TypeError: getElementById is not a function in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: getElementById is not a function in JavaScript
The "getElementById is not a function" error occurs for 2 reasons:
- Misspelling the
getElementByIdmethod (the name is case-sensitive) - Using the
getElementByIdmethod on an element instead of thedocumentobject.
# Spelling the getElementById() method incorrectly
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
// ⛔️ notice capital D in id - (should be getElementById) const btn = document.getElementByID('btn'); // ✅ correct const btn = document.getElementById('btn');
We misspelled the document.getElementById method which caused the error.
# Calling the getElementById() on an element that is not the document
The error also occurs if you call the getElementById() method on an element
that is not the document.
// ------------------------------------------- // ⛔️ using the method on another element instead of the document btn.getElementById('box'); // ✅ correct const box = document.getElementById('box')
In the second example, we called the getElementById method on an element
that's not the document object.
document object.# Using the document.getElementById() method correctly
Make sure to spell the getElementById() method correctly, as it is
case-sensitive, and only call the method on the document object.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <!-- 👇️ button with `id` of `btn` --> <button id="btn">Click me</button> <!-- ✅ Your JS script here ✅ --> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
Now we can call the getElementById method on the document object.
// ✅ Works const btn = document.getElementById('btn'); console.log(btn); // 👉️ button#btn
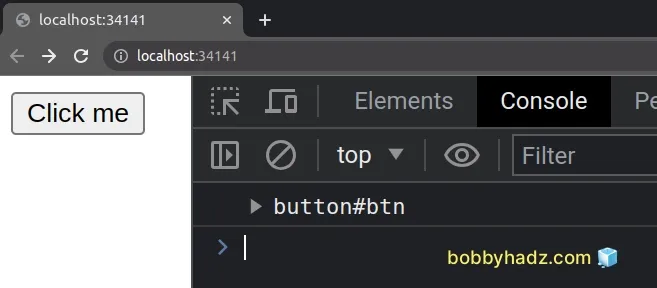
We spelled the getElementById method correctly and called it on the document
object, so everything worked as expected.
The document.getElementById method can only be called on the document object
because there is only 1 element with a given id in the DOM.
# Make sure to specify the correct identifier in the call to getElementById
Assuming we have the HTML from the previous code sample.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <!-- 👇️ button with `id` of `btn` --> <button id="btn">Click me</button> <!-- ✅ Your JS script here ✅ --> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
When calling the document.getElementById() method, make sure to pass it the
correct id as identifiers are case-sensitive.
// ✅ Works const btn = document.getElementById('btn'); console.log(btn); // 👉️ button#btn // ⛔️ returns null const notBtn = document.getElementById('BTN'); console.log(notBtn); // 👉️ null
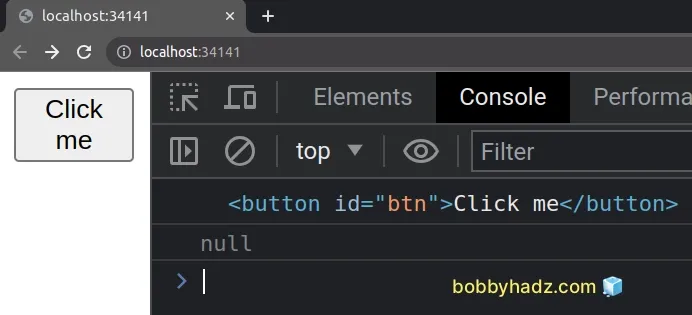
The first call to the getElementById() method works as expected and returns
the correct element.
The second call to the method returns null because we misspelled the id of
the element.
When the getElementById method is called with an id that doesn't exist,
null is returned.
# Using querySelector instead of getElementById
There are other methods like
querySelector
that can be called on the document object or a specific element.
Here is an example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <div id="box"> <div class="first">Box 1</div> <div class="second">Box 2</div> </div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
// 👇️ calling getElementById() on the document const box = document.getElementById('box'); // 👇️ calling querySelector on an element const second = box.querySelector('.second'); console.log(second); // 👉️ div.second
The querySelector method takes a selector and returns the first element in the
DOM that matches the given selector.

