ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tkinter' in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·4 min
# ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tkinter' in Python
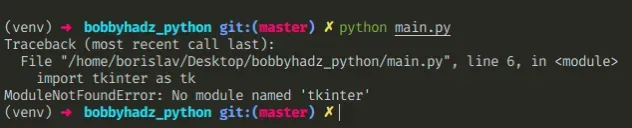
The Python "ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'tkinter'" occurs when
tkinter is not installed in our Python environment.
To solve the error, install the module and import it as
import tkinter as tk.
# Installing the tkinter module
Open your terminal and run the following command to install tkinter.
# 👇️ === UBUNTU / DEBIAN === sudo apt-get install python3-tk # 🚨 Make sure to specify the correct Python version. # For example, my Python v is 3.10, so I would install as sudo apt-get install python3.10-tk # 👇️ === MacOS === brew install python-tk@3.10 # 🚨 Make sure to specify the correct Python version. # For example, if you run Python v3.9 run adjust command to brew install python-tk@3.9 # 👇️ === Fedora === sudo dnf install python3-tkinter # 👇️ === CentOS === sudo yum install python3-tkinter # 👇️ === Arch Linux (Manjaro, Antegros) === sudo pacman -S tk
You can check your Python version with the python --version command.
python --version # For macOS and Linux python3 --version # Py alias for Windows py --version
Make sure to specify the correct Python version when running the installation command as shown in the code sample above.
For example, if your Python version is 3.10.5, you would specify 3.10 as
your version when running the suitable command from the code sample above.
# Tick the tcl/tk and IDLE option on Windows
If you are on Windows, you have to make sure to tick the checkbox tcl/tk and
IDLE when installing Python.
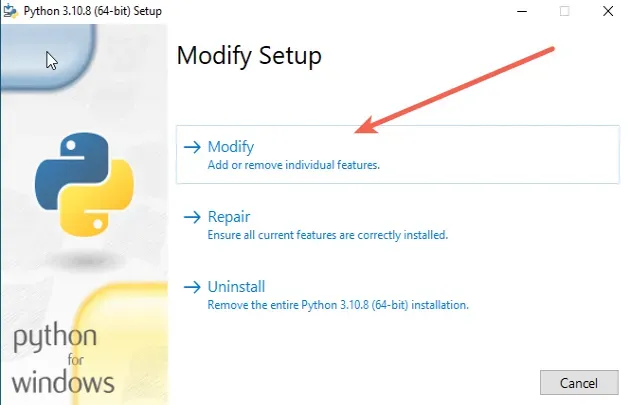
If you already installed Python,
download the installer, run it and click
Modify.
Then check the tcl/tk and IDLE checkbox to install tkinter for your Python
version.
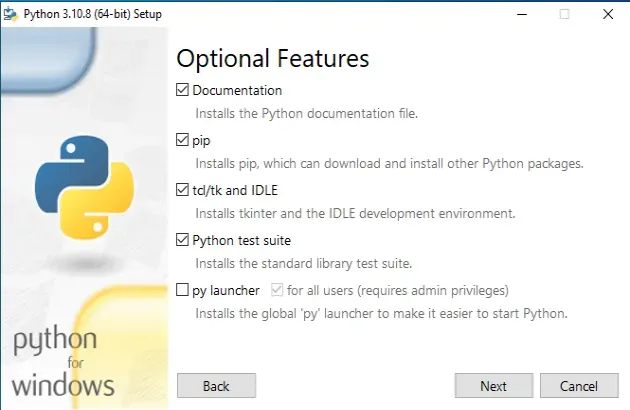
Make sure to tick the following options if you get prompted:
- tcl/tk and IDLE (installs tkinter and the IDLE development environment)
- Install launcher for all users (recommended)
- Add Python to PATH (this adds Python to your PATH environment variable)
# Tkinter is a built-in module in Python 3
Tkinter comes as a built-in module in Python 3 and is made available without requiring installation.
Now you should be able to import and use the tkinter module.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk root = tk.Tk() frm = ttk.Frame(root, padding=10) frm.grid() ttk.Label(frm, text="Hello World!").grid(column=0, row=0) ttk.Button(frm, text="Quit", command=root.destroy).grid(column=1, row=0) root.mainloop()
tkinter is imported using a lowercase t, whereas in Python 2, it is imported with an uppercase TWhen you run your code with python file_name.py, you might be running the
script with Python 2.
Use the python --version command if you need to check your Python version.
python --version
You can try to run the script with python3 file_name.py to have the command
scoped to Python 3.
If you get the error "AttributeError: module 'tkinter' has no attribute 'Tk'", click on the following article.
# An import statement that works in both Python 3 and Python 2
If your code can be run using both Python 3 and 2, use a try/except statement for a universal import.
try: import tkinter as tk # Using Python 3 from tkinter import ttk except ImportError: import Tkinter as tk # Falls back to import from Python 2
We try to import the tkinter module (Python 3) and if we get an ImportError,
we know the file is run in Python 2, so we import using an uppercase T and
alias the import to tk.
If you aren't sure what version of Python you're using, run the
python --version command.
python --version
# Using the tkinter module in a virtual environment
If you are in a virtual environment, the version of Python corresponds to the version that was used to create the virtual environment.
Here is an example of creating a virtual environment using Python 3 where
tkinter is available without installation required.
# 👇️ Use the correct version of Python when creating VENV python3 -m venv venv # 👇️ Activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ Activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ Activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1
If the python3 -m venv venv command doesn't work, try the following 2
commands:
python -m venv venvpy -m venv venv
Make sure to use the correct activation command depending on your operating system.
Once you activate the virtual environment, try running your script directly with
python script_name.py.
# Make sure you haven't named your file tkinter.py
If the error persists, make sure you haven't named a module in your project as
tkinter.py because that would shadow the original tkinter module.
You also shouldn't be declaring a variable named tkinter as that would also
shadow the original module.
# NameError: name 'tk' is not defined in Python
If you get an error such as "NameError: name 'tk' is not defined", then you have
forgotten to import tkinter before using it.
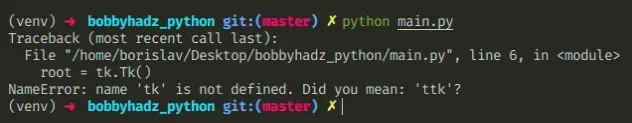
root = tk.Tk() NameError: name 'tk' is not defined. Did you mean 'ttk'?
We have to import the tkinter module to solve the error.
# ✅ Import tkinter as tk first import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk root = tk.Tk() frm = ttk.Frame(root, padding=10) frm.grid() ttk.Label(frm, text="Hello World!").grid(column=0, row=0) ttk.Button(frm, text="Quit", command=root.destroy).grid(column=1, row=0) root.mainloop()
Even though the tkinter module is in the Python standard library, we still
have to import it before using it.
An alternative to importing the entire tkinter module is to import only the
classes and methods that your code uses.
# ✅ Importing tkinter first from tkinter import Tk, ttk root = Tk() frm = ttk.Frame(root, padding=10) frm.grid() ttk.Label(frm, text="Hello World!").grid(column=0, row=0) ttk.Button(frm, text="Quit", command=root.destroy).grid(column=1, row=0) root.mainloop()
The example shows how to only import the Tk class and ttk module from
tkinter.
Instead of accessing the members on the module, e.g. tk.Tk(), we now access
them directly.
This should be your preferred approach because it makes your code easier to read.
import tkinter as tk, it is much harder to see which functions or classes from the tkinter module are being used in the file.Conversely, when we import specific functions, it is much easier to see which
classes from the tkinter module are being used.
You can view all of the classes and modules tkinter provides by visiting the
official docs.

