NPM install flags explained (with examples)
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# NPM install flags explained (with examples)
This article goes over some of the most commonly used NPM install flags and their shorthands.
The --save flag is set to true by default, so it doesn't have to be
specified in newer NPM versions.
npm install express --save
When the --save flag is used, the package you are installing appears in the
dependencies object of your package.json file.
The flag can also be specified using the shorthand of -S.
npm install express -S
# The --save-dev flag
When the --save-dev flag is used, the installed package appears in the
devDependencies section of your package.json file.
npm install nodemon --save-dev
The flag is used when installing development dependencies, e.g. a server that is only used during development or test frameworks.
The flag can also be specified using the shorthand of -D.
npm install nodemon -D
# The --global flag
The global flag is used to install a package globally.
npm install --global create-react-app
When you install a package globally, it can be accessed directly from the command line.
create-react-app --version
The flag can also be specified using the shorthand of -g.
npm install -g create-react-app
# The --silent flag
The --silent flag can be used to suppress the output from the npm install
command.
npm install --silent express
When the --silent flag is used, the log level of npm is set to silent and no
output is produced.
The flag can also be specified using the shorthand of -s.
npm install -s express
# The --save-exact flag
When the --save-exact flag is used, the installed dependencies are saved to
package.json with an exact version rather than using npm's default semver
range operator.
npm install --save-exact express
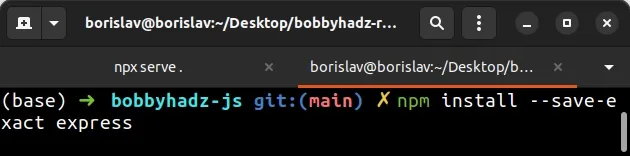
when you use the flag, you are guaranteed to install the same major, minor and
patch version every time you run npm install.
The flag can also be specified using the shorthand of -E.
npm install -E express
# The --dry-run flag
When the --dry-run flag is used, npm doesn't make any changes to your
package.json file.
npm install react --dry-run
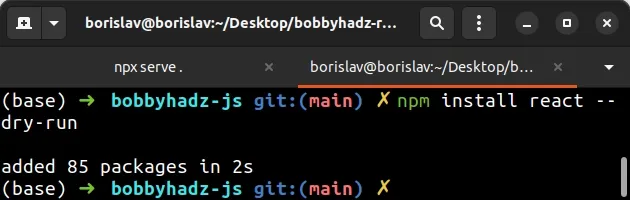
Instead, it only reports what it would have done had the command been issued without the flag.
# The --force flag
When the --force flag is used, npm fetches remote resources even if a local
copy exists on disk.
npm install react --force
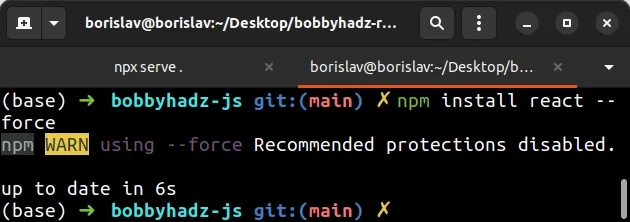
The flag can also be specified using the shorthand of -f.
npm install react -f
# The --legacy-peer-deps flag
The --legacy-peer-deps flag ignores all peer dependencies when installing (in
the style on npm version 4 through 6).
npm install react --legacy-peer-deps
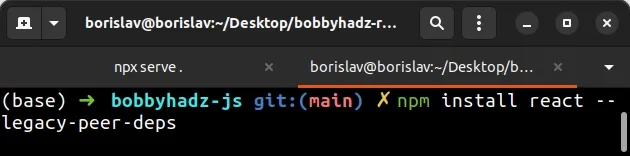
The flag is often used when you get errors when installing a package due to it clashing with other packages.
The issue mainly occurs when multiple packages depend on different versions of another package.
# The --strict-peer-deps flag
When --strict-peer-deps is set to true and --legacy-peer-deps is not set,
any conflicting peerDependencies are treated as an install failure.
npm install react --strict-peer-deps
By default, npm tries to resolve conflicting peerDependencies.
# The --package-lock flag
When the --package-lock flag is set to true, the
package-lock.json file is ignored
when installing.
npm install react --package-lock

The command also prevents npm install from writing to package-lock.json.

