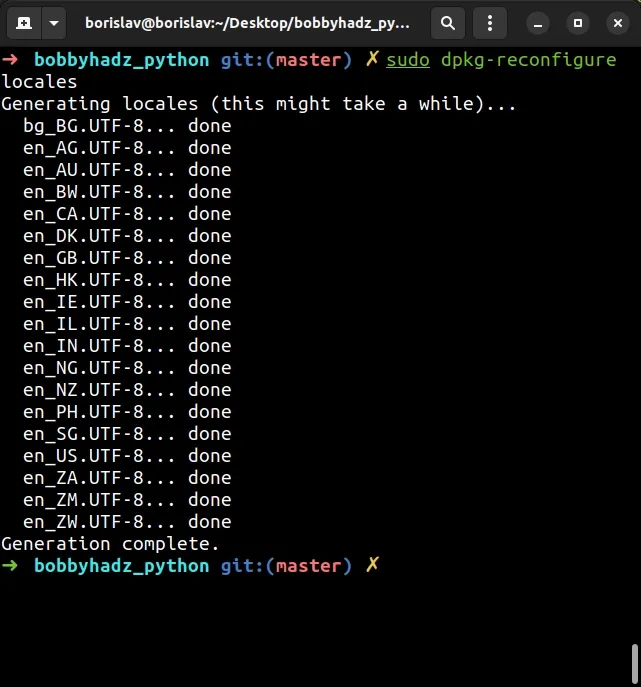
sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales
You need to be root to run the command.
You will get prompted multiple times, but press Enter to keep the defaults.
The command will generate the necessary locales.
You can also run the sudo locale-gen command.
sudo locale-gen
# Setting the environment variables in your profile file
The export syntax only sets the environment variable for the current shell
session.
If the error is resolved, you could set the LC_ALL and LC_CTYPE environment
variables toward the end of your ~/.bashrc, ~/.bash_profile or ~/.zshrc
file.
You can use the gedit command to edit your profile file.
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc sudo gedit ~/.bash_profile sudo gedit ~/.zshrc
Or the nano command if you prefer to add the line in your terminal.
sudo nano ~/.bashrc sudo nano ~/.bash_profile sudo nano ~/.zshrc
Run the following command in another terminal window.
locale -a

On some machines, the encoding is utf-8 and on other machines, the encoding is
utf8 (without the hyphen).
If your encoding is utf-8 (with the hyphen), add the following environment
variables at the end of your ~/.bashrc, ~/.bash_profile or ~/.zshrc file.
# Add this at the end of your profile file export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8" export LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
If your encoding doesn't have a hyphen (utf8), add the following environment
variables at the end of your ~/.bashrc, ~/.bash_profile or ~/.zshrc file.
# Add this at the end of your profile file export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF8" export LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF8"
If you don't have any of the specified files, check if you have a file named
~/.profile or create a ~/.bash_profile file.
Once you set the environment variables, source your profile file.
source ~/.bashrc source ~/.bash_profile source ~/.zshrc
You can also close and reopen your terminal to restart the shell session if the issue persists.
When you start your PC, the profile file is run and the environment variables are set, so the issue should be resolved.
# Setting an incorrect locale causes the error
You will also get the error if you specify:
- An incorrect locale.
- A locale that you haven't yet installed.
Here is an example.
import locale # ⛔️ locale.Error: unsupported locale setting locale.setlocale(locale.LC_ALL, 'abc')
The string abc is not a valid locale.
You can use the locale -a command to list the available locales on your
machine.
locale -a

When setting the locale, make sure to specify the encoding as well, e.g.
en_US.UTF-8.
import locale locale.setlocale(locale.LC_ALL, 'en_US.UTF-8') print(locale.getlocale()) # 👉️ ('en_US', 'UTF-8')
If you get the error when running custom code from a third-party library, try
setting your locale to en_US.UTF-8 at the top of your entry file (e.g.
main.py).
import locale locale.setlocale(locale.LC_ALL, 'en_US.UTF-8') # 👇️ Your other code below ...
Alternatively, you can set the locale for all categories to the user's default
setting by passing an empty string as the second argument to the setlocale()
method.
import locale locale.setlocale(locale.LC_ALL, '')
If you need to install extra locales, issue the following commands.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install locales
You can also install a specific locale by running the following command.
Make sure to replace de_DE with the name of the locale you want to install,
e.g. ru_RU or fr_FR.
sudo locale-gen de_DE sudo locale-gen de_DE.UTF-8
The following page has a table containing the most commonly used locale names.
After you install the locales, run the following command.
sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales
You need to be root to run the command.
You will get prompted multiple times, but press Enter to keep the defaults.

If the error persists, try running the sudo locale-gen command.
sudo locale-gen

# Solving the error in Docker
If you got the error in a Docker container, install the locales package and
set the LANGUAGE and LC_ALL environment variables.
RUN apt-get -y install locales RUN sed -i '/en_US.UTF-8/s/^# //g' /etc/locale.gen && locale-gen ENV LANGUAGE en_US:en ENV LANG en_US.UTF-8 ENV LC_ALL en_US.UTF-8
The commands:
- Install the
localepackage. - Use the
locale-genpackage to generate the necessary locales. - Sets the
LANGUAGE,LANGandLC_ALLenvironment variables.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

