TypeError: sort is not a function in JavaScript [Solved]
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: sort is not a function in JavaScript [Solved]
The "TypeError: sort is not a function" error occurs when we call the sort()
method on a value that is not an array.
To solve the error, convert the value to an array, or make sure to only call
the sort method on valid arrays.
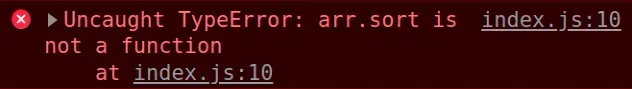
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const arr = {}; // ⛔️ Uncaught TypeError: arr.sort is not a function const result = arr.sort();

We called the Array.sort() method on an object which caused the error.
# Only call the sort() method on valid arrays
To solve the error, console.log the value you're calling the sort method on
and make sure it's a valid array.
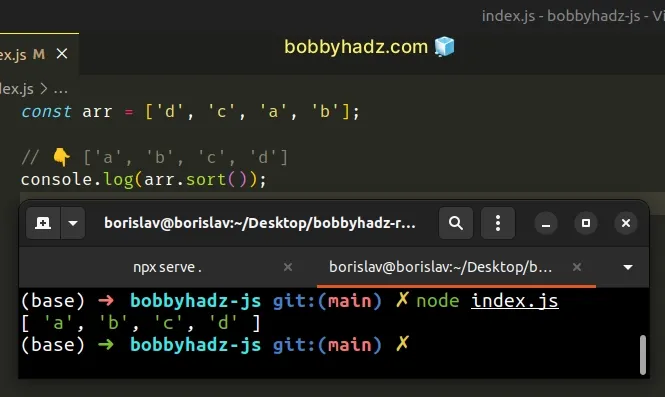
const arr = ['d', 'c', 'a', 'b']; // 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] console.log(arr.sort());
If you have an object that has a property with an array value, access the
property before calling Array.map().
const obj = { letters: ['d', 'b', 'c', 'a'], }; const result = obj.letters.sort(); console.log(result); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' ] // 👇️ { letters: [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' ] } console.log(obj);
The object has a letters property of type array which we accessed before
calling the Array.map() method.
If you have an array-like object that you need to sort, use the Array.from()
method to convert the value to an array before calling sort().
const set = new Set(['c', 'b', 'a']); const result = Array.from(set).sort(); console.log(result); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
The Array.from() method takes an iterable, converts it to an array and returns
the result.
# Check if the value is an array before calling sort()
You can conditionally check if the value is an array by using the Array.isArray() method.
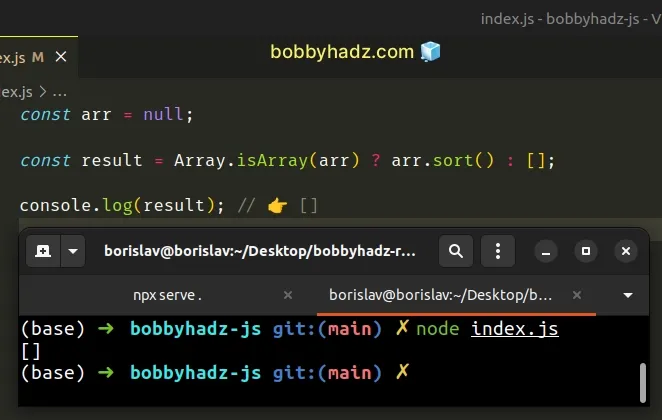
const arr = null; const result = Array.isArray(arr) ? arr.sort() : []; console.log(result); // 👉️ []
We used the ternary operator which is very similar to an if/else statement.
If the value is an array, we return the result of calling the sort method,
otherwise, we return an empty array.
This way, we won't get an error, even if the value is not an array.
You can also use a simple if statement to check if the value is an array.
const arr = null; let result = []; if (Array.isArray(arr)) { result = arr.sort(); } console.log(result); // 👉️ []
If the value is an array, the if block runs where we call the Array.sort()
method.
You should also make sure that you have parsed the value to a native JavaScript
array before calling the sort method.
# Convert the value to an array before calling sort()
If you have an array-like object, use the Array.from() method to convert it to
an array.
const set = new Set(['c', 'b', 'a']); const result = Array.from(set).sort(); console.log(result); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
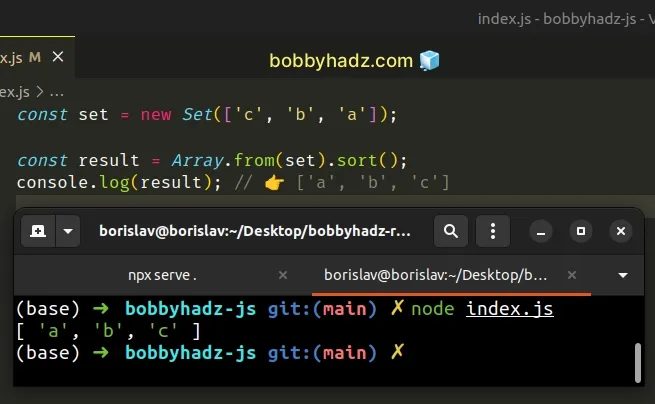
We used the Array.from() method to convert the Set object to an array before
calling sort().
You could also use the spread syntax to achieve the same result.
const set = new Set(['c', 'b', 'a']); const result = [...set].sort(); console.log(result); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
Either way, the array-like object is converted to an array, on which we can call
the sort() method.

