How to Change the Active Element using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 5, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Change the Active Element using JavaScript
To change the active element, call the focus() method on the element you
want to focus.
If the element can't be focused by default, set its tabIndex property to
-1 before calling the focus method.
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" autofocus /> <div id="box">Hello world</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
// ✅ set activeElement to another element const box = document.getElementById('box'); box.tabIndex = '-1'; box.focus(); // ✅ set activeElement back to `body` // document.activeElement.blur(); // 👇️ <body> element // console.log(document.activeElement);
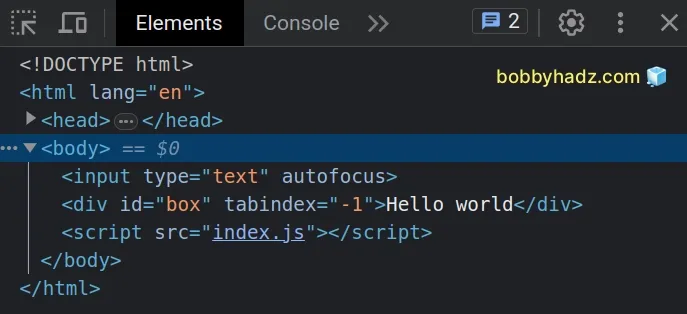
input element with the autofocus attribute set, so the element automatically gets focused on page load.To change the focus to a div element, we set the
tabIndex
property on the element to -1.
If I load the page, I can see that the div element has focus.

Setting the tabindex property is not required for some elements, e.g. form
elements.
# Changing the active element back to the default (the body element)
To change the active element on the page back to the default (the body element),
call the blur() method, e.g.
document.activeElement.blur().
The blur method removes the focus from the element it was called on.
// ✅ set activeElement back to `body` document.activeElement.blur(); // 👇️ <body> element console.log(document.activeElement);
By calling the blur() method on the active element, we are able to remove
focus from it. This sets the focus on the body element on the page.
If you console.log the value of document.activeElement after calling the
blur method, you will see the body element logged to the console.

