TypeError: Promise.then is not a function in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# TypeError: Promise.then is not a function in JavaScript
The "TypeError: Promise.then is not a function" error occurs when the then()
method is called on a value that is not a promise.
To solve the error, convert the value to a promise before calling the method
or make sure to only call the then() method on valid promises.
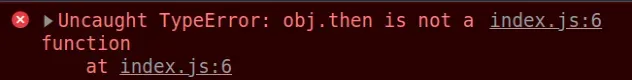
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const obj = {}; // ⛔️ TypeError: then is not a function obj.then(value => { console.log(value); });
We called the Promise.then() method on an object that is not a promise, so the error occurred.
# Only call the .then() method on valid promises
To solve the error, make sure to only call the then() method on valid promises.
const p1 = Promise.resolve('Hello'); p1.then(value => { console.log(value); // 👉️ Hello });
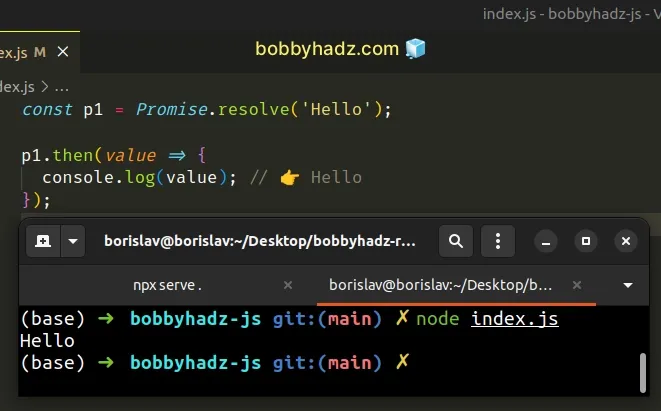
We used the Promise.resolve() method
to return a promise that resolves with the string Hello.
You can resolve the promise with any other value by passing it to the
Promise.resolve() method.
Alternatively, you can use the
Promise()
constructor and call the resolve function manually.
function sum(a, b) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { resolve(a + b); }); } sum(5, 5).then(result => { console.log(result); // 👉️ 10 });
The Promise() constructor also returns a promise object, but for our purposes
it's a little more verbose than calling the Promise.resolve() method directly.
# Check if the value is a Promise before calling .then()
If the error persists, console.log the value you're calling the then()
method on and make sure it's a promise.
Here is a code sample that
checks if the value is a promise
before calling the then() method.
const p1 = null; if (typeof p1 === 'object' && p1 !== null && 'then' in p1) { p1.then(value => { console.log(value); }); }
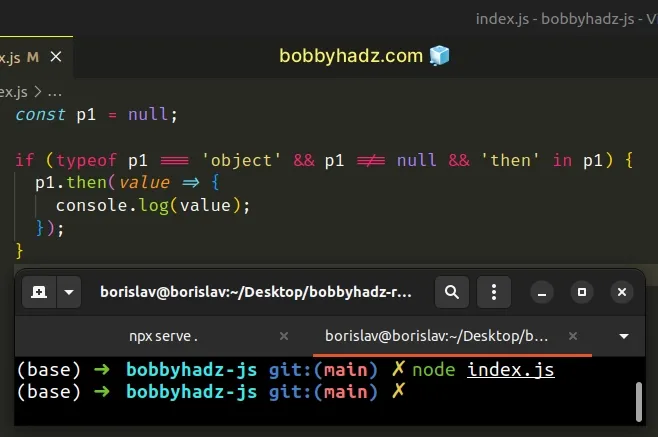
if condition uses the logical AND (&&) operator, so for the if block to run, all conditions have to be met.We first
check if the p1 variable stores a value with a type of object
because promises have a type of object.
Then we
check if the value is not equal to null.
Unfortunately, if you check the type of null with console.log(typeof null),
you will get an "object" value back, so we have to make sure the value is not
null.
The last thing we check for is that the object contains the then property.
Then we know we can safely call the then() method on the object.
This approach is called duck-typing.
Note that the then() method and functions that were marked as async always
return a promise.

