TypeError: querySelectorAll is not a function in JS [Fixed]
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: querySelectorAll is not a function in JS [Fixed]
The "TypeError: querySelectorAll is not a function" error occurs for multiple reasons:
- Calling the method on an object that is not a valid DOM element or the
documentobject. - Placing the JS script tag above the code that declares the DOM elements.
- Misspelling the
querySelectorAllmethod (it's case-sensitive).
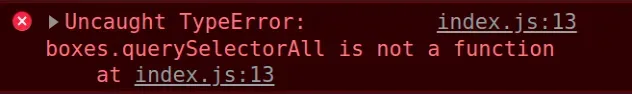
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const boxes = document.querySelectorAll('.box'); console.log(boxes); // 👉️ [div.box, div.box, div.box] // ⛔️ TypeError: boxes.querySelectorAll is not a function const blue = boxes.querySelectorAll('.blue');
We called the document.querySelectorAll method on line 1 successfully.
The querySelectorAll method returns a NodeList, which is an array-like object.
We then tried to call the querySelectorAll method on the NodeList and got the
error back.
querySelectorAll method can only be called on a DOM element or the document object.Make sure to only call the querySelectorAll method on a valid DOM element or
the document object and place your JS script tag at the bottom of the body
tag, after the DOM elements have been declared.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div class="box">Box 1</div> <div class="box"> <div class="blue">Box 2</div> </div> <div class="box">Box 3</div> <!-- ✅ Your JS script here ✅ --> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
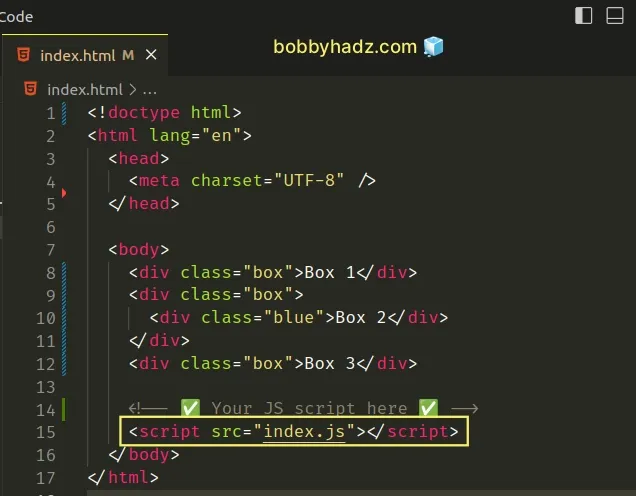
Notice that the JS script tag is placed after the DOM elements.
Had we placed the script above the code that declares the DOM elements, we wouldn't be able to access them.
Here's the code for the index.js file.
const blue = document.querySelectorAll('.box .blue'); console.log(blue); // 👉️ [div.blue]
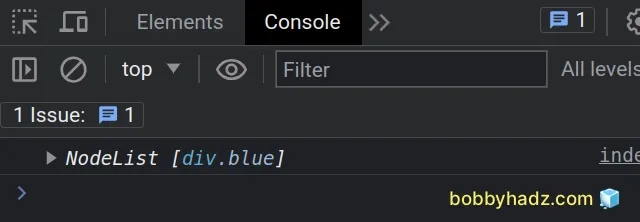
We called the querySelectorAll method on the document object. You can either
call the method on the document object or a valid DOM element.
If the error persists, make sure you haven't misspelled querySelectorAll as it
is case-sensitive.
console.log the object you're calling the querySelectorAll method on and see if it is a valid DOM element.# Check if the element exists before calling querySelectorAll
If the element you're calling the method on sometimes doesn't exist, you can
conditionally check if the element is there before calling the
querySelectorAll method.
For example, a basic DOM element has a type of object, so we can check if the
value is an object and contains the querySelectorAll property before calling
the method.
const box = null; if ( typeof box === 'object' && box !== null && 'querySelectorAll' in box ) { console.log(box.querySelectorAll('.blue')); }
Our if condition uses the logical AND (&&) operator, so for the if block to
run, all conditions have to be met.
We first
check if the box variable stores a value with a type of object,
because DOM elements have a type of object.
Then we
check if the variable is not equal to null.
Unfortunately, if you console.log(typeof null), you would get an "object"
value back, so we have to make sure the value is not null.
console.log(typeof null); // 👉️ object
querySelectorAll property.Then we know we can safely call the querySelectorAll method on the object.
# Conclusion
To solve the "querySelectorAll is not a function" error, make sure to only
call the querySelectorAll method on a valid DOM element or the document
object and place your JS script tag at the bottom of the body tag, after the DOM
elements have been declared.

