Replace/Remove characters that Don't match Regex in JS
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Replace/Remove characters that Don't match Regex
To replace or remove characters that don't match a regex, call the replace()
method on the string passing it a regular expression that uses the caret ^
symbol, e.g. /[^a-z]+/.
The replace method will return a new string where the not matching
characters are replaced or removed.
const str = 'Hello123!@#'; // ✅ Remove not matching const result1 = str.replace(/[^a-zA-Z]+/, ''); console.log(result1); // 👉️ Hello // ✅ Replace not matching const result2 = str.replace(/[^a-zA-Z]+/, '!'); console.log(result2); // 👉️ Hello! // ✅ Replace each occurrence of not matching const result3 = str.replace(/[^a-zA-Z]/g, '='); console.log(result3); // 👉️ "Hello======"
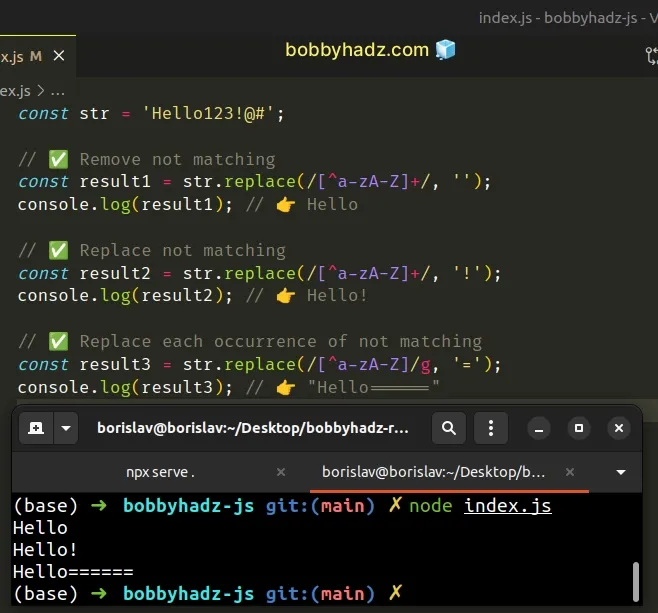
The String.replace() method returns a new string with one, some, or all matches of a regular expression replaced with the provided replacement.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pattern | The pattern to look for in the string. Can be a string or a regular expression. |
| replacement | A string used to replace the substring match by the supplied pattern. |
The first example shows how to remove all characters that are not lowercase or uppercase Latin letters.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
The square brackets [] are called a character class.
^ means "not the following".In our case, anything that is not a Latin letter in the range of a-z.
+ matches the preceding item (the character class) one or more times. In other words, we consider multiple non-lowercase or uppercase, Latin letters to be a single match.For any character that is not a lowercase or uppercase Latin letter, we provided an empty string as a replacement to remove the character from the string.
The String.replace() method returns a new string with the matches of the
pattern replaced. The method doesn't change the original string.
Strings are immutable in JavaScript.
# Replace the characters that don't match the regex
You can also use the String.replace() method to replace the characters that
don't match the regular expression.
const str = 'Hello123!@#'; const result = str.replace(/[^a-zA-Z]+/, '!'); console.log(result); // 👉️ Hello!
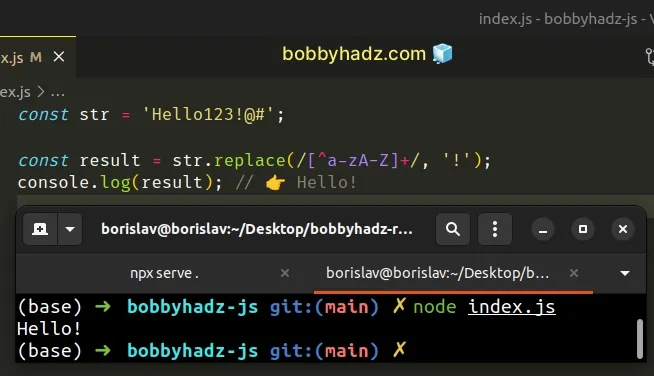
The code sample replaces one or more occurrences of non-letters with an exclamation point.
In other words, we replace multiple non-matching characters next to one another with a single replacement.
# Replace each occurrence of a character that doesn't match the regex
If you need to replace each occurrence of a character that doesn't match the
regex with a specific character, remove the plus + symbol from the regex.
const str = 'abc123'; const result = str.replace(/[^a-z]/g, '!'); console.log(result); // 👉️ "abc!!!"
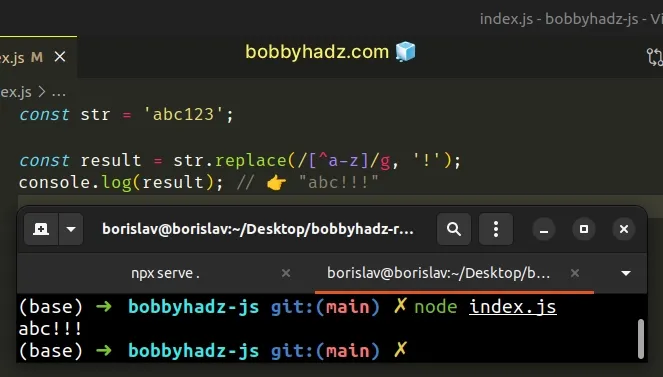
g (global) flag because we want to match all occurrences of a non-lowercase, Latin letter, and not just the first occurrence.If you only need to replace the first occurrence of a non-matching character,
remove the g flag.
const str = 'abc123'; const result3 = str.replace(/[^a-z]/, '!'); console.log(result3); // 👉️ "abc!23"
In this example, we only replaced the first occurrence of a non-matching
character. This is the default behavior of the replace method.
If you ever need help reading a regular expression, check out this regular expression cheat sheet by MDN.
It contains a table with the name and the meaning of each special character with examples.

