The YAML equivalent of an Array of Objects in JSON
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# The YAML equivalent of an Array of Objects in JSON
The YAML equivalent of an array of objects in JSON is a sequence of objects.
Each object in the sequence has to start with a hyphen -.
Assume you have the following array of objects in JSON.
[ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "languages": ["Java", "JavaScript"] }, { "id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "languages": ["Python", "JavaScript"] }, { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "languages": ["Typescript", "JavaScript"] } ]
It translates to the following YAML sequence.
- id: 1 name: Alice languages: - Java - JavaScript - id: 2 name: Bobby languages: - Python - JavaScript - id: 3 name: Carl languages: - Typescript - JavaScript
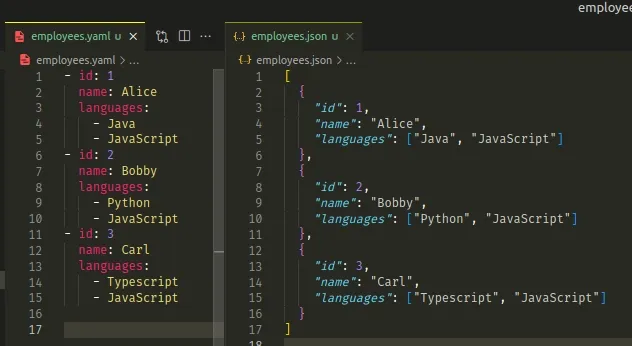
Make sure the keys in the objects are indented consistently.
For example, the following YAML code is syntactically correct.
# ✅ Code indented correctly - id: 1 name: Alice languages: - Java - JavaScript
Whereas the following code causes a syntax error.
# ⛔️ Error: YAMLException: bad indentation of a mapping entry at line 2, column 10: - id: 1 name: Alice languages: - Java - JavaScript
Notice that the name key is not indented consistently with the other keys.
Notice that the first property (id) of each object is prefixed with a hyphen
- to mark each object as an element in an array (YAML sequence).
Let's look at an example of an array of objects that has nested object values.
[ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "languages": [ "Java", "JavaScript" ], "address": { "country": "Austria", "city": "Vienna" } }, { "id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "languages": [ "Python", "JavaScript" ], "country": "Belgium", "city": "Ghent" }, { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "languages": [ "Typescript", "JavaScript" ], "address": { "country": "Canada", "city": "Ottawa" } } ]
The JSON above translates to the following YAML.
- id: 1 name: Alice languages: - Java - JavaScript address: country: Austria city: Vienna - id: 2 name: Bobby languages: - Python - JavaScript country: Belgium city: Ghent - id: 3 name: Carl languages: - Typescript - JavaScript address: country: Canada city: Ottawa
If you need to represent an array in YAML, you would use the following syntax.
- Alice - Bobby - Carl
Notice that each element is prefixed with a hyphen and the elements are indented consistently.
The YAML sequence above translates to the following JSON array.
[ "Alice", "Bobby", "Carl" ]
If you need to represent a simple object, you would separate each key and value with a colon.
For example, the following YAML.
id: 1 name: Alice salary: 500 is_programmer: true
Translates to the following JSON object.
{ "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": 500, "is_programmer": true }
If your object contains a property that has an array value, each array element must start with a hyphen.
id: 1 name: Alice salary: 500 is_programmer: true languages: - Java - JavaScript - Python
The YAML above translates to the following JSON object.
{ "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": 500, "is_programmer": true, "languages": [ "Java", "JavaScript", "Python" ] }
If your object has a nested object property, you would define it as follows.
id: 1 name: Alice salary: 500 is_programmer: true languages: - Java - JavaScript - Python address: country: Austria city: Vienna
The YAML above translates to the following JSON.
{ "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": 500, "is_programmer": true, "languages": [ "Java", "JavaScript", "Python" ], "address": { "country": "Austria", "city": "Vienna" } }
If you need to specify an array property of the object, you would prefix each element with a hyphen.
id: 1 name: Alice salary: 500 is_programmer: true languages: - Java - JavaScript - Python address: country: Austria city: Vienna post_codes: - 123 - 456 - 789
The YAML above translates to the following JSON.
{ "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": 500, "is_programmer": true, "languages": [ "Java", "JavaScript", "Python" ], "address": { "country": "Austria", "city": "Vienna", "post_codes": [ 123, 456, 789 ] } }
If you need to define an object that has a key with a value that is an array of objects, use the following syntax.
Accounting: - id: 1 name: Alice start_date: 2023-01-01 - id: 2 name: Bobby start_date: 2023-01-05 - id: 3 name: Carl start_date: 2023-01-03
The YAML above translates to the following JSON.
{ "Accounting": [ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "start_date": "2023-01-01T00:00:00.000Z" }, { "id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "start_date": "2023-01-05T00:00:00.000Z" }, { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "start_date": "2023-01-03T00:00:00.000Z" } ] }
You might also see hyphens being placed on separate lines.
Accounting: - id: 1 name: Alice start_date: 2023-01-01 - id: 2 name: Bobby start_date: 2023-01-05 - id: 3 name: Carl start_date: 2023-01-03
The YAML above is also perfectly valid syntax and translates to the same JSON.
{ "Accounting": [ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "start_date": "2023-01-01T00:00:00.000Z" }, { "id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "start_date": "2023-01-05T00:00:00.000Z" }, { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "start_date": "2023-01-03T00:00:00.000Z" } ] }
If some of your nested objects have keys that have object values, you would use the following syntax.
Accounting: - id: 1 name: Alice start_date: 2023-01-01 address: country: Austria city: Vienna - id: 2 name: Bobby start_date: 2023-01-05 address: country: Belgium city: Brussels - id: 3 name: Carl start_date: 2023-01-03 address: country: Canada city: Ottawa
The YAML above translates to the following JSON.
{ "Accounting": [ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "start_date": "2023-01-01T00:00:00.000Z", "address": { "country": "Austria", "city": "Vienna" } }, { "id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "start_date": "2023-01-05T00:00:00.000Z", "address": { "country": "Belgium", "city": "Brussels" } }, { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "start_date": "2023-01-03T00:00:00.000Z", "address": { "country": "Canada", "city": "Ottawa" } } ] }

