TypeError: startsWith is not a function in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: startsWith is not a function in JavaScript
The "TypeError: startsWith is not a function" error occurs when we call the
startsWith() method on a value that is not a string.
To solve the error, convert the value to a string using the toString()
method or make sure to only call the startsWith method on strings.
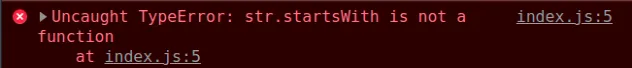
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const str = 123; // ⛔️ TypeError: startsWith is not a function const result = str.startsWith('1');
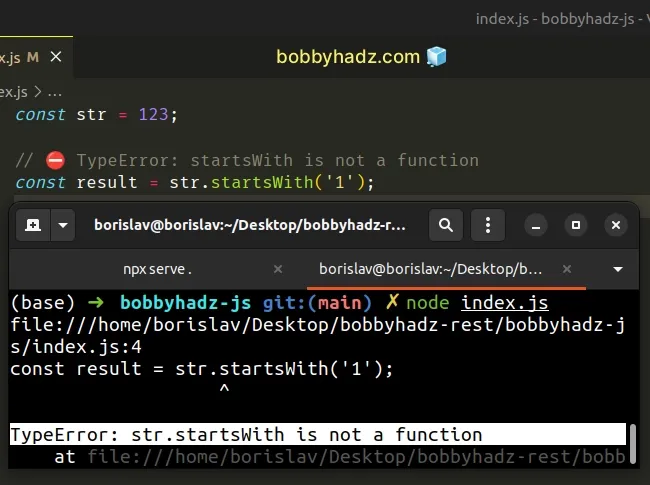
We called the String.startsWith() method on a number and got the error back.
# Only call the startsWith method on strings
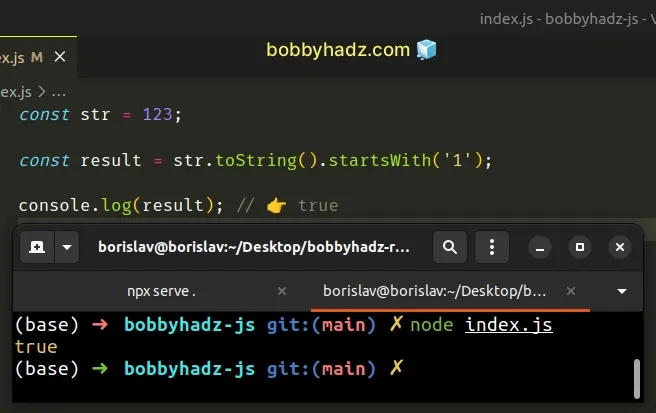
To solve the error, make sure to only call the startsWith() method on strings.
You can convert most values to a string by using the toString() method.
const str = 123; const result = str.toString().startsWith('1'); console.log(result); // 👉️ true
You can also use the String() constructor to convert a value to a string.
const str = 123; const result = String(str).startsWith('1'); console.log(result); // 👉️ true
The String() constructor converts the supplied value to a string and returns
the result.
# Check if the value is of type string before calling startsWith()
Alternatively, you can check if the value is a string before calling the
startsWith() method.
const str = null; const result = typeof str === 'string' ? str.startsWith('a') : false; console.log(result); // 👉️ false
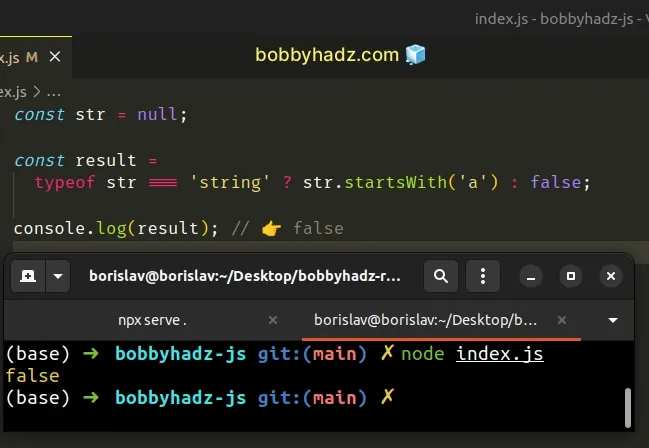
We used the ternary operator to
check if the str variable stores a string.
If it does, the value to the left of the comma is returned, otherwise, the value to the right is returned.
You can also use a simple if statement to achieve the same result.
const str = null; let result = false; if (typeof str === 'string') { result = str.startsWith('a'); } console.log(result); // 👉️ false
startsWith method, otherwise, we return false.If the error persists, console.log the value you're calling the startsWith
method on and check its type using the typeof operator, e.g.
console.log(typeof myStr).
console.log(typeof 'bobbyhadz.com'); // 👉️ string console.log(typeof {}); // 👉️ object console.log(typeof 123); // 👉️ number
# Accessing a string property on an object before calling startsWith()
If the value is an object, there's a very good chance that you are forgetting to
access a specific property on which you need to call the startsWith() method.
// ✅ with objects const obj = { name: 'bobby', }; const result1 = obj.name.startsWith('bo'); console.log(result1); // 👉️ true // ----------------------------------------- // ✅ with arrays const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; const result2 = arr[0].startsWith('bo'); console.log(result2); // 👉️ true
We accessed a property on the object and an element in the array before calling
the startsWith() method.
# Check if all strings in an array start with a specific substring
If you want to check if all strings in an array start with a specific substring,
use the every() method to iterate over the array and then call the
startsWith method on each string.
const arr = ['ab', 'ac', 'ad']; const result = arr.every(str => str.startsWith('a')); console.log(result); // 👉️ true
every() method takes a function and calls the function with each element in the array until the function returns a falsy value or iterates over the entire array.On each iteration, we call the startsWith method on the string and return the
result.

